|
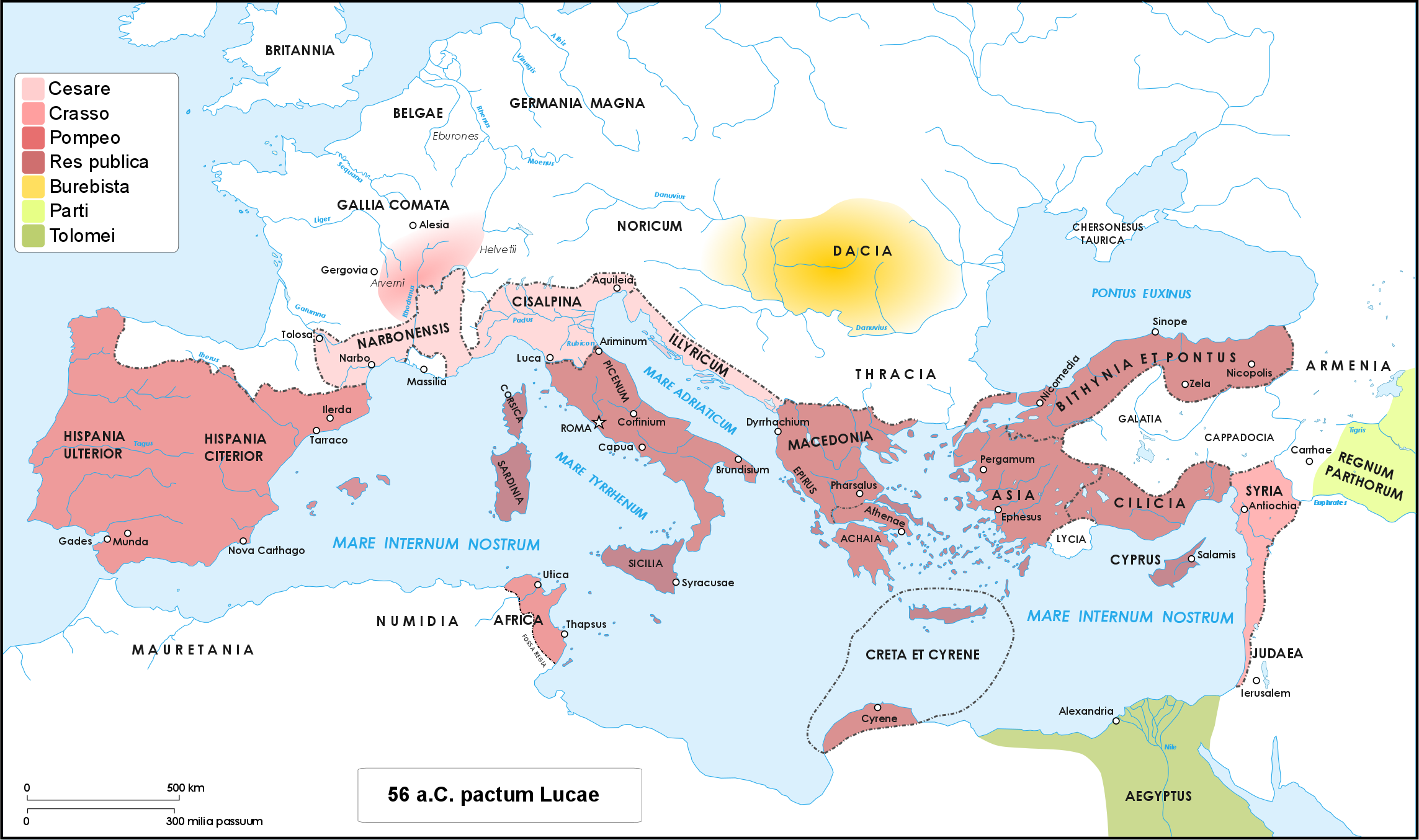
Caesar's Civil War
Caesar's civil war (49–45 BC) was a civil war during the late Roman Republic between two factions led by Julius Caesar and Pompey. The main cause of the war was political tensions relating to Caesar's place in the Republic on his expected return to Rome on the expiration of his Lex Vatinia, governorship in Roman Gaul, Gaul. Before the war, Caesar had led an Gallic Wars, invasion of Gaul for almost ten years. A build-up of tensions starting in late 50 BC, with both Caesar and Pompey refusing to back down, led to the outbreak of civil war. Pompey and his allies induced the Roman Senate, Senate to demand Caesar give up his provinces and armies in the opening days of 49 BC. Caesar refused and instead Crossing the Rubicon, marched on Rome. The war was fought in Italy, Illyria, Greece in the Roman era, Greece, Ptolemaic Egypt, Egypt, Africa (Roman province), Africa, and Hispania. The decisive events occurred in Greece in 48 BC: Pompey defeated Caesar at the Battle of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crisis Of The Roman Republic
The crisis of the Roman Republic was an extended period of political instability and social unrest from about to 44 BC that culminated in the demise of the Roman Republic and the advent of the Roman Empire. The causes and attributes of the crisis changed throughout the decades, including brigandage, wars internal and external, overwhelming corruption, land reform, the expansion of Roman citizenship, and even the changing composition of the Roman army. Modern scholars also disagree about the nature of the crisis. Traditionally, the expansion of citizenship (with all its rights, privileges, and duties) was looked upon negatively by the contemporary Sallust, the modern Edward Gibbon, and others of their respective schools, both ancient and modern, because it caused internal dissension, disputes with Rome's Italian allies, slave revolts, and riots.Fields, p. 41, citing Sallust, ''Iugurthinum'' 86.2. However, other scholars have argued that as the Republic was meant to be ''res pub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gaius Trebonius
Gaius Trebonius (c. 92 BC – January 43 BC) was a military commander and politician of the late Roman Republic, who became suffect consul in 45 BC. He was an associate of Julius Caesar, having served as his legate and having fought on his side during the civil war, and was among the tyrannicides who killed the dictator. Early career Born c. 92 BC, Trebonius' father was an '' eques'', but had not been a magistrate, and the son was considered a '' novus homo'' ("new man"), one of several in Caesar's circle. He served as quaestor around 60 BC, during which he attempted to prevent the adoption of Publius Clodius Pulcher into a plebeian family, against the wishes of the triumvirs. However, by the time Trebonius was elected plebeian tribune in 55 BC, he had become one of their supporters. During that year, Trebonius proposed a ''Lex Trebonia'' to the Tribal Assembly that the consuls Pompey and Crassus receive the provinces of Syria, Hispania Citerior and Hispania Ulterior. Further, t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marcus Petreius
Marcus Petreius (110 BC – April 46 BC) was a Roman politician and general. He was a client of Pompey and like Pompey he came from Picenum a region in eastern Italy. He cornered and killed the notorious rebel Catiline at Pistoia. Career The chronology of the early stages of Petreius’ career is unclear. He was in any case the first in his family line to enter into the Senate. Sallust describes him as a military man, who in 62 BC already had a thirty-year-long career in the army as Military tribune, Prefect and Legate behind him. Petreius served at the latest in 64 BC as Praetor, although the exact year he took on this position is unknown. Petreius first served under Pompeius Strabo during the Social War (91-87 BC). In 76–71 BC he served Pompey as a Legate in Spain fighting Sertorius. In 63/62 BC he served as Legate under the Consul Gaius Antonius Hybrida. He led the Senatorial forces in the victory over the revolutionary Lucius Sergius Catilina at Pistoria in early 62 BC ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lucius Afranius (consul)
Lucius Afranius (died 46 BC) was an ancient Roman plebeian and a client of Pompey the Great. He served Pompey as a legate during his Iberian campaigns, his eastern campaigns and remained in his service right through to the Civil War A civil war is a war between organized groups within the same Sovereign state, state (or country). The aim of one side may be to take control of the country or a region, to achieve independence for a region, or to change government policies.J .... He died in Africa right after the Battle of Thapsus in 46 BC. Early career Lucius Afranius was born into a humble family in Picenum. As a Picentine, he was favoured during his career by Pompey, who was a scion of Picenum's most distinguished family. Afranius probably served under Pompey's father Gnaeus Pompeius Strabo during the Social War (91–87 BC), Social War and under Pompey himself during the Sulla's civil war, Civil War. Sertorian War Afranius served as a legate under Pompey during hi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marcus Bibulus
Marcus Calpurnius Bibulus ( – 48 BC) was a politician of the Roman Republic. He was a conservative and upholder of the established social order who served in several magisterial positions alongside Julius Caesar and conceived a lifelong enmity towards him. In 59 BC, he was consul alongside Julius Caesar. Their partnership was contentious to the extent that Caesar's supporters assaulted Bibulus in Rome's main forum on the eve of an important vote. Bibulus withdrew from public politics for the rest of his term. Between 51 and 50 BC, he was governor of Syria, where he was effective but alienated the army by taking too much personal credit for the repulse of the Parthians. In 49, after Caesar's civil war broke out, Bibulus aligned himself with Pompey and was in charge of the fleet tasked with preventing Caesar from shipping his army across the Adriatic. He failed to stop Caesar's first fleet but was successful in delaying Caesarian reinforcements from landing in Gree ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lucius Domitius Ahenobarbus (consul 54 BC)
Lucius Domitius Ahenobarbus, consul in 54 BC, was an enemy of Julius Caesar and a strong supporter of the aristocratic () party in the late Roman Republic. He was Nero's great-great-grandfather. Biography Ahenobarbus was born as the son of consul Gnaeus Domitius Ahenobarbus. His grandfather Gnaeus Domitius Ahenobarbus was a general and consul who led a campaign to conquer southern Gaul against the Allobroges. He is first mentioned in 70 BC by Cicero as a witness against Verres. In 61, he was curule aedile, when he exhibited a hundred Numidian lions, and continued the games so long that the people were obliged to leave the circus before the exhibition was over, in order to take food, which was the first time they had done so. This pause in the games was called ''diludium''. He married Porcia, the sister of Cato the Younger, and in his aedileship supported the latter in his proposals against bribery at elections, which were directed against Pompey, who was purchasing votes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Publius Attius Varus
Publius Attius Varus (died 17 March 45 BC) was the Roman governor of Africa during the civil war between Julius Caesar and Pompey. He declared against Caesar, and initially fought Gaius Scribonius Curio, who was sent against him in 49 BC. Political career Varus held the office of praetor no later than 53 BC. No record of his earlier political career survives. He was promagistrate, and likely propraetor, in Africa in 52 and possibly earlier. Role in civil war On the outbreak of the civil war, Varus, an adherent of the optimates, was stationed in Picenum at the head of a considerable force. Upon the approach of Caesar, he was forced to evacuate the area. He and his levies joined Pompey in Apulia. When Pompey left Italy for Greece, Varus crossed over into Africa, and took possession of his former province, which had been allotted to Q. Aelius Tubero for the purpose of obtaining grain. Excluded from his province by Varus, Tubero then went to join Pompey. Varus was well known in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metellus Scipio
Quintus Caecilius Metellus Pius Scipio (c. 95 – 46 BC), often referred to as Metellus Scipio, was a Roman senator and military commander. During the civil war between Julius Caesar and the senatorial faction led by Pompey, he was a staunch supporter of the latter. He led troops against Caesar's forces, mainly in the battles of Pharsalus and Thapsus, where he was defeated. He later committed suicide. Ronald Syme called him "the last Scipio of any consequence in Roman history." Family connections and name The son of Publius Cornelius Scipio Nasica, praetor about 95 BC, and Licinia, Scipio was the grandson of Publius Cornelius Scipio Nasica, consul in 111, and Lucius Licinius Crassus, consul in 95. His great-grandfather was Scipio Nasica Serapio, the man who murdered Tiberius Gracchus in 133 BC. Through his mother Cornelia, Serapio was also the grandson of Scipio Africanus. Scipio's father died not long after his praetorship, and was survived by two sons and two daughters. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Titus Labienus
Titus Labienus (17 March 45 BC) was a high-ranking military officer in the late Roman Republic. He served as tribune of the Plebs in 63 BC. Although mostly remembered as one of Julius Caesar's best lieutenants in Gaul and mentioned frequently in the accounts of his military campaigns, Labienus chose to oppose him during the Civil War and was killed at Munda. He was the father of Quintus Labienus. Biography Early career As his praetorship was in 60 or 59 BC, Titus Labienus most likely was born around 100 BC.Tyrrell (3) Many sources suggest that he came from the town of Cingulum in Picenum. His family was of equestrian status. He most likely had early ties with Pompey during his time as a patron for Picenum and his desire to rise in military rank. His early service was c. 78–75 BC in Cilicia under Publius Servilius Vatia Isauricus fighting pirates and the Isaurian hill tribes. Tribune of the Plebs, Trial of Gaius Rabirius In 63 BC, Titus Labienus was a tribune of the Ple ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pompey
Gnaeus Pompeius Magnus (; 29 September 106 BC – 28 September 48 BC), known in English as Pompey ( ) or Pompey the Great, was a Roman general and statesman who was prominent in the last decades of the Roman Republic. As a young man, he was a partisan and protégé of the dictator Sulla, after whose death he achieved much military and political success himself. He was an ally and a rival of Julius Caesar, and died in civil war with him. A member of the senatorial nobility, Pompey entered into a military career while still young. He rose to prominence serving Sulla as a commander in the civil war of 83–81 BC. Pompey's success as a general while young enabled him to advance directly to his first consulship without following the traditional '' cursus honorum'' (the required steps to advance in a political career). He was elected as consul on three occasions (70, 55, 52 BC). He celebrated three triumphs, served as a commander in the Sertorian War, t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cleopatra
Cleopatra VII Thea Philopator (; The name Cleopatra is pronounced , or sometimes in both British and American English, see and respectively. Her name was pronounced in the Greek dialect of Egypt (see Koine Greek phonology). She was also styled as Thea Neotera () and Philopatris (); see 70/69 BC10 or 12 August 30 BC) was Queen of the Ptolemaic Kingdom of Ancient Egypt, Egypt from 51 to 30 BC, and the last active Hellenistic pharaoh.She was also a diplomat, Ancient navies and vessels, naval commander, linguist, and Ancient Greek medicine, medical author; see and . A member of the Ptolemaic dynasty, she was a descendant of its founder Ptolemy I Soter, a Ancient Macedonians, Macedonian Greek general and Government of Macedonia (ancient kingdom)#Companions, friends, councils, and assemblies, companion of Alexander the Great. writes about Ptolemy I Soter: "The Ptolemaic dynasty, of which Cleopatra was the last representative, was founded at the end of the f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |