|
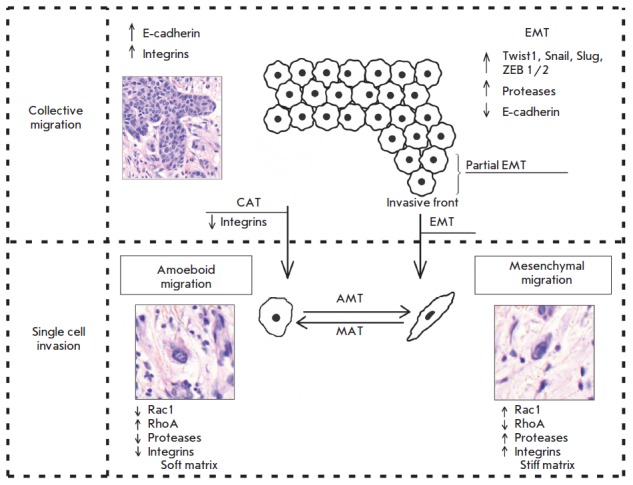
Cancer Invasion
Invasion is the process by which cancer cells directly extend and penetrate into neighboring tissues in cancer. It is generally distinguished from metastasis, which is the spread of cancer cells through the circulatory system or the lymphatic system to more distant locations. Yet, lymphovascular invasion is generally the first step of metastasis. There exist two main patterns of cancer cell invasion by cell migration: collective cell migration and individual cell migration, by which tumor cells overcome barriers of the extracellular matrix and spread into surrounding tissues. Each pattern of cell migration exhibits distinct morphological features and is governed by specific biochemical and molecular genetic mechanisms. Two types of migrating tumor cells, mesenchymal (fibroblast-like) and amoeboid, can be observed in various patterns of cancer cell invasion. This article describes the key differences between the variants of cancer cell migration, the role of epithelial-mesenc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
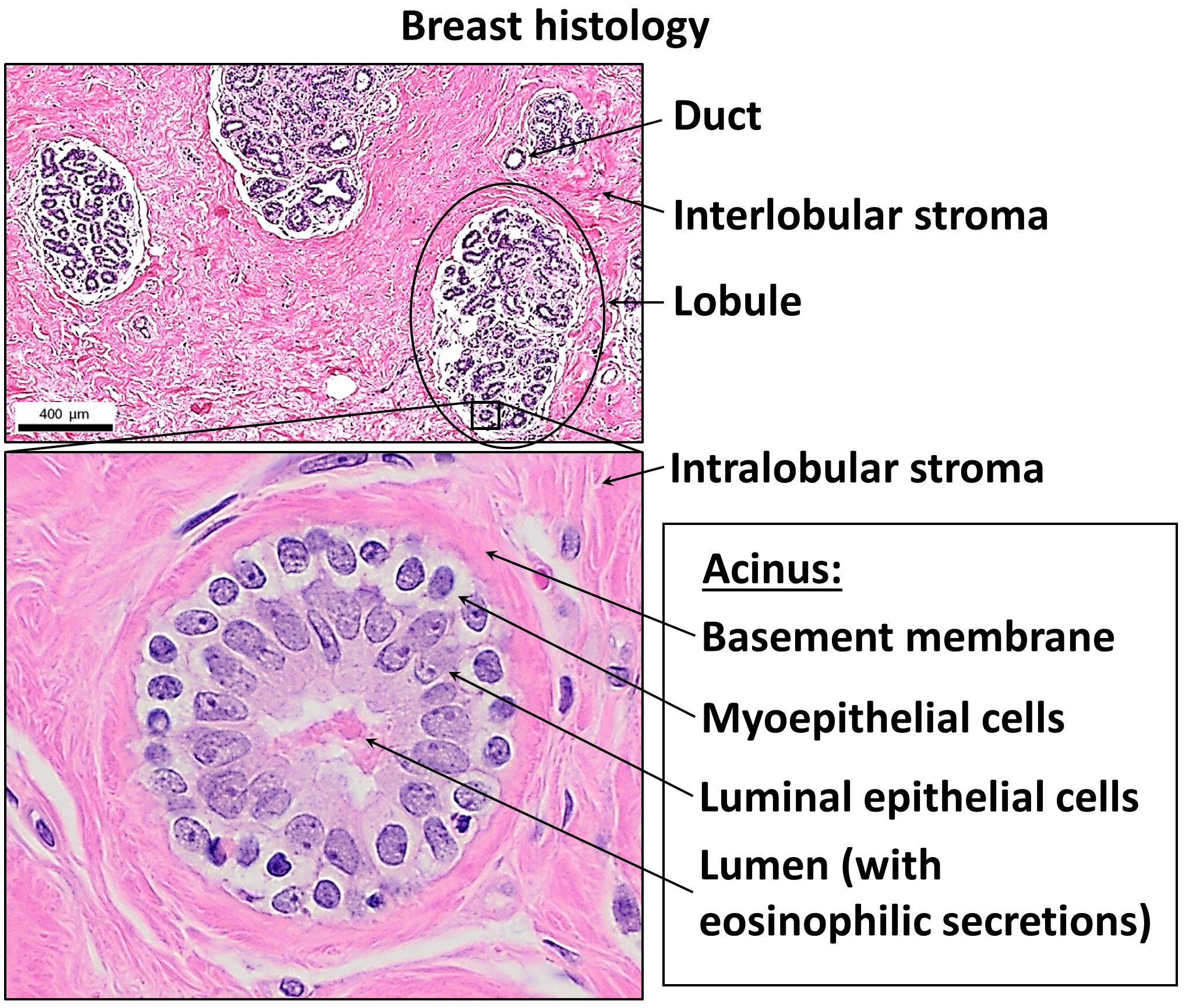
Histopathology Of Invasive Ductal Carcinoma, Intermediate Magnification
Histopathology (compound of three Greek words: 'tissue', 'suffering', and ''-logia'' 'study of') is the microscopic examination of tissue in order to study the manifestations of disease. Specifically, in clinical medicine, histopathology refers to the examination of a biopsy or surgical specimen by a pathologist, after the specimen has been processed and histological sections have been placed onto glass slides. In contrast, cytopathology examines free cells or tissue micro-fragments (as "cell blocks "). Collection of tissues Histopathological examination of tissues starts with surgery, biopsy, or autopsy. The tissue is removed from the body or plant, and then, often following expert dissection in the fresh state, placed in a fixative which stabilizes the tissues to prevent decay. The most common fixative is 10% neutral buffered formalin (corresponding to 3.7% w/v formaldehyde in neutral buffered water, such as phosphate buffered saline). Preparation for histology ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organ Failure
Organ dysfunction is a condition where an organ does not perform its expected function. Organ failure is organ dysfunction to such a degree that normal homeostasis cannot be maintained without external clinical intervention or life support. It is not a diagnosis. It can be classified by the cause, but when the cause is not known, it can also be classified by whether the onset is chronic or acute. Multiple organ failure can be associated with sepsis Sepsis is a potentially life-threatening condition that arises when the body's response to infection causes injury to its own tissues and organs. This initial stage of sepsis is followed by suppression of the immune system. Common signs and s ... and is often fatal. Countries such as Spain have shown a rise in mortality risk due to a large elderly population there. There are tools physicians use when diagnosing multiple organ failure and when prognosing the outcome. The Sequential Organ Failure Assessment (SOFA) score uses ea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Embryogenesis
An embryo ( ) is the initial stage of development for a multicellular organism. In organisms that reproduce sexually, embryonic development is the part of the life cycle that begins just after fertilization of the female egg cell by the male sperm cell. The resulting fusion of these two cells produces a single-celled zygote that undergoes many cell divisions that produce cells known as blastomeres. The blastomeres (4-cell stage) are arranged as a solid ball that when reaching a certain size, called a morula, (16-cell stage) takes in fluid to create a cavity called a blastocoel. The structure is then termed a blastula, or a blastocyst in mammals. The mammalian blastocyst hatches before implantating into the endometrial lining of the womb. Once implanted the embryo will continue its development through the next stages of gastrulation, neurulation, and organogenesis. Gastrulation is the formation of the three germ layers that will form all of the different parts o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cell Polarity
Cell polarity refers to spatial differences in shape, structure, and function within a cell. Almost all cell types exhibit some form of polarity, which enables them to carry out specialized functions. Classical examples of polarized cells are described below, including epithelial cells with apical-basal polarity, neurons in which signals propagate in one direction from dendrites to axons, and migrating cells. Furthermore, cell polarity is important during many types of asymmetric cell division to set up functional asymmetries between daughter cells. Many of the key molecular players implicated in cell polarity are well conserved. For example, in metazoan cells, the complex plays a fundamental role in cell polarity. While the biochemical details may vary, some of the core principles such as negative and/or positive feedback between different molecules are common and essential to many known polarity systems. Examples of polarized cells Epithelial cells Epithelial cells adhe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epithelial Cell
Epithelium or epithelial tissue is a thin, continuous, protective layer of Cell (biology), cells with little extracellular matrix. An example is the epidermis, the outermost layer of the skin. Epithelial (Mesothelium, mesothelial) tissues line the outer surfaces of many internal organ (anatomy), organs, the corresponding inner surfaces of body cavities, and the inner surfaces of blood vessels. Epithelial tissue is one of the four basic types of animal Tissue (biology), tissue, along with connective tissue, muscle tissue and nervous tissue. These tissues also lack blood or lymph supply. The tissue is supplied by nerves. There are three principal shapes of epithelial cell: squamous (scaly), columnar, and cuboidal. These can be arranged in a singular layer of cells as simple epithelium, either simple squamous, simple columnar, or simple cuboidal, or in layers of two or more cells deep as stratified (layered), or ''compound'', either squamous, columnar or cuboidal. In some tissues, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intercellular Adhesion Molecule
In molecular biology, intercellular adhesion molecules (ICAMs) and vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 (VCAM-1) are part of the immunoglobulin superfamily. They are important in inflammation, immune responses and in intracellular signalling events. The ICAM family consists of five members, designated ICAM-1 to ICAM-5. They are known to bind to leucocyte integrins CD11/ CD18 such as LFA-1 and Macrophage-1 antigen, during inflammation and in immune responses. In addition, ICAMs may exist in soluble forms in human plasma, due to activation and proteolysis mechanisms at cell surfaces. Mammalian intercellular adhesion molecules include: * ICAM-1 ICAM-1 (Intercellular adhesion molecule, Intercellular Adhesion Molecule 1) also known as CD54 (Cluster of Differentiation 54) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''ICAM1'' gene. This gene encodes a cell surface glycoprotein which is ty ... * ICAM2 * ICAM3 * ICAM4 * ICAM5 References Cell biology Protein families [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apoptosis
Apoptosis (from ) is a form of programmed cell death that occurs in multicellular organisms and in some eukaryotic, single-celled microorganisms such as yeast. Biochemistry, Biochemical events lead to characteristic cell changes (Morphology (biology), morphology) and death. These changes include Bleb (cell biology), blebbing, Plasmolysis, cell shrinkage, Karyorrhexis, nuclear fragmentation, Pyknosis, chromatin condensation, Apoptotic DNA fragmentation, DNA fragmentation, and mRNA decay. The average adult human loses 50 to 70 1,000,000,000, billion cells each day due to apoptosis. For the average human child between 8 and 14 years old, each day the approximate loss is 20 to 30 billion cells. In contrast to necrosis, which is a form of traumatic cell death that results from acute cellular injury, apoptosis is a highly regulated and controlled process that confers advantages during an organism's life cycle. For example, the separation of fingers and toes in a developing human embryo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Regression (medicine)
Regression in medicine is the partial or complete reversal of a disease's signs and symptoms. *Clinically, regression generally refers to a decrease in severity of symptoms without completely disappearing. At a later point, symptoms may return. These symptoms are then called recidive. *In cancer, regression refers to a specific decrease in the size or extent of a tumour. In histopathology, ''histological regression'' is one or more areas within a tumor in which neoplastic cells have disappeared or decreased in number. In melanomas, this means complete or partial disappearance from areas of the dermis (and occasionally from the epidermis The epidermis is the outermost of the three layers that comprise the skin, the inner layers being the dermis and Subcutaneous tissue, hypodermis. The epidermal layer provides a barrier to infection from environmental pathogens and regulates the ...), which have been replaced by fibrosis, accompanied by melanophages, new blood vessels, and a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reactive Oxygen Species
In chemistry and biology, reactive oxygen species (ROS) are highly Reactivity (chemistry), reactive chemicals formed from diatomic oxygen (), water, and hydrogen peroxide. Some prominent ROS are hydroperoxide (H2O2), superoxide (O2−), hydroxyl radical (OH.), and singlet oxygen(1O2). ROS are pervasive because they are readily produced from O2, which is abundant. ROS are important in many ways, both beneficial and otherwise. ROS function as signals, that turn on and off biological functions. They are intermediates in the redox behavior of O2, which is central to fuel cells. ROS are central to the photodegradation of organic pollutants in the atmosphere. Most often however, ROS are discussed in a biological context, ranging from their effects on aging and their role in causing dangerous genetic mutations. Inventory of ROS ROS are not uniformly defined. All sources include superoxide, singlet oxygen, and hydroxyl radical. Hydrogen peroxide is not nearly as reactive as these s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypoxia (medical)
Hypoxia is a condition in which the body or a region of the body is deprived of an adequate oxygen supply at the tissue (biology), tissue level. Hypoxia may be classified as either ''Generalized hypoxia, generalized'', affecting the whole body, or ''local'', affecting a region of the body. Although hypoxia is often a pathological condition, variations in arterial oxygen concentrations can be part of the normal physiology, for example, during strenuous physical exercise. Hypoxia differs from hypoxemia and anoxemia, in that hypoxia refers to a state in which oxygen present in a tissue or the whole body is insufficient, whereas hypoxemia and anoxemia refer specifically to states that have low or no Oxygen saturation (medicine), oxygen in the blood. Hypoxia in which there is complete absence of oxygen supply is referred to as anoxia. Hypoxia can be due to external causes, when the breathing gas is hypoxic, or internal causes, such as reduced effectiveness of gas transfer in the lung ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Basement Membrane
The basement membrane, also known as base membrane, is a thin, pliable sheet-like type of extracellular matrix that provides cell and tissue support and acts as a platform for complex signalling. The basement membrane sits between epithelial tissues including mesothelium and endothelium, and the underlying connective tissue. Structure As seen with the electron microscope, the basement membrane is composed of two layers, the basal lamina and the reticular lamina. The underlying connective tissue attaches to the basal lamina with collagen VII anchoring fibrils and fibrillin microfibrils. The basal lamina layer can further be subdivided into two layers based on their visual appearance in electron microscopy. The lighter-colored layer closer to the epithelium is called the lamina lucida, while the denser-colored layer closer to the connective tissue is called the lamina densa. The electron-dense lamina densa layer is about 30–70 nanometers thick and consists of an und ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |