|
Caledonian Railway Lines To Edinburgh
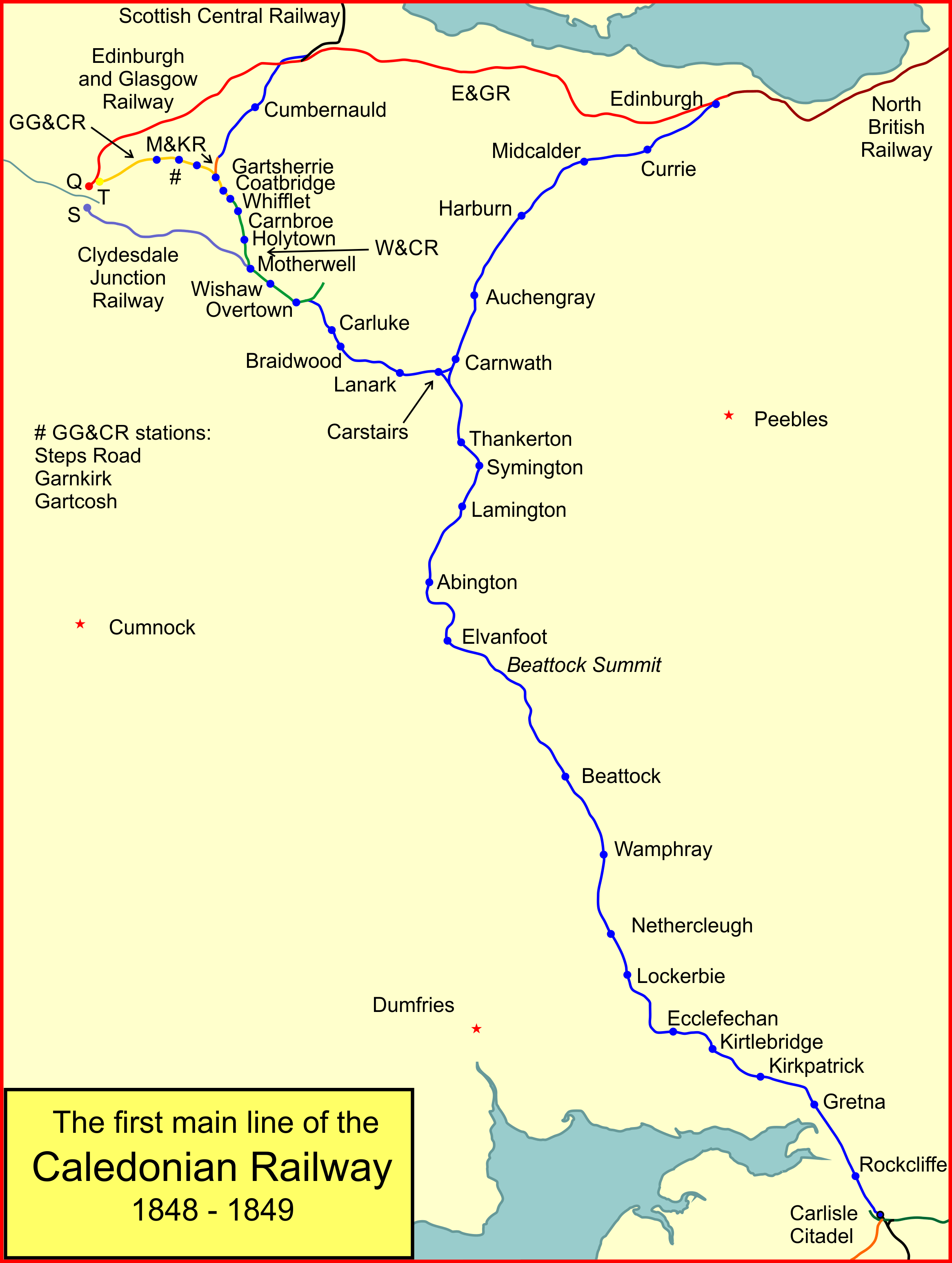
The Caledonian Railway lines to Edinburgh started with the main line that reached Edinburgh in 1848 as part of its route connecting the city with Glasgow and Carlisle. The potential of the docks at Granton and Leith led to branch line extensions, and residential development encouraged branch lines in what became the suburbs of Edinburgh. In 1869 a line was opened from Carfin through Shotts giving the Caledonian a shorter route between Glasgow and Edinburgh. In the twentieth century the industrial decline of the areas served resulted in closures. However the main line from Carstairs and the Glasgow route through Shotts have increased their passenger services considerably, and some reopenings of stations have taken place. History First main line to Edinburgh The Caledonian Railway entered Edinburgh on 15 February 1848 when it opened its Edinburgh line from Carstairs railway station, Carstairs to a terminus at Lothian Road. A locomotive depot was established at Dalry Road. This co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caley Main Line
Caley may refer to: People * Earle R. Caley (1900–1984), an American chemist * George Caley (1770–1829), an English botanist and explorer who was primarily active in Australia * John Caley (1760–1834), an English archivist and antiquarian See also * Caleys, department store in Windsor, England * George Cayley * Glasgow Caledonian University {{Disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
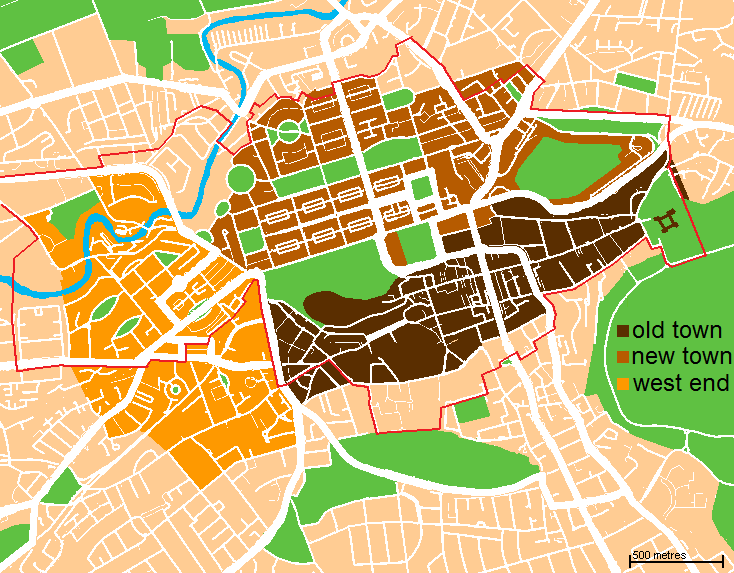
New Town, Edinburgh
The New Town is a central area of Edinburgh, the capital of Scotland. It was built in stages between 1767 and around 1850, and retains much of its original neo-classical and Georgian period architecture. Its best known street is Princes Street, facing Edinburgh Castle and the Old Town across the geological depression of the former Nor Loch. Together with the West End, the New Town was designated a UNESCO World Heritage Site alongside the Old Town in 1995. The area is also famed for the New Town Gardens, a heritage designation since March 2001. Proposal and planning The idea of a New Town was first suggested in the late 17th century when the Duke of Albany and York (later King James VII and II), when resident Royal Commissioner at Holyrood Palace, encouraged the idea of having an extended regality to the north of the city and a North Bridge. He gave the city a grant:That, when they should have occasion to enlarge their city by purchasing ground without the town, or to buil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caledonian Main Line
The Caledonian Railway main line in Scotland connected Glasgow and Edinburgh with Carlisle, Cumbria, Carlisle, via Carstairs and Beattock. It was opened in 1847 by the Caledonian Railway. The approach to Glasgow used railways already built, primarily for mineral traffic; these were later by-passed by a more direct route. Today, the route forms the northern section of the West Coast Main Line, and was electrified in the early 1970s. Opening From 1830 onwards considerable attention was given to the means by which Glasgow and Edinburgh might be connected to London, and as English railways began to develop into a network, the urgency of making a railway accelerated. The difficult terrain of the Southern Uplands and Cumberland made the selection of a route controversial. After much difficulty, the Caledonian Railway was authorised to build a line via Beattock; this was known as the ''Annandale Route''. On 10 September 1847 the line was opened between Carlisle and Beattock. The st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caledonian Railway
The Caledonian Railway (CR) was one of the two biggest of the five major Scottish railway companies prior to the 1923 Grouping. It was formed in 1845 with the objective of forming a link between English railways and Glasgow. It progressively extended its network and reached Edinburgh and Aberdeen, with a dense network of branch lines in the area surrounding Glasgow. It was absorbed into the London, Midland and Scottish Railway in 1923. Many of its principal routes are still used, and the original main line between Carlisle, Cumbria, Carlisle and Glasgow is in use as part of the West Coast Main Line railway (with a modified entry into Glasgow itself). Introduction In the mid-1830s, railways in England evolved from local concerns to longer routes that connected cities, and then became networks. In Scotland it was clear that this was the way forward, and there was a desire to connect the Central Belt to the incipient English network. There was controversy over the route that such ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Extractivism
Extractivism is the removal of natural resources particularly for export with minimal processing. This economic model is common throughout the Global South and the Arctic region, but also happens in some sacrifice zones in the Global North in European extractivism. The concept was coined in Portuguese as "extractivismo" in 1996 to describe the for-profit exploitation of forest resources in Brazil. Many actors are involved in the process of extractivism. These mainly include Multinational corporation, transnational corporations (TNCs) as the main players, but are not limited to them, because they also include the government and some (chiefly economic) community members. Trends have demonstrated that countries do not often extract their own resources; extraction is often led from abroad. Extractivism is controversial because it exists at the intersection where economic growth and environmental protection meet. This intersection is known as the green economy. Extractivism has evolve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Currie Railway Station
Currie railway station was opened in 1874 and served the area of the village of Currie that now forms part of the city of Edinburgh. Although primarily built as a goods line to serve the many mills on the Water of Leith, a passenger service was provided by the Caledonian Railway using the Balerno Loop and after grouping by the London, Midland and Scottish Railway, seeing formal closure to passenger traffic shortly after nationalisation. The station was the largest on the 'loop' line and lay in rural surroundings and had once been popular with families having a day out in the country. History Opened by the Caledonian Railway, it became part of the London Midland and Scottish Railway during the Grouping of 1923, and the LMS ran the last train to serve the station in 1943 with the expectation that the line would re-open after the war. The line passed to the Scottish Region of British Railways upon nationalisation in 1948 who then officially closed Currie in 1949. The line had man ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Balerno Railway Station
Balerno railway station was opened in 1874 and served the area of the village of Balerno that now forms part of the city of Edinburgh. Although primarily built as a goods line, with a dedicated goods station at Balerno, serving the many mills on the Water of Leith, a passenger service was provided by the Caledonian Railway using the Balerno Loop and after grouping by the London, Midland and Scottish Railway, seeing formal closure to passenger traffic shortly after nationalisation. The station was the only one with a separately served goods station on the 'loop' line and lay in rural surroundings that had been popular with families having a day out in the country. History Opened by the Caledonian Railway, it became part of the London Midland and Scottish Railway during the Grouping of 1923, and the LMS ran the last train to serve the station in 1943 with the expectation that the line would re-open after the war. The line passed to the Scottish Region of British Railways upon nat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Water Of Leith
The Water of Leith (Scottish Gaelic: ''Uisge Lìte'') is the main river flowing through central Edinburgh, Scotland, that starts in the Pentlands Hills and flows into the port of Leith and then into the sea via the Firth of Forth. Name The name ''Leith'' may be of Common Brittonic, Brittonic origin and derived from ''*lejth'' meaning 'damp, moist' (Welsh language, Welsh ''llaith''). It is less likely that the name derives from the Old Norse ''lodda'' meaning a river. The Scottish Gaelic, Gaelic form of the name is ''Lìte'' (Leith), with ''Uisge Lìte'' being the full translation of "Water of Leith". The ''Dictionary of the Scots Language'' defines the term "water" here as "A large stream, usu. thought of as intermediate in size between a Burn (landform), Burn and a river." Course The length of the main stream is . Its source is the Colzium Springs in the Pentland Hills. The river travels through Harperrig Reservoir, past the ruins of Cairns Castle, on to Balerno, Currie, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Slateford Railway Station
Slateford railway station is a railway station serving Slateford in the city of Edinburgh, Scotland. It is located on the Shotts Line from to via Shotts. The station has two platforms, connected by a stairway footbridge, and CCTV. It is managed by ScotRail. It is currently served, Monday to Saturday, by one ScotRail service each hour from Glasgow Central to Edinburgh Waverley with a two-hourly Sunday service. There are also additional services, one from Motherwell to Edinburgh in the early morning with a late evening return and a morning peak service from Glasgow Central to Edinburgh via Carstairs, returning in the evening peak. The staple passenger traction calling at this station is the Class 385 Scotrail “Express” Electric Multiple Unit, however it is also served by Class 380 “Desiro” EMUs. As this station lies on the spur of the West Coast Main Line from Carstairs to Edinburgh, a variety of CrossCountry Class 220 ''Voyager'', Avanti West Coast Class 221 ''Sup ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Balerno Rly
Balerno () is a village on the outskirts of Edinburgh, Scotland situated south-west of the city centre, next to Currie and then Juniper Green. Traditionally in the county of Midlothian it now administratively falls within the jurisdiction of the City of Edinburgh Council. The village lies at the confluence of the Water of Leith and the Bavelaw Burn. In the 18th and 19th century, the area was home to several mills using waterpower. In the 20th century, the mills closed and the village now forms a residential suburb of Edinburgh. History Balerno's name derives from the Scottish Gaelic ''Baile Àirneag'', meaning "townland/town of the sloe trees". The earliest written records of Balhernoch or Balernach are found in the late 13th century. The 18th century brought substantial development to the area, with several new flax, snuff and paper mills springing up around the Water of Leith and its tributary, the Bavelaw Burn (evidence of flax production can be seen in Harlaw Woods). Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caley Edinburgh Lines
{{Disambiguation ...
Caley may refer to: People * Earle R. Caley (1900–1984), an American chemist * George Caley (1770–1829), an English botanist and explorer who was primarily active in Australia * John Caley (1760–1834), an English archivist and antiquarian See also * Caleys, department store in Windsor, England * George Cayley * Glasgow Caledonian University Glasgow Caledonian University, informally GCU, Caledonian or Caley (), is a public university in Glasgow, Scotland. It was formed in 1993 by the merger of The Queen's College, Glasgow (founded in 1875) and Glasgow Polytechnic (originally Glasg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blackford Railway Station 1813656 2e9a2c68
Blackford might refer to: People with the surname * Charles Minor Blackford (1833–1903), American lawyer *Hosea Blackford, a fictional character in books by Harry Turtledove *Ian Blackford (born 1961), Scottish politician *Inger Mewburn (Inger Blackford Mewburn, born 1970), Australian academic * Isaac Blackford (1786–1859), American judge and politician * Richard Blackford (born 1954), English composer *Russell Blackford, Australian writer, philosopher, and critic * Steven Blackford (1977–2004), American wrestler Places ;Australia * Blackford, South Australia ;United Kingdom * Blackford, Cumbria, England * Blackford, Somerset, England *Blackford, Sedgemoor, Somerset, a village in Wedmore parish *Blackford, Edinburgh, Scotland **Blackford Hill ** Blackford Pond * Blackford, Perth and Kinross, Scotland ;United States *Blackford, Kentucky *Blackford County, Indiana Other uses *Blackford Oakes, the fictional protagonist in a series of books by William F. Buckley, Jr. See also * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |