|
Camera Control Unit
The camera control unit (CCU) is typically part of a live television broadcast chain. It is responsible for powering the professional video camera, handling signals sent over the camera cable to and from the camera, and can be used to control various camera parameters remotely. History Before cameras became self-contained units, broadcast cameras required vast racks of control units just to generate a usable picture. In outside broadcast production, these racks took up an entire section of the OB truck and were operated by a small team of skilled engineers. These vision engineers had two roles. Firstly, they set up the CCUs at the start of a production and ensured that the picture created was of broadcast quality. This process included a lengthy alignment process in which the vision engineer would work with the camera operator, to adjust the settings on both the actual camera and the CCU in tandem. During production, it was the vision engineers' job to operate the CCUs and co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sony CCUs
is a Japanese multinational conglomerate headquartered at Sony City in Minato, Tokyo, Japan. The Sony Group encompasses various businesses, including Sony Corporation (electronics), Sony Semiconductor Solutions (imaging and sensing), Sony Entertainment (including Sony Pictures and Sony Music Group), Sony Interactive Entertainment (video games), Sony Financial Group, and others. Sony was founded in 1946 as by Masaru Ibuka and Akio Morita. In 1958, the company adopted the name Initially an electronics firm, it gained early recognition for products such as the TR-55 transistor radio and the CV-2000 home video tape recorder, contributing significantly to Japan's post-war economic recovery. After Ibuka's retirement in the 1970s, Morita served as chairman until 1994, overseeing Sony's rise as a global brand recognized for innovation in consumer electronics. Landmark products included the Trinitron color television, the Walkman portable audio player, and the co-developmen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shutter Speed
In photography, shutter speed or exposure time is the length of time that the film or digital sensor inside the camera is exposed to light (that is, when the camera's shutter (photography), shutter is open) when taking a photograph. The amount of light that reaches the Photographic film, film or image sensor is proportional to the exposure time. of a second will let half as much light in as . Introduction The camera's shutter speed, the lens's aperture or f-stop, and the scene's luminance together determine the amount of light that reaches the film or sensor (the exposure (photography), exposure). Exposure value (EV) is a quantity that accounts for the shutter speed and the f-number. Once the sensitivity to light of the recording surface (either film or sensor) is set in numbers expressed in "Film speed#ISO, ISOs" (e.g. 200 ISO, 400 ISO), the light emitted by the scene photographed can be controlled through aperture and shutter-speed to match the film or sensor sensitivit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Color Burst
Colorburst is an analog and composite video signal generated by a video-signal generator used to keep the chrominance subcarrier synchronized in a color television signal. By synchronizing an oscillator with the colorburst at the back porch (beginning) of each scan line, a television receiver is able to restore the suppressed carrier of the chrominance (color) signals, and in turn decode the color information. The most common use of colorburst is to genlock equipment together as a common reference with a vision mixer in a television studio using a multi-camera setup. Explanation In NTSC, its frequency is exactly 315/88 = 3.579 MHz with a phase of 180°. PAL uses a frequency of exactly 4.43361875 MHz, with its phase alternating between 135° and 225° from line to line. Since the colorburst signal has a known amplitude, it is sometimes used as a reference level when compensating for amplitude variations in the overall signal. SECAM is unique in not having ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genlock
Genlock (generator locking) is a common technique where the video output of one source (or a specific reference signal from a signal generator) is used to synchronize other picture sources together. The aim in video applications is to ensure the coincidence of signals in time at a combining or switching point. When video instruments are synchronized in this way, they are said to be ''generator-locked'', or ''genlocked''. Possible problems Video signals generated and output by generator-locked instruments are said to be syntonized. Syntonized video signals will be precisely frequency-locked, but because of delays caused by the unequal transmission path lengths, the synchronized signals will exhibit differing phases at various points in the television system. Modern video equipment such as production switchers that have multiple video inputs often include a variable delay on each input to compensate for the phase differences and time all the input signals to precise phase coinc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microphone
A microphone, colloquially called a mic (), or mike, is a transducer that converts sound into an electrical signal. Microphones are used in many applications such as telephones, hearing aids, public address systems for concert halls and public events, motion picture production, live and recorded audio engineering, sound recording, two-way radios, megaphones, and radio and television broadcasting. They are also used in computers and other electronic devices, such as mobile phones, for recording sounds, speech recognition, Voice over IP, VoIP, and other purposes, such as Ultrasonic transducer, ultrasonic sensors or knock sensors. Several types of microphone are used today, which employ different methods to convert the air pressure variations of a sound wave to an electrical signal. The most common are the dynamic microphone, which uses a coil of wire suspended in a magnetic field; the condenser microphone, which uses the vibrating Diaphragm (acoustics), diaphragm as a capacitor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Component Video
Component video is an analog video signal that has been split into two or more component channels. In popular use, it refers to a type of component analog video (CAV) information that is transmitted or stored as three separate signals. Component video can be contrasted with '' composite video'' in which all the video information is combined into a single signal that is used in analog television. Like composite, component cables do not carry audio and are often paired with audio cables. When used without any other qualifications, the term ''component video'' usually refers to analog component video with sync on luma (Y) found on analog high-definition televisions and associated equipment from the 1990s through the 2000s when they were largely replaced with HDMI and other all-digital standards. Component video cables and their RCA jack connectors on equipment are normally color-coded red, green and blue, although the signal is not in RGB. YPbPr component video can be los ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Composite Video
Composite video, also known as CVBS (composite video baseband signal or color, video, blanking and sync), is an analog video format that combines image information—such as brightness (luminance), color (chrominance), and synchronization, into a single signal transmitted over one channel. It is most commonly used for standard-definition television, and is sometimes referred to as ''SD video''. The signal is typically carried on a yellow RCA connector, with separate connectors used for left and right audio channels. In professional equipment, a BNC connector is often used instead. Other connector types may appear in compact consumer devices like digital cameras. Composite video supports several line resolutions, including 405-line, 525-line, and 625-line interlaced formats. It exists in three major regional variants based on analog color encoding standards: NTSC, PAL, and SECAM. The same format can also be used to transmit monochrome (black-and-white) video. Signal comp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Serial Digital Interface
Serial digital interface (SDI) is a family of digital video Interface (computing), interfaces first standardized by SMPTE (The Society of Motion Picture and Television Engineers) in 1989. For example, ITU-R BT.656 and SMPTE 259M define digital video interfaces used for Broadcasting, broadcast-grade video. A related standard, known as high-definition serial digital interface (HD-SDI), is standardized in SMPTE 292M; this provides a nominal data rate of 1.485 Gbit/s. Additional SDI standards have been introduced to support increasing video resolutions (High definition video, HD, Ultra high definition, UHD and beyond), High frame rate, frame rates, 3D video, stereoscopic (3D) video, and color depth. Dual link HD-SDI consists of a pair of SMPTE 292M links, standardized by SMPTE 372M in 1998; this provides a nominal 2.970 Gbit/s interface used in applications (such as digital cinema or HDTV 1080P) that require greater fidelity and resolution than standard HDTV can provide. 3 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Analog Signal
An analog signal (American English) or analogue signal (British and Commonwealth English) is any continuous-time signal representing some other quantity, i.e., ''analogous'' to another quantity. For example, in an analog audio signal, the instantaneous signal voltage varies continuously with the pressure of the sound waves. In contrast, a digital signal represents the original time-varying quantity as a sampled sequence of quantized values. Digital sampling imposes some bandwidth and dynamic range constraints on the representation and adds quantization noise. The term ''analog signal'' usually refers to electrical signals; however, mechanical, pneumatic, hydraulic, and other systems may also convey or be considered analog signals. Representation An analog signal uses some property of the medium to convey the signal's information. For example, an aneroid barometer uses rotary position as the signal to convey pressure information. In an electrical signal, the voltage, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
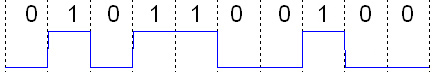
Digital Signal
A digital signal is a signal that represents data as a sequence of discrete values; at any given time it can only take on, at most, one of a finite number of values. This contrasts with an analog signal, which represents continuous values; at any given time it represents a real number within a continuous range of values. Simple digital signals represent information in discrete bands of levels. All levels within a band of values represent the same information state. In most digital circuits, the signal can have two possible valid values; this is called a binary signal or logic signal. They are represented by two voltage bands: one near a reference value (typically termed as ''ground'' or zero volts), and the other a value near the supply voltage. These correspond to the two values ''zero'' and ''one'' (or ''false'' and ''true'') of the Boolean domain, so at any given time a binary signal represents one binary digit (bit). Because of this discretization, relatively smal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Video Router
A video router, also known as a video matrix switch or SDI router, is an electronic switch designed to route video signals from multiple input sources such as cameras, VT/DDR, computers and DVD players, to one or more display devices, such as monitors, projectors, and TVs. Inputs and outputs The number of inputs and outputs varies dramatically. Routers are normally described by a ''number of inputs by number of outputs'' e.g. , , . Some video routers, by the use of additional drop-in cards, allow the system to be expanded for more inputs or outputs, or to support other formats. Signals The signal format that the router transports can be anything from analogue composite video using PAL and NTSC. Also multi-format routers can route more than one Digital video signal format, serial digital interface (SDI), HD-SDI, component video. Some routers have the ability to internally convert digital to analog and analog to digital. For HD Video, HDMI Matrix switch can be used to s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vision Mixer
A vision mixer is a device used to select between different live video sources and, in some cases, compositing live video sources together to create visual effects. In most of the world, both the equipment and its operator are called a vision mixer or video mixer; however, in the United States, the equipment is called a video switcher, production switcher or video production switcher, and its operator is known as a technical director. The role of the vision mixer for video is similar to what a mixing console does for audio. Typically a vision mixer would be found in a video production environment such as a production control room of a television studio, production truck or post-production facility. Capabilities and usage Besides hard cuts (switching directly between two input signals), mixers can also generate a variety of other transitions, from simple dissolves to pattern wipes. Additionally, most vision mixers can perform keying operations (called mattes in thi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |