|
Capture Of Wejh
The capture of Wejh (modern-day Al Wajh, Saudi Arabia) took place on 23–24 January 1917 when British-led Arab forces landed by sea and, with the support of naval bombardments, defeated the Ottoman garrison. The attack was intended to threaten the flanks of an Ottoman advance from their garrison in Medina to Mecca, which had been Battle of Mecca (1916), captured by Arab forces in 1916. The sea-based force was to have attacked in co-operation with a larger force under Arab leader Faisal I of Iraq, Faisal but these men were held up after capturing a quantity of supplies and gold en-route to Wejh. The sea-based force under Royal Navy leadership captured Wejh with naval artillery support, defeating the 1,300-strong Ottoman garrison. The capture of the town safeguarded Mecca, as the Ottoman troops were withdrawn to static defence duties in and around Medina. Background The Arab Revolt began in June 1916 when disaffected Arab tribesmen unsuccessfully rose against the Ottoman garrison ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arab Revolt
The Arab Revolt ( ar, الثورة العربية, ) or the Great Arab Revolt ( ar, الثورة العربية الكبرى, ) was a military uprising of Arab forces against the Ottoman Empire in the Middle Eastern theatre of World War I. On the basis of the McMahon–Hussein Correspondence, an agreement between the British government and Hussein bin Ali, Sharif of Mecca, the revolt was officially initiated at Mecca on June 10, 1916. The aim of the revolt was to create a single unified and independent Arab state stretching from Aleppo in Syria to Aden in Yemen, which the British had promised to recognize. The Sharifian Army led by Hussein and the Hashemites, with military backing from the British Egyptian Expeditionary Force, successfully fought and expelled the Ottoman military presence from much of the Hejaz and Transjordan. The rebellion eventually took Damascus and set up the Arab Kingdom of Syria, a short-lived monarchy led by Faisal, a son of Hussein. Followin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yanbu
Yanbu ( ar, ينبع, lit=Spring, translit=Yanbu'), also known simply as Yambu or Yenbo, is a city in the Al Madinah Province of western Saudi Arabia. It is approximately 300 kilometers northwest of Jeddah (at ). The population is 222,360 (2020 census). Many residents are foreign expatriates working in the oil refineries and petrochemical industry, mostly from Asia, but there are also large numbers from the Middle East, Europe, and North America. Yanbu has three primary sections; Yanbu Al-Bahr, Yanbu Al-Nakhl and Yanbu Al-Sina'iya as well as a major Red Sea port. History Pre-modern era Yanbu's history dates back at least 2,500 years, when it was a staging point on the spice and incense route from Yemen to Egypt and the Mediterranean region. Sharm Yanbu ( ar, شرم ينبع), historically known as Charmuthas, which is a small peninsula located to the north of Yanbu was mentioned by the Greek historian Diodorus Siculus. The Invasion of Dul Ashir took place in Yan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battles Of The Arab Revolt
A battle is an occurrence of combat in warfare between opposing military units of any number or size. A war usually consists of multiple battles. In general, a battle is a military engagement that is well defined in duration, area, and force commitment. An engagement with only limited commitment between the forces and without decisive results is sometimes called a skirmish. The word "battle" can also be used infrequently to refer to an entire operational campaign, although this usage greatly diverges from its conventional or customary meaning. Generally, the word "battle" is used for such campaigns if referring to a protracted combat encounter in which either one or both of the combatants had the same methods, resources, and strategic objectives throughout the encounter. Some prominent examples of this would be the Battle of the Atlantic, Battle of Britain, and Battle of Stalingrad, all in World War II. Wars and military campaigns are guided by military strategy, whereas bat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battles Of World War I Involving The United Kingdom
A battle is an occurrence of combat in warfare between opposing military units of any number or size. A war usually consists of multiple battles. In general, a battle is a military engagement that is well defined in duration, area, and force commitment. An engagement with only limited commitment between the forces and without decisive results is sometimes called a skirmish. The word "battle" can also be used infrequently to refer to an entire operational campaign, although this usage greatly diverges from its conventional or customary meaning. Generally, the word "battle" is used for such campaigns if referring to a protracted combat encounter in which either one or both of the combatants had the same methods, resources, and strategic objectives throughout the encounter. Some prominent examples of this would be the Battle of the Atlantic, Battle of Britain, and Battle of Stalingrad, all in World War II. Wars and military campaigns are guided by military strategy, whereas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conflicts In 1917
Conflict may refer to: Arts, entertainment, and media Films * ''Conflict'' (1921 film), an American silent film directed by Stuart Paton * ''Conflict'' (1936 film), an American boxing film starring John Wayne * ''Conflict'' (1937 film), a Swedish drama film directed by Per-Axel Branner * ''Conflict'' (1938 film), a French drama film directed by Léonide Moguy * ''Conflict'' (1945 film), an American suspense film starring Humphrey Bogart * ''Catholics: A Fable'' (1973 film), or ''The Conflict'', a film starring Martin Sheen * ''Judith'' (1966 film) or ''Conflict'', a film starring Sophia Loren * ''Samar'' (1999 film) or ''Conflict'', a 1999 Indian film by Shyam Benegal Games * ''Conflict'' (series), a 2002–2008 series of war games for the PS2, Xbox, and PC * ''Conflict'' (video game), a 1989 Nintendo Entertainment System war game * '' Conflict: Middle East Political Simulator'', a 1990 strategy computer game Literature and periodicals * ''Conflict'' (novel) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Aqaba
The Battle of Aqaba (6 July 1917) was fought for the Red Sea port of Aqaba (now in Jordan) during the Arab Revolt of World War I. The attacking forces, led by Sherif Nasir and Auda abu Tayi and advised by T. E. Lawrence ("Lawrence of Arabia"), were victorious over the Ottoman Empire defenders. Background Gilbert Clayton had already told Lawrence, "The move to Aqaba on the part of Feisal is not at present desirable..." This was due to the McMahon-Hussein Correspondence being superseded by the Sykes-Picot Agreement. Lawrence, however, decided to go his own way, without orders. Lawrence called it a private venture, void of British support, since "Feisal provided money, camels, stores and explosives." The 600-mile desert journey was led by Sherif Nasir, while Lawrence was accompanied by Nesib el-Bekri and Auda Abu Tayi, leader of the northern Howeitat tribe of Bedouin. Total strength on 9 May 1917, when they embarked, was 45 Howeitat and Ageyl camel men. Aqaba was surro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
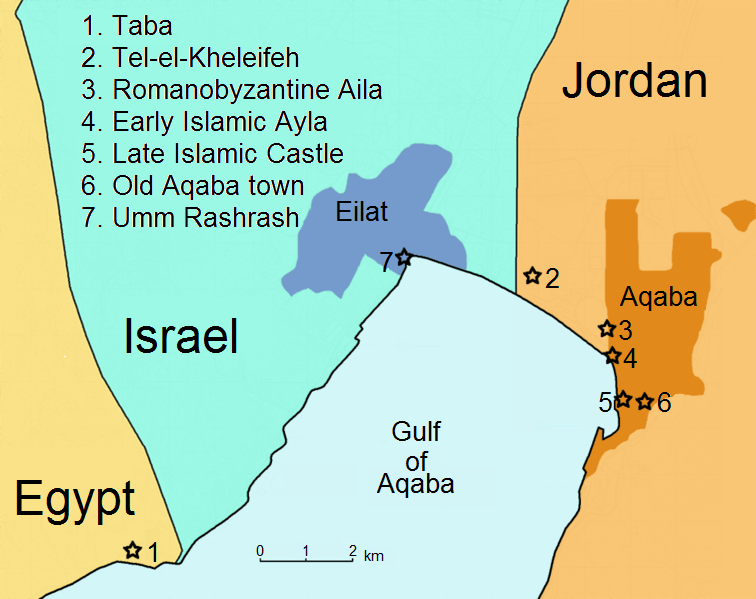
Aqaba
Aqaba (, also ; ar, العقبة, al-ʿAqaba, al-ʿAgaba, ) is the only coastal city in Jordan and the largest and most populous city on the Gulf of Aqaba. Situated in southernmost Jordan, Aqaba is the administrative centre of the Aqaba Governorate. The city had a population of 148,398 in 2015 and a land area of . Today, Aqaba plays a major role in the development of the Jordanian economy, through the vibrant trade and tourism sectors. The Port of Aqaba also serves other countries in the region. Aqaba's strategic location at the northeastern tip of the Red Sea between the continents of Asia and Africa has made its port important over the course of thousands of years. The ancient city was called '' Elath'', adopted in Latin as ''Aela'' and in Arabic as ''Ayla''. Its strategic location and proximity to copper mines made it a regional hub for copper production and trade in the Chalcolithic period. Aela became a bishopric under Byzantine rule and later became a Latin Catholic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tabuk, Saudi Arabia
Tabuk ( ar, تَبُوْك '), also spelled ''Tabouk'', is the capital city of the Tabuk Region in northwestern Saudi Arabia. It has a population of 667,000 (as of 2021). It is close to the Jordanian–Saudi Arabia border, and houses the largest air force base in Saudi Arabia. History Ptolemy mentioned a place by the name 'Tabawa', at the northwestern corner of Arabia. This name may be a reference to 'Tabuka' or 'Tabuk'. If this is true, the town may be as old as Ptolemy's time. Pre-Islamic Arab poets, such as Antra and Nabiqa, mentioned its mountain 'Hasmi' in their poems. Tabouk became famous for the Expedition to Tabuk in 630 CE, during the period of prophet Muhammad. Since then, it remained a gateway of North Arabia. It was also visited by a number of European travelers such as Doughty in 1877 and Huber in 1884. Tabuk was captured by the Arab forces in 1918, 3 weeks after the British capture of Damascus. Tabuk became a centre of military activity during the 1991 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abdullah I Of Jordan
AbdullahI bin Al-Hussein ( ar, عبد الله الأول بن الحسين, translit=Abd Allāh al-Awwal bin al-Husayn, 2 February 1882 – 20 July 1951) was the ruler of Jordan from 11 April 1921 until his assassination in 1951. He was the Emir of Transjordan, a British protectorate, until 25 May 1946, after which he was king of an independent Jordan. As a member of the Hashemite dynasty, the royal family of Jordan since 1921, Abdullah was a 38th-generation direct descendant of Muhammad. Born in Mecca, Hejaz, Ottoman Empire, Abdullah was the second of four sons of Hussein bin Ali, Sharif of Mecca, and his first wife, Abdiyya bint Abdullah. He was educated in Istanbul and Hejaz. From 1909 to 1914, Abdullah sat in the Ottoman legislature, as deputy for Mecca, but allied with Britain during World War I. During the war, he played a key role in secret negotiations with the United Kingdom that led to the Great Arab Revolt against Ottoman rule that was led by his father Sharif Hus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Red Sea
The Red Sea ( ar, البحر الأحمر - بحر القلزم, translit=Modern: al-Baḥr al-ʾAḥmar, Medieval: Baḥr al-Qulzum; or ; Coptic: ⲫⲓⲟⲙ ⲛ̀ϩⲁϩ ''Phiom Enhah'' or ⲫⲓⲟⲙ ⲛ̀ϣⲁⲣⲓ ''Phiom ǹšari''; Tigrinya: ቀይሕ ባሕሪ ''Qeyih Bahri''; ) is a seawater inlet of the Indian Ocean, lying between Africa and Asia. Its connection to the ocean is in the south, through the Bab el Mandeb strait and the Gulf of Aden. To its north lie the Sinai Peninsula, the Gulf of Aqaba, and the Gulf of Suez (leading to the Suez Canal). It is underlain by the Red Sea Rift, which is part of the Great Rift Valley. The Red Sea has a surface area of roughly 438,000 km2 (169,100 mi2), is about 2250 km (1398 mi) long, and — at its widest point — 355 km (220.6 mi) wide. It has an average depth of 490 m (1,608 ft), and in the central ''Suakin Trough'' it reaches its maximum depth of . The Red Sea also ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |