|
Cam Engine
A cam engine is a reciprocating engine where instead of the conventional crankshaft, the pistons deliver their force to a cam that is then caused to rotate. The output work of the engine is driven by this cam mechanism. A variation of the cam engine, the swashplate engine (also the closely related wobble-plate engine), was briefly popular. Cam engines are generally thought of as internal combustion engines, although they have also been used as hydraulic and pneumatic motors. Hydraulic motors, particularly the swashplate type, are widely and successfully used. Internal combustion engines, though, remain almost unknown. The mechanical design of a cam engine differs from that of conventional crankshaft-driven internal combustion engines. The engine's design incorporates a cam mechanism instead of a crankshaft, presenting distinctive challenges and opportunities for enhancing performance. History The history of cam engines is connected to the development of engines, especially ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reciprocating Engine
A reciprocating engine, more often known as a piston engine, is a heat engine that uses one or more reciprocating pistons to convert high temperature and high pressure into a rotating motion. This article describes the common features of all types. The main types are: the internal combustion engine, used extensively in motor vehicles; the steam engine, the mainstay of the Industrial Revolution; and the Stirling engine for niche applications. Internal combustion engines are further classified in two ways: either a spark-ignition (SI) engine, where the spark plug initiates the combustion; or a compression-ignition (CI) engine, where the air within the cylinder is compressed, thus heating it, so that the heated air ignites fuel that is injected then or earlier.''Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach'' by Yunus A. Cengal and Michael A. Boles Common features in all types There may be one or more pistons. Each piston is inside a cylinder, into which a gas is introduced, e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Desmodromic Valve
:''In general mechanical terms, the word ''desmodromic'' is used to refer to mechanisms that have different controls for their actuation in different directions.'' A desmodromic valve is a reciprocating engine poppet valve that is positively closed by a cam and leverage system, rather than by a more conventional spring. The valves in a typical four-stroke engine allow the air/fuel mixture into the cylinder (engine), cylinder at the beginning of the cycle and exhaust spent gases at the end of the cycle. In a conventional four-stroke engine, valves are opened by a cam and closed by return spring. A desmodromic valve has two cams and two actuators, for positive opening and closing without a return spring. Etymology The word comes from the Greek language, Greek words ''desmos'' (, translated as "bond" or "knot") and ''dromos'' (, "track" or "way"). This denotes the major characteristic of the valves being continuously "bound" to the camshaft. Idea The common valve spring system is s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
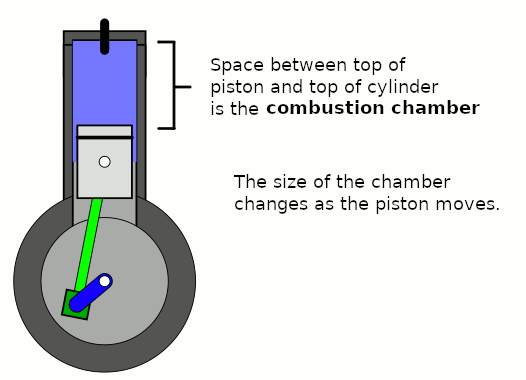
Combustion Chamber
A combustion chamber is part of an internal combustion engine in which the air–fuel ratio, fuel/air mix is burned. For steam engines, the term has also been used for an extension of the Firebox (steam engine), firebox which is used to allow a more complete combustion process. Internal combustion engines In an internal combustion engine, the pressure caused by the burning air/fuel mixture applies direct force to part of the engine (e.g. for a piston engine, the force is applied to the top of the piston), which converts the gas pressure into mechanical energy (often in the form of a rotating output shaft). This contrasts an external combustion engine, where the combustion takes place in a separate part of the engine to where the gas pressure is converted into mechanical energy. Spark-ignition engines In spark ignition engines, such as petrol engine, petrol (gasoline) engines, the combustion chamber is usually located in the cylinder head. The engines are often designed such ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nutation (engineering)
In engineering, a nutating motion is similar to that seen in a swashplate mechanism. In general, a nutating plate is carried on a skewed bearing on the main shaft and does not itself rotate, whereas a swashplate is fixed to the shaft and rotates with it. The motion is similar to the motions of coin or a tire wobbling on the ground after being dropped with the flat side down. ''Precession'' is the physical term for this kind of motion. Nutating mixers are used in gentle three-dimensional (gyrating) agitation of chemical or biological scientific procedures by repetitively moving the vessels holding the liquids. The nutating motion is widely employed in flowmeters and pumps. The displacement of volume for one revolution is first determined. The speed of the device in revolutions per unit time is measured. In the case of flowmeters, the product of the rotational speed and the displacement per revolution is then taken to find the flow rate. A nutating disc engine was patented ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aircraft Engine
An aircraft engine, often referred to as an aero engine, is the power component of an aircraft propulsion system. Aircraft using power components are referred to as powered flight. Most aircraft engines are either piston engines or gas turbines, although a few have been rocket powered and in recent years many small UAVs have used electric motors. Manufacturing industry The largest manufacturer of turboprop engines for general aviation is Pratt & Whitney. General Electric announced in 2015 entrance into the market. Development history * 1903: Manly-Balzer engine sets standards for later radial engines. * 1910: Coandă-1910, an unsuccessful ducted fan aircraft exhibited at Paris Aero Salon, powered by a piston engine. The aircraft never flew, but a patent was filed for routing exhaust gases into the duct to augment thrust. * 1914: Auguste Rateau suggests using exhaust-powered compressor – a turbocharger – to improve high-altitude performance; not accepted after the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Axial Engine
An axial engine (sometimes known as a barrel engine or Z-crank engine) is a type of reciprocating engine with pistons arranged around an output shaft with their axes parallel to the shaft. Barrel refers to the cylindrical shape of the cylinder group (result of the pistons being spaced evenly around the central crankshaft and aligned parallel to the crankshaft axis) whilst the Z-crank alludes to the shape of the crankshaft. As a cam engine, an axial engine can use either a swashplate or a wobble plate to translate the piston motion to rotation. A wobble plate is similar to a swashplate, in that the pistons press down on the plate in sequence, imparting a lateral moment that is translated into rotary motion. This motion can be simulated by placing a compact disc on a ball bearing at its centre and pressing down at progressive places around its circumference. The difference is that while a wobble plate nutates, a swash-plate rotates. An alternative design, the Rand cam engine, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Swashplate
A swashplate, also known as slant disk, is a mechanical engineering device used to translate the motion of a rotating shaft into reciprocating motion, or vice versa. The working principle is similar to crankshaft, Scotch yoke, or wobble, nutator, and Z-crank drives in engine designs. It was originally invented to replace a crankshaft, and is one of the most popular concepts used in crankless engines. It was invented by Anthony Michell in 1917. Construction A swashplate consists of a disk attached to a shaft. If the disk were aligned perpendicular to the shaft, then rotating the shaft would merely turn the disk with no reciprocating (or ''swashplate'') effect. But instead the disk is mounted at an oblique angle, which causes its edge to appear to describe a path that oscillates along the shaft's length as observed from a non-rotating point of view away from the shaft. The greater the disk's angle to the shaft, the more pronounced is this apparent linear motion. The apparent l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Propeller Speed Reduction Unit
A propeller speed reduction unit is a Transmission (mechanics), gearbox or a belt and pulley device used to reduce the output revolutions per minute (rpm) from the higher input rpm of the powerplant.Gunston 2006, p. 82. This allows the use of small Engine displacement, displacement internal combustion engines to turn Propeller (aircraft), aircraft propellers within an efficient speed range. History and operation The Wright brothers recognised the need for propeller reduction gearing in 1903, but it was not generally used on aircraft engines until larger engines were designed in the 1920s. Large engines with high crankshaft speeds and power outputs demanded propeller reduction, pilots noted the increase in performance of similar aircraft fitted with reduction gearing. Types Types of propeller speed reduction units include: *Chain drive *Single reduction or Gear#Spur, spur gear *Internal spur gear *Farman or Bevel gear, bevel epicyclic gearing, planetary type *Fixed sun gear *Fi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thrust Block
Thrust is a reaction force described quantitatively by Newton's third law. When a system expels or accelerates mass in one direction, the accelerated mass will cause a force of equal magnitude but opposite direction to be applied to that system. The force applied on a surface in a direction perpendicular or normal to the surface is also called thrust. Force, and thus thrust, is measured using the International System of Units (SI) in newtons (symbol: N), and represents the amount needed to accelerate 1 kilogram of mass at the rate of 1 meter per second per second. In mechanical engineering, force orthogonal to the main load (such as in parallel helical gears) is referred to as static thrust. Examples A fixed-wing aircraft propulsion system generates forward thrust when air is pushed in the direction opposite to flight. This can be done by different means such as the spinning blades of a propeller, the propelling jet of a jet engine, or by ejecting hot gases from a roc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anthony Michell
Anthony George Maldon Michell FRS (21 June 1870 – 17 February 1959) was an Australian mechanical engineer of the early 20th century. Early life Michell was born in London while his parents were on a visit to England from Australia to which they had emigrated 17 years earlier. The family returned to Maldon, Victoria, in 1872, where young Anthony attended one of the state primary schools newly established in that area. He later returned to England and attended the Perse Grammar School while his elder brother, John Henry, attended Trinity College, Cambridge. On leaving school, A.G.M. Michell matriculated and spent one year as a non-collegiate student at Cambridge. In 1889, he returned to Australia and studied civil engineering at the University of Melbourne, graduating in 1895. For the next two years he obtained practical experience in structural engineering with the firm Johns and Waygood. He then returned to University, and completed a Master of Civil Engineering degree in 189 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
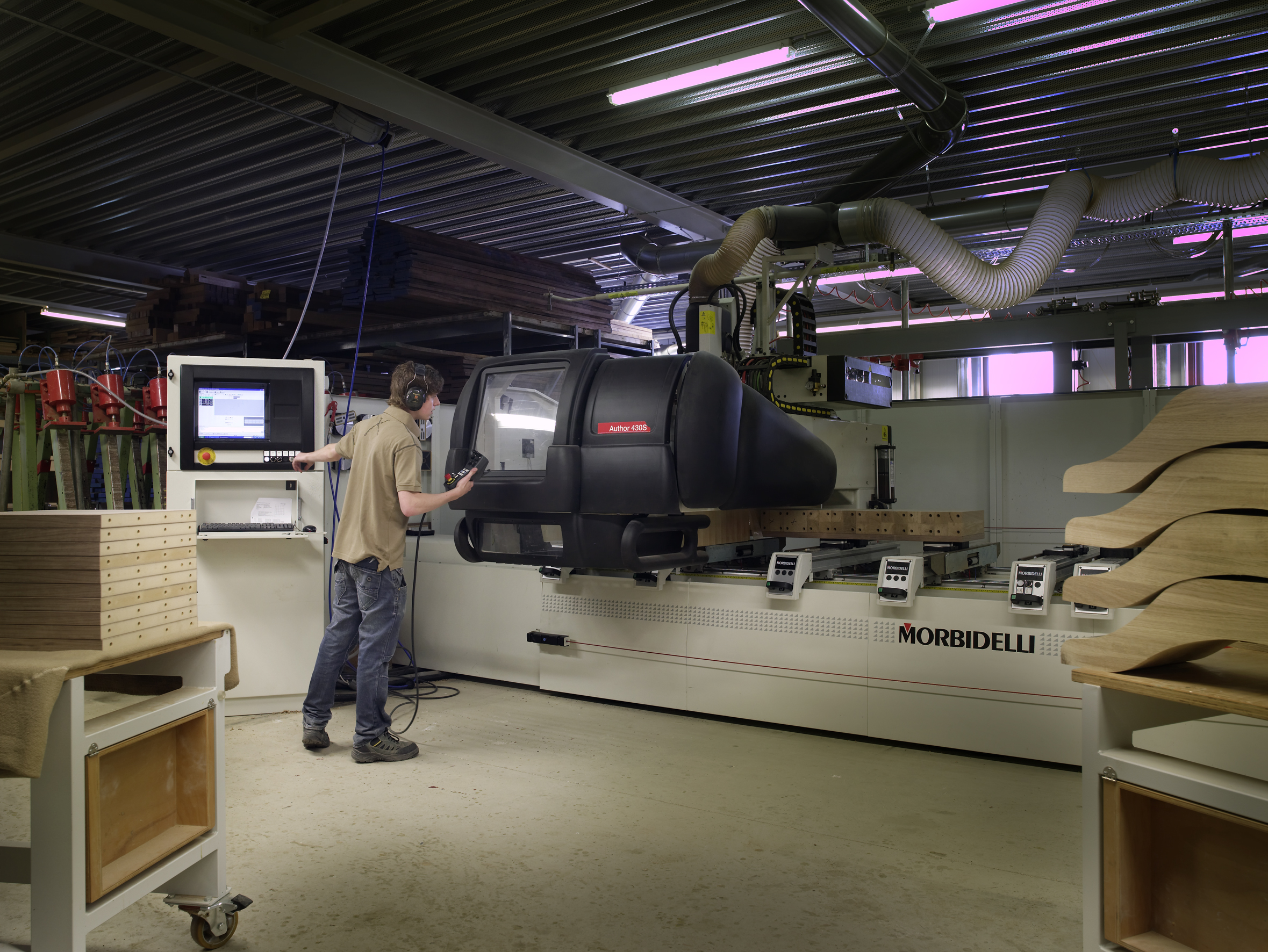
Numerical Control
Computer numerical control (CNC) or CNC machining is the automated control of machine tools by a computer. It is an evolution of numerical control (NC), where machine tools are directly managed by data storage media such as punched cards or punched tape. Because CNC allows for easier programming, modification, and real-time adjustments, it has gradually replaced NC as computing costs declined. A CNC machine is a motorized maneuverable tool and often a motorized maneuverable platform, which are both controlled by a computer, according to specific input instructions. Instructions are delivered to a CNC machine in the form of a sequential program of machine control instructions such as G-code and M-code, and then executed. The program can be written by a person or, far more often, generated by graphical computer-aided design (CAD) or computer-aided manufacturing (CAM) software. In the case of 3D printers, the part to be printed is "sliced" before the instructions (or the prog ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pressure Volume Diagram
Pressure (symbol: ''p'' or ''P'') is the force applied perpendicular to the surface of an object per unit area over which that force is distributed. Gauge pressure (also spelled ''gage'' pressure)The preferred spelling varies by country and even by industry. Further, both spellings are often used ''within'' a particular industry or country. Industries in British English-speaking countries typically use the "gauge" spelling. is the pressure relative to the ambient pressure. Various units are used to express pressure. Some of these derive from a unit of force divided by a unit of area; the SI unit of pressure, the pascal (Pa), for example, is one newton per square metre (N/m2); similarly, the pound-force per square inch (psi, symbol lbf/in2) is the traditional unit of pressure in the imperial and US customary systems. Pressure may also be expressed in terms of standard atmospheric pressure; the unit atmosphere (atm) is equal to this pressure, and the torr is defined as of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |