|
Captaincy Of São Tomé
The Captaincies of the Portuguese Empire () were the socio-administrative territorial divisions and hereditary lordships established initially by Henry the Navigator, as part of the Donatário system in order to settle and developed the Portuguese overseas Empire. Pioneered on the island of Madeira and institutionalized in the archipelago of the Azores, the captaincy system was eventually adapted to the New World. Captaincies The prince and his successors (the Donatários) remained on the mainland, owing to their responsibilities related to the Royal Household, during the epic period of trans-Atlantic exploration.Susana Goulart Costa (2008), p.232 When the King constituted and bestowed the Donatary system, he never specifically thought of sending his donatários to the archipelagos. Before the discovery of Brazil (1522), the captaincy system already operated in the Atlantic possessions of Madeira and the Azores, in addition other islands and settlements along the African coast. A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henry The Navigator
Princy Henry of Portugal, Duke of Viseu ( Portuguese: ''Infante Dom Henrique''; 4 March 1394 – 13 November 1460), better known as Prince Henry the Navigator (), was a Portuguese prince and a central figure in the early days of the Portuguese Empire and in the 15th-century European maritime exploration. Through his administrative direction, he is regarded as the main initiator of what would be known as the Age of Discovery. Henry was the fourth child of King John I of Portugal, who founded the House of Aviz. After procuring the new caravel ship, Henry was responsible for the early development of Portuguese exploration and maritime trade with other continents through the systematic exploration of Western Africa, the islands of the Atlantic Ocean, and the search for new routes. He encouraged his father to conquer Ceuta (1415), the Muslim port on the North African coast across the Straits of Gibraltar from the Iberian Peninsula. He learned of the opportunity offered by the Sah ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
João Soares De Albergaria
João Soares de Albergaria (c. 1415 – 1499), also referred to as João Soares (or João Soares Velho),Gaspar Frutuoso, ''Saudades da Terra'', (1873) Book III was the second Portuguese Dontary-Captain of the islands of Santa Maria and São Miguel, succeeding his maternal uncle Gonçalo Velho Cabral in the title. After selling his rights to the Captaincy of São Miguel to Rui Gonçalves da Câmara, he continued as Donatary-Captain of Santa Maria. Biography Early life João Soares de Albergaria was the son of Fernão Soares de Albergaria and Teresa Velho Cabral, the latter a sister of Gonçalo Velho Cabral. He married Brites Godins, who quickly became sick. Their marriage would not produce heirs. In 1474, due to his wife's illness, Albergaria moved to the island of Madeira in order to "find remedies and medics", as well as a milder climate for her to convalesce in. They lodged with the family of the Captain of Funchal João Gonçalves Zarco and that of his brother, Rui Gon� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tomé De Sousa
Tomé de Sousa (1503–1579) was the first governor-general of the Portuguese colony of Brazil from 1549 until 1553. He was a nobleman and soldier born in Rates, Póvoa de Varzim. Sousa was born a noble and participated in military expeditions in Africa, fought the Moors and commanded the nau ''Conceição'' to Portuguese India, part of the armada of Fernão de Andrade. Sousa was the first knight commander of the medieval Monastery of Rates, re-established in 1100 AD and dissolved in the 16th century. Before Brazil Born into nobility, Sousa was fathered by a Prior and a descendant of King Afonso III, Dom João de Sousa.Sousa, Rainer Gonçalves. “Governo De Tomé De Sousa.” ''Govero De Tomé De Sousa'', Mundo Educação Despite being born illegitimately, he worked for the royal court from a young age with the support of Antônio de Ataíde, his cousin and the count of Castenheira. Before becoming governor-general of Brazil, Sousa fought as a soldier in Morocco and Nort ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Captaincy Of Porto Seguro
A captaincy ( , , ) is a historical administrative division of the former Spanish and Portuguese colonial empires. It was instituted as a method of organization, directly associated with the home-rule administrations of medieval feudal governments in which the monarch delimited territories for colonization that were administered by men of confidence. The same term was or is used in some other countries, such as Croatia, Hungary, Italy, Ottoman Empire, Slovakia or Austria. Captaincy system Portuguese Empire The Captaincies of the Portuguese Empire were developed successively, based on the original donatário system established by King John I of Portugal in Madeira, and expanded with each successive new colony discovered.Susana Goulart Costa (2008), p.232 Prince Henry the Navigator instituted the Captaincy system to promote development of Portuguese discoveries, but it was in the Azores, where this system effectively functioned. The prince and his successors (the Donatários) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Martim Afonso De Sousa
Martim Afonso de Sousa ( – 21 July 1564) was a Portuguese '' fidalgo'', explorer and colonial administrator. Life Martim Afonso de Sousa was born in Vila Viçosa, and had been raised in the Duke of Bragança household and was a personal friend since childhood of King John III of Portugal, being also a cousin. When he left the service of the Duke of Bragança, in 1516, to stay at the court of the Royal House, he began to take mathematics, cosmography and geography classes with the chief cosmographer Pedro Nunes. He justified the decision by saying: "The duke can make me mayor, but the king can make me duke", but that never happened. After the death of Manuel I of Portugal, he accompanied the widowed Queen D. Leonor of Austria to Castile, where he married Ana Pimentel, from an illustrious Spanish family, around June 1523. Ana Pimentel was the daughter of Arias Maldonado, commendator of Estriana and governor of Salamanca and Talavera and of D. Joana Pimentel, daughter of D. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Captaincy Of São Vicente
The Captaincy of São Vicente (1534–1709) was a land grant and colonial administration in the far southern part of the colonial Portuguese Empire in Colonial Brazil. History In 1534 King John III of Portugal granted the captaincy to Martim Afonso de Sousa, a Portuguese admiral. De Sousa had founded the first two permanent Portuguese settlements in Brazil in 1532: São Vicente (near the present port of Santos) and Piratininga (later to become São Paulo). De Sousa received two tracts of land: * one centered on the settlement of São Vicente, extending along the coastline from Cananéia to Bertioga (within present-day São Paulo state) * the other extended from Parati to Cabo Frio (within present-day Rio de Janeiro state). These two tracts, separated by the Captaincy of Santo Amaro, formed the Captaincy of São Vicente. In 1681 the São Paulo settlement succeeded São Vicente as the capital of the captaincy, and the name of the latter gradually fell into disuse. S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Duarte Coelho Pereira
Duarte Coelho Pereira ( – ) was a nobleman, military leader, and colonial administrator in the Portuguese colony of Brazil. He was the first Donatario (Lord Proprietor) of the captaincy of Pernambuco and founder of Olinda. Early life The birth and childhood of Duarte Coelho Pereira are obscured from history. His father's name was Gonçalo Coelho, but it is not clear which of six men named Gonçalo Coelho may have sired Duarte. Often biographers have assigned his parentage to either the ''escrivão da fazenda real'' or the fourth ''senhor'' of Felgueiras, however archival and heraldric evidence supports neither of these men nor points conclusively to any of the four other prominent men named Gonçalo Coelho in this period. That he was not noble at birth is suggested in the fact that coeval writers, some of whom would have known his parentage, are silent as to Duarte Coelho's ancestry. It was common in this era for genealogies to be “adjusted” for famous men, thus existing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Captaincy Of Pernambuco
The Captaincy of Pernambuco or New Lusitania () was a hereditary land grant and administrative subdivision of northern Portuguese Brazil during the colonial period from 1534 to 1821, with a brief interruption from 1630 to 1654 when it was part of Dutch Brazil. At the time of the Independence of Brazil, it became a province of United Kingdom of Portugal, Brazil and the Algarves. Captaincies were originally horizontal tracts of land (generally) 50 leagues wide extending from the Atlantic Ocean to the Treaty of Tordesillas#Tordesillas meridian, Tordesillas meridian. During the earliest years of colonial Brazil, the Captaincy of Pernambuco was one of only two prosperous captaincies in Brazil (the other being Captaincy of São Vicente), primarily due to growing sugar cane. As a result of the failure of other captaincies, in part due to the invasion of the Northeast coast of Brazil by the Dutch during the Seventeenth Century, Pernambuco's geographical area grew as failed captaincies wer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
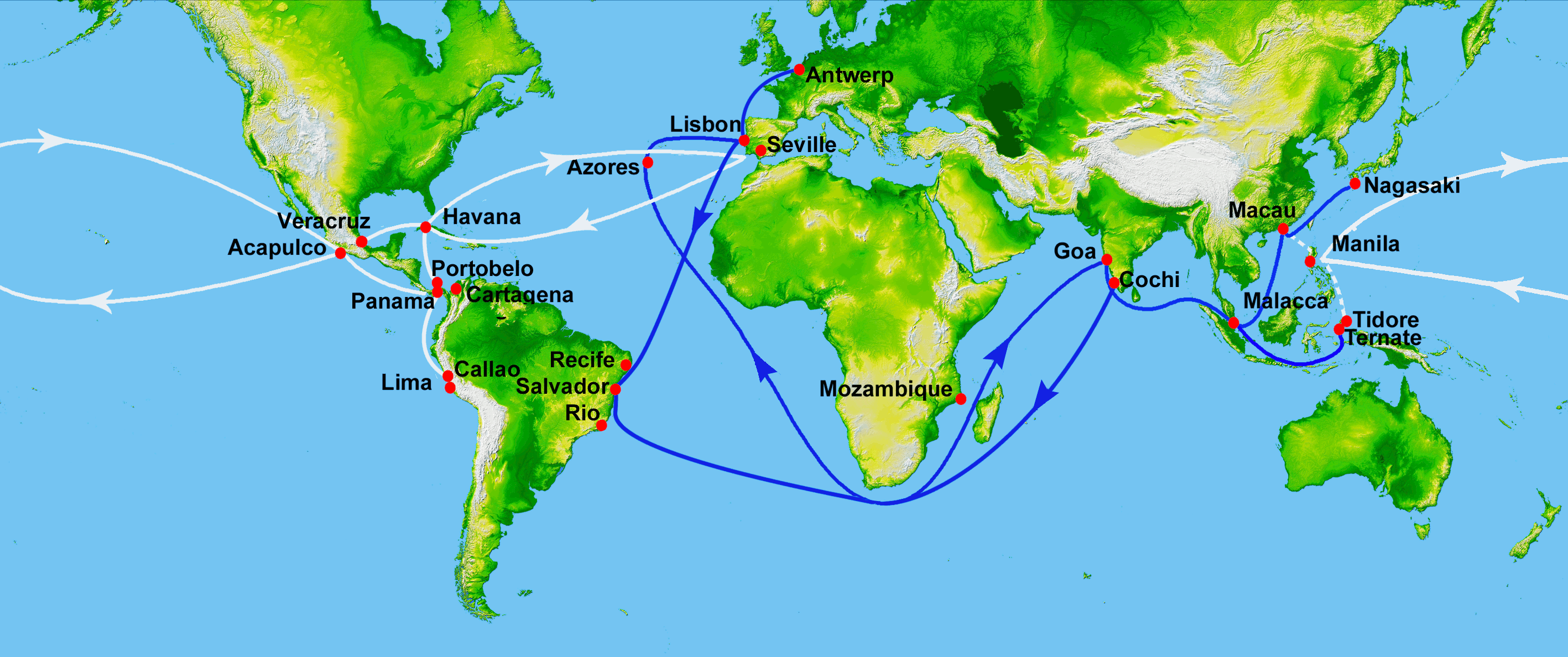
Tordesilhas Line
The Treaty of Tordesillas, signed in Tordesillas, Spain, on 7 June 1494, and ratified in Setúbal, Portugal, divided the newly discovered lands outside Europe between the Kingdom of Portugal and the Crown of Castile, along a meridian west of the Cape Verde islands, off the west coast of Africa. That line of demarcation was about halfway between Cape Verde (already Portuguese) and the islands visited by Christopher Columbus on his first voyage (claimed for Castile and León), named in the treaty as Cipangu and Antillia (Cuba and Hispaniola). The lands to the east would belong to Portugal and the lands to the west to Castile, modifying an earlier bull by Pope Alexander VI. The treaty was signed by Spain on , and by Portugal on . The other side of the world was divided a few decades later by the Treaty of Zaragoza, signed on , which specified the antimeridian to the line of demarcation specified in the Treaty of Tordesillas. Portugal and Spain largely respected the treaties, whi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Equator
The equator is the circle of latitude that divides Earth into the Northern Hemisphere, Northern and Southern Hemisphere, Southern Hemispheres of Earth, hemispheres. It is an imaginary line located at 0 degrees latitude, about in circumference, halfway between the North Pole, North and South Pole, South poles. The term can also be used for any other celestial body that is roughly spherical. In three-dimensional space, spatial (3D) geometry, as applied in astronomy, the equator of a rotating spheroid (such as a planet) is the parallel (circle of latitude) at which latitude is defined to be 0°. It is an imaginary line on the spheroid, equidistant from its geographical pole, poles, dividing it into northern and southern hemispheres. In other words, it is the intersection of the spheroid with the plane (geometry), plane perpendicular to its axis of rotation and midway between its geographical poles. On and near the equator (on Earth), noontime sunlight appears almost directly o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Treaty Of Tordesillas
The Treaty of Tordesillas, signed in Tordesillas, Spain, on 7 June 1494, and ratified in Setúbal, Portugal, divided the newly discovered lands outside Europe between the Kingdom of Portugal and the Crown of Castile, along a meridian (geography), meridian west of the Portuguese Cape Verde, Cape Verde islands, off the west coast of Africa. That line of demarcation was about halfway between Cape Verde (already Portuguese) and the islands visited by Christopher Columbus on his first voyage (claimed for Castile and León), named in the treaty as names of Japan, Cipangu and Antillia (Cuba and Hispaniola). The lands to the east would belong to Portugal and the lands to the west to Castile, modifying an earlier papal bull, bull by Pope Alexander VI. The treaty was signed by Spain on , and by Portugal on . The other side of the world was divided a few decades later by the Treaty of Zaragoza, signed on , which specified the #Antimeridian: Moluccas and Treaty of Zaragoza, antimeridian to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |