|
Canto (gene Curation Tool)
Canto is a web-based tool to support the curation of gene-specific scientific data, by both professional biocurators and publication authors. Canto was developed as part of the PomBase project, and is funded by the Wellcome Trust. Canto enables experts (biocurators and publication authors) to provide detailed, standardized, sharable annotation from research publications and was originally created for the fission yeast community. Canto is a generic tool that can be readily configured for use with other organisms and other databases and now supports pathogen-host interactions for PHI-base (Rothamsted research) and the curation of phenotypes and genetic interactions at FlyBase (University of Cambridge), and all gene-specific datatypes for the emerging model species ''Schizosaccharomyces japonicus'' in JaponicusDB. Curation using ontology terms Canto supports the use of bio-ontologies (including the Gene Ontology, Protein Ontology, The Fission Yeast Phenotype Ontology FYPO, and th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Cambridge
The University of Cambridge is a Public university, public collegiate university, collegiate research university in Cambridge, England. Founded in 1209, the University of Cambridge is the List of oldest universities in continuous operation, world's third-oldest university in continuous operation. The university's founding followed the arrival of scholars who left the University of Oxford for Cambridge after a dispute with local townspeople. The two ancient university, ancient English universities, although sometimes described as rivals, share many common features and are often jointly referred to as Oxbridge. In 1231, 22 years after its founding, the university was recognised with a royal charter, granted by Henry III of England, King Henry III. The University of Cambridge includes colleges of the University of Cambridge, 31 semi-autonomous constituent colleges and List of institutions of the University of Cambridge#Schools, Faculties, and Departments, over 150 academic departm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University College London
University College London (Trade name, branded as UCL) is a Public university, public research university in London, England. It is a Member institutions of the University of London, member institution of the Federal university, federal University of London, and is the second-largest list of universities in the United Kingdom by enrolment, university in the United Kingdom by total enrolment and the largest by postgraduate enrolment. Established in 1826 as London University (though without university degree-awarding powers) by founders who were inspired by the radical ideas of Jeremy Bentham, UCL was the first university institution to be established in London, and the first in England to be entirely secular and to admit students regardless of their religion. It was also, in 1878, among the first university colleges to admit women alongside men, two years after University College, Bristol, had done so. Intended by its founders to be Third-oldest university in England debate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PomBase
PomBase is a model organism database that provides online access to the fission yeast Schizosaccharomyces pombe genome sequence and annotated features, together with a wide range of manually curated functional gene-specific data. The PomBase website was redeveloped in 2016 to provide users with a more fully integrated, better-performing service (described in ). Data Curation and Quality Control PomBase staff manually curate a wide variety of data types using both primary literature and bioinformatics sources, and numerous mechanisms are employed to ensure both syntactical and biological content validity. Types of data curated include: * Genome sequence and features (e.g. physical location of genes in the genome) * Protein and ncRNA functions, the cellular processes they participate in and where they localize * Phenotypes associated with different alleles and genotypes * Specific protein modification sites and when they occur * Human and budding yeast orthologs of ''S. pombe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wellcome Trust
The Wellcome Trust is a charitable foundation focused on health research based in London, United Kingdom. It was established in 1936 with legacies from the pharmaceutical magnate Henry Wellcome (founder of Burroughs Wellcome, one of the predecessors of GSK plc) to fund research to improve human and animal health. The aim of the Trust is to "support science to solve the urgent health challenges facing everyone." It had a financial endowment of £29.1 billion in 2020, making it the fourth wealthiest charitable foundation in the world. In 2012, the Wellcome Trust was described by the ''Financial Times'' as the United Kingdom's largest provider of non-governmental funding for scientific research, and one of the largest providers in the world. According to their annual report, the Wellcome Trust spent GBP £1.1 billion on charitable activities across their 2019/2020 financial year. According to the OECD, the Wellcome Trust's financing for 2019 development increased by 2 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PHI-base
The Pathogen-Host Interactions database (PHI-base) is a biological database that contains manually curated information on genes experimentally proven to affect the outcome of Host–pathogen interaction, pathogen-host interactions. The database has been maintained by researchers at Rothamsted Experimental Station, Rothamsted Research and external collaborators since 2005. PHI-base has been part of the UK node of ELIXIR, the European life-science infrastructure for biological information, since 2016. Background The Pathogen-Host (biology), Host Interactions database was developed to utilise the growing number of verified genes that mediate an organism's ability to cause disease and/or trigger host responses. The web-accessible database catalogues experimentally verified pathogenicity, virulence, and effector genes from bacterial, fungal, and oomycete pathogens which infect animal, plant, and fungal hosts. PHI-base was the first online resource devoted to the identifica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rothamsted Research
Rothamsted Research, previously known as the Rothamsted Experimental Station and then the Institute of Arable Crops Research, is one of the oldest agricultural experiment station, agricultural research institutions in the world, having been founded in 1843. It is located at Harpenden in the English county of Hertfordshire and is a Charitable organization, registered charity under English law. Two of the station's best known and longest-running experiments are the Broadbalk Experiment, planted annually with winter wheat since 1843, and the Park Grass Experiment, a biological study that started in 1856 and has been continuously monitored ever since. History The Rothamsted Experimental Station was founded in 1843 by John Bennet Lawes, a noted Victorian era entrepreneur and scientist who had founded one of the first artificial fertilizer manufacturing factories in 1842, on his 16th-century estate, Rothamsted Manor, to investigate the impact of inorganic and organic fertilizers on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
FlyBase
FlyBase is an online bioinformatics database and the primary repository of genetic and molecular data for the insect family Drosophilidae. For the most extensively studied species and model organism, ''Drosophila melanogaster'', a wide range of data are presented in different formats. Information in FlyBase originates from a variety of sources ranging from large-scale genome projects to the primary research literature. These data types include mutant phenotypes; molecular characterization of mutant alleles; and other deviations, cytological maps, wild-type expression patterns, anatomical images, transgenic constructs and insertions, sequence-level gene models, and molecular classification of gene product functions. Query tools allow navigation of FlyBase through DNA or protein sequence, by gene or mutant name, or through terms from the several ontologies used to capture functional, phenotypic, and anatomical data. The database offers several different query tools in order to provid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gene Ontology
The Gene Ontology (GO) is a major bioinformatics initiative to unify the representation of gene and gene product attributes across all species. More specifically, the project aims to: 1) maintain and develop its controlled vocabulary of gene and gene product attributes; 2) annotate genes and gene products, and assimilate and disseminate annotation data; and 3) provide tools for easy access to all aspects of the data provided by the project, and to enable functional interpretation of experimental data using the GO, for example via enrichment analysis. GO is part of a larger classification effort, the Open Biomedical Ontologies, being one of the Initial Candidate Members of the OBO Foundry. Whereas gene nomenclature focuses on gene and gene products, the Gene Ontology focuses on the function of the genes and gene products. The GO also extends the effort by using a markup language to make the data (not only of the genes and their products but also of curated attributes) machine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein Ontology
The Protein Information Resource (PIR), located at Georgetown University Medical Center, is an integrated public bioinformatics resource to support genomic and proteomic research, and scientific studies. It contains protein sequences databases History PIR was established in 1984 by the National Biomedical Research Foundation as a resource to assist researchers and customers in the identification and interpretation of protein sequence information. Prior to that, the foundation compiled the first comprehensive collection of macromolecular sequences in the Atlas of Protein Sequence and Structure, published from 1964 to 1974 under the editorship of Margaret Dayhoff. Dayhoff and her research group pioneered in the development of computer methods for the comparison of protein sequences, for the detection of distantly related sequences and duplications within sequences, and for the inference of evolutionary histories from alignments of protein sequences. Winona Barker and Robert Ledley ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sequence Ontology
The Sequence Ontology (SO) is an ontology Ontology is the philosophical study of existence, being. It is traditionally understood as the subdiscipline of metaphysics focused on the most general features of reality. As one of the most fundamental concepts, being encompasses all of realit ... suitable for describing biological sequences. It is designed to make the naming of DNA sequence features and variants consistent and therefore machine-readable and searchable. References External links * {{cite web , url= http://www.sequenceontology.org/ , title= The Sequence Ontology , publisher= Sequence Ontology , access-date= 2011-09-19 Ontology (information science) Biological databases ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
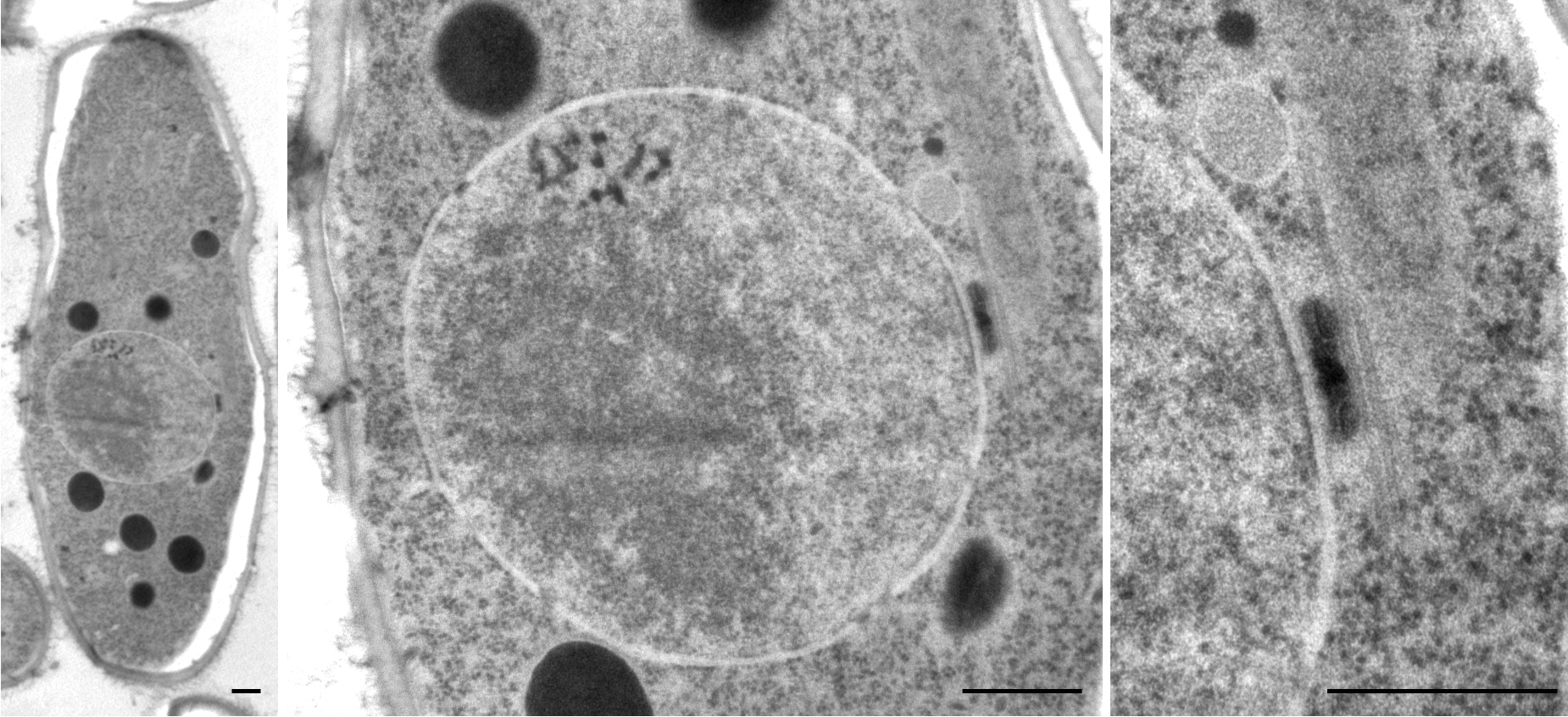
Schizosaccharomyces Pombe
''Schizosaccharomyces pombe'', also called "fission yeast", is a species of yeast used in traditional brewing and as a model organism in molecular and cell biology. It is a unicellular eukaryote, whose cells are rod-shaped. Cells typically measure 3 to 4 micrometres in diameter and 7 to 14 micrometres in length. Its genome, which is approximately 14.1 million base pairs, is estimated to contain 4,970 protein-coding genes and at least 450 non-coding RNAs. These cells maintain their shape by growing exclusively through the cell tips and divide by medial fission to produce two daughter cells of equal size, which makes them a powerful tool in cell cycle research. Fission yeast was isolated in 1893 by Paul Lindner from East African millet beer. The species name ''pombe'' is the Swahili word for beer. It was first developed as an experimental model in the 1950s: by Urs Leupold for studying genetics, and by Murdoch Mitchison for studying the cell cycle. Paul Nurse, a fission ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Model Organism
A model organism is a non-human species that is extensively studied to understand particular biological phenomena, with the expectation that discoveries made in the model organism will provide insight into the workings of other organisms. Model organisms are widely used to research human disease when human experimentation would be unfeasible or unethical. This strategy is made possible by the common descent of all living organisms, and the conservation of metabolic and developmental pathways and genetic material over the course of evolution. Research using animal models has been central to most of the achievements of modern medicine. It has contributed most of the basic knowledge in fields such as human physiology and biochemistry, and has played significant roles in fields such as neuroscience and infectious disease. The results have included the near- eradication of polio and the development of organ transplantation, and have benefited both humans and animals. From 19 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |