|
Candidate Solution
In mathematical optimization and computer science, a feasible region, feasible set, or solution space is the set of all possible points (sets of values of the choice variables) of an optimization problem that satisfy the problem's constraints, potentially including inequalities, equalities, and integer constraints. This is the initial set of candidate solutions to the problem, before the set of candidates has been narrowed down. For example, consider the problem of minimizing the function x^2+y^4 with respect to the variables x and y, subject to 1 \le x \le 10 and 5 \le y \le 12. \, Here the feasible set is the set of pairs (''x'', ''y'') in which the value of ''x'' is at least 1 and at most 10 and the value of ''y'' is at least 5 and at most 12. The feasible set of the problem is separate from the objective function, which states the criterion to be optimized and which in the above example is x^2+y^4. In many problems, the feasible set reflects a constraint that on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IP Polytope With LP Relaxation
IP most often refers to: * Intellectual property, creations of the mind for which exclusive legal rights are recognized * Internet Protocol, a set of rules for sending data across a network IP or Ip or ip may also refer to: Businesses and organizations * IP College (Indraprastha College for boys), a constituent college of the University of Delhi, New Delhi, India * Imperial Police, a former Indian police agency * ''Inicjatywa Pracownicza'' (Workers' Initiative), a Polish trade union * International Paper, an American pulp and paper company * Iraqi Police * Atyrau Airways (IATA code: IP) * Italiana Petroli, an Italian petroleum brand owned by Anonima Petroli Italiana Places * Ipswich, for Ipswich and surrounding areas, England * Ip, Sălaj, Romania * Ip (river), a river in Sălaj County, Romania * IP Casino Resort Spa, in Biloxi, Mississippi, US Science and technology Biology and medicine * Immunoprecipitation, a molecular biology technique * Incontinentia pigmenti, a genetic dis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vertex (geometry)
In geometry, a vertex (: vertices or vertexes), also called a corner, is a point (geometry), point where two or more curves, line (geometry), lines, or line segments Tangency, meet or Intersection (geometry), intersect. For example, the point where two lines meet to form an angle and the point where edge (geometry), edges of polygons and polyhedron, polyhedra meet are vertices. Definition Of an angle The ''vertex'' of an angle is the point where two Line (mathematics)#Ray, rays begin or meet, where two line segments join or meet, where two lines intersect (cross), or any appropriate combination of rays, segments, and lines that result in two straight "sides" meeting at one place. :(3 vols.): (vol. 1), (vol. 2), (vol. 3). Of a polytope A vertex is a corner point of a polygon, polyhedron, or other higher-dimensional polytope, formed by the intersection (Euclidean geometry), intersection of Edge (geometry), edges, face (geometry), faces or facets of the object. In a polygon, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Element (mathematics)
In mathematics Mathematics is a field of study that discovers and organizes methods, Mathematical theory, theories and theorems that are developed and Mathematical proof, proved for the needs of empirical sciences and mathematics itself. There are many ar ..., an element (or member) of a set is any one of the distinct objects that belong to that set. For example, given a set called containing the first four positive integers (A = \), one could say that "3 is an element of ", expressed notationally as 3 \in A . Sets Writing A = \ means that the elements of the set are the numbers 1, 2, 3 and 4. Sets of elements of , for example \, are subsets of . Sets can themselves be elements. For example, consider the set B = \. The elements of are ''not'' 1, 2, 3, and 4. Rather, there are only three elements of , namely the numbers 1 and 2, and the set \. The elements of a set can be anything. For example the elements of the set C = \ are the color red, the number 12, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Search Algorithm
In computer science, a search algorithm is an algorithm designed to solve a search problem. Search algorithms work to retrieve information stored within particular data structure, or calculated in the Feasible region, search space of a problem domain, with Continuous or discrete variable, either discrete or continuous values. Although Search engine (computing), search engines use search algorithms, they belong to the study of information retrieval, not algorithmics. The appropriate search algorithm to use often depends on the data structure being searched, and may also include prior knowledge about the data. Search algorithms can be made faster or more efficient by specially constructed database structures, such as search trees, hash maps, and database indexes. Search algorithms can be classified based on their mechanism of searching into three types of algorithms: linear, binary, and hashing. Linear search algorithms check every record for the one associated with a target key i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mathematics
Mathematics is a field of study that discovers and organizes methods, Mathematical theory, theories and theorems that are developed and Mathematical proof, proved for the needs of empirical sciences and mathematics itself. There are many areas of mathematics, which include number theory (the study of numbers), algebra (the study of formulas and related structures), geometry (the study of shapes and spaces that contain them), Mathematical analysis, analysis (the study of continuous changes), and set theory (presently used as a foundation for all mathematics). Mathematics involves the description and manipulation of mathematical object, abstract objects that consist of either abstraction (mathematics), abstractions from nature orin modern mathematicspurely abstract entities that are stipulated to have certain properties, called axioms. Mathematics uses pure reason to proof (mathematics), prove properties of objects, a ''proof'' consisting of a succession of applications of in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Necessary And Sufficient Conditions
In logic and mathematics, necessity and sufficiency are terms used to describe a conditional or implicational relationship between two statements. For example, in the conditional statement: "If then ", is necessary for , because the truth of is guaranteed by the truth of . (Equivalently, it is impossible to have without , or the falsity of ensures the falsity of .) Similarly, is sufficient for , because being true always implies that is true, but not being true does not always imply that is not true. In general, a necessary condition is one (possibly one of several conditions) that must be present in order for another condition to occur, while a sufficient condition is one that produces the said condition. The assertion that a statement is a "necessary ''and'' sufficient" condition of another means that the former statement is true if and only if the latter is true. That is, the two statements must be either simultaneously true, or simultaneously false. In ordinary ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bounded Set
In mathematical analysis and related areas of mathematics, a set is called bounded if all of its points are within a certain distance of each other. Conversely, a set which is not bounded is called unbounded. The word "bounded" makes no sense in a general topological space without a corresponding metric. '' Boundary'' is a distinct concept; for example, a circle (not to be confused with a disk) in isolation is a boundaryless bounded set, while the half plane is unbounded yet has a boundary. A bounded set is not necessarily a closed set and vice versa. For example, a subset of a 2-dimensional real space constrained by two parabolic curves and defined in a Cartesian coordinate system is closed by the curves but not bounded (so unbounded). Definition in the real numbers A set of real numbers is called ''bounded from above'' if there exists some real number (not necessarily in ) such that for all in . The number is called an upper bound of . The terms ''bounded from b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bounded Unbounded
Boundedness, bounded, or unbounded may refer to: Economics * Bounded rationality, the idea that human rationality in decision-making is bounded by the available information, the cognitive limitations, and the time available to make the decision * Bounded emotionality, a concept within communication theory that stems from emotional labor and bounded rationality Linguistics * Boundedness (linguistics), whether a situation has a clearly defined beginning or end Mathematics * Boundedness axiom, the axiom schema of replacement * Bounded deformation, a function whose distributional derivatives are not quite well-behaved-enough to qualify as functions of bounded variation, although the symmetric part of the derivative matrix does meet that condition * Bounded growth, occurs when the growth rate of a mathematical function is constantly increasing at a decreasing rate * Bounded operator, a linear transformation ''L'' between normed vector spaces for which the ratio of the norm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Empty Set
In mathematics, the empty set or void set is the unique Set (mathematics), set having no Element (mathematics), elements; its size or cardinality (count of elements in a set) is 0, zero. Some axiomatic set theories ensure that the empty set exists by including an axiom of empty set, while in other theories, its existence can be deduced. Many possible properties of sets are vacuously true for the empty set. Any set other than the empty set is called ''non-empty''. In some textbooks and popularizations, the empty set is referred to as the "null set". However, null set is a distinct notion within the context of measure theory, in which it describes a set of measure zero (which is not necessarily empty). Notation Common notations for the empty set include "", "\emptyset", and "∅". The latter two symbols were introduced by the Bourbaki group (specifically André Weil) in 1939, inspired by the letter Ø () in the Danish orthography, Danish and Norwegian orthography, Norwegian a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Global Optimum
In mathematical analysis, the maximum and minimum of a function are, respectively, the greatest and least value taken by the function. Known generically as extremum, they may be defined either within a given range (the ''local'' or ''relative'' extrema) or on the entire domain (the ''global'' or ''absolute'' extrema) of a function. Pierre de Fermat was one of the first mathematicians to propose a general technique, adequality, for finding the maxima and minima of functions. As defined in set theory, the maximum and minimum of a set are the greatest and least elements in the set, respectively. Unbounded infinite sets, such as the set of real numbers, have no minimum or maximum. In statistics, the corresponding concept is the sample maximum and minimum. Definition A real-valued function ''f'' defined on a domain ''X'' has a global (or absolute) maximum point at ''x''∗, if for all ''x'' in ''X''. Similarly, the function has a global (or absolute) minimum point at ''x''∗, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
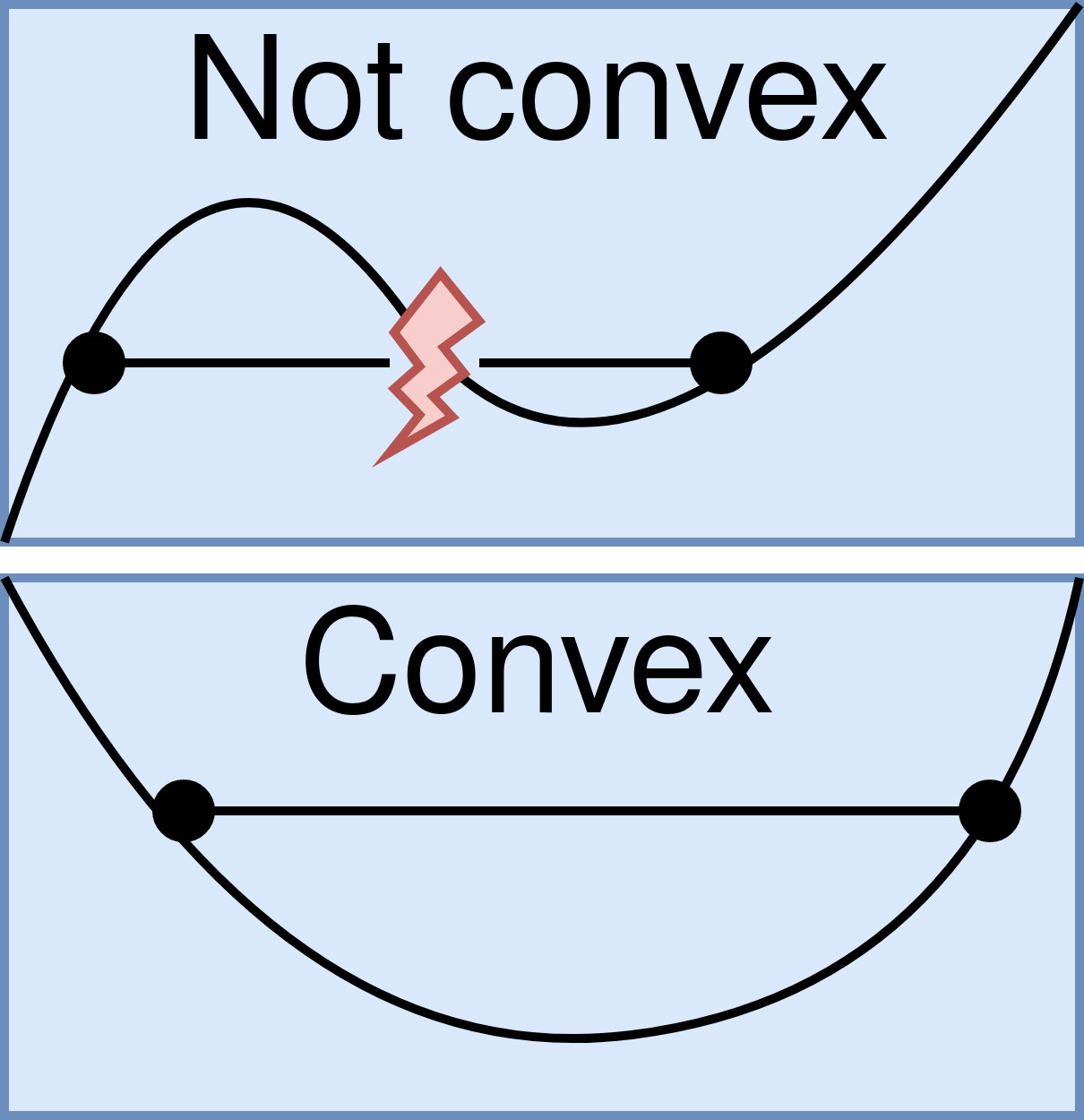
Convex Function
In mathematics, a real-valued function is called convex if the line segment between any two distinct points on the graph of a function, graph of the function lies above or on the graph between the two points. Equivalently, a function is convex if its epigraph (mathematics), ''epigraph'' (the set of points on or above the graph of the function) is a convex set. In simple terms, a convex function graph is shaped like a cup \cup (or a straight line like a linear function), while a concave function's graph is shaped like a cap \cap. A twice-differentiable function, differentiable function of a single variable is convex if and only if its second derivative is nonnegative on its entire domain of a function, domain. Well-known examples of convex functions of a single variable include a linear function f(x) = cx (where c is a real number), a quadratic function cx^2 (c as a nonnegative real number) and an exponential function ce^x (c as a nonnegative real number). Convex functions pl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |