|
Cyr61
Cysteine-rich angiogenic inducer 61 (CYR61) or CCN family member 1 (CCN1), is a matricellular protein that in humans is encoded by the ''CYR61'' gene. CYR61 is a secreted, extracellular matrix (ECM)-associated signaling protein of the CCN family ( CCN intercellular signaling protein). CYR61 is capable of regulating a broad range of cellular activities, including cell adhesion, migration, proliferation, differentiation, apoptosis, and senescence through interaction with cell surface integrin receptors and heparan sulfate proteoglycans. During embryonic development, CYR61 is critical for cardiac septal morphogenesis, blood vessel formation in placenta, and vascular integrity. In adulthood CYR61 plays important roles in inflammation and tissue repair, and is associated with diseases related to chronic inflammation, including rheumatoid arthritis, atherosclerosis, diabetes-related nephropathy and retinopathy, and many different forms of cancers. CCN protein family CYR61 was first ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CCN Intercellular Signaling Protein
CCN proteins are a family of extracellular matrix (ECM)-associated proteins involved in intercellular signaling. Due to their dynamic role within the ECM they are considered matricellular proteins. Background The acronym CCN is derived from the first three members of the family discovered, namely CYR61 (cysteine-rich angiogenic protein 61 or CCN1), CTGF (connective tissue growth factor or CCN2), and NOV (nephroblastoma overexpressed or CCN3). Together with three Wnt-induced secreted proteins, they comprise the CCN family of matricellular proteins. These proteins have now been renamed CCN1-6 by international consensus. Members of the CCN protein family are characterized by having four conserved cysteine-rich domains, which include the insulin-like growth factor-binding domain (IGFBP), the Von Willebrand factor type C domain (VWC), the thrombospondin type 1 repeat (TSR), and a C-terminal domain (CT) with a cysteine knot motif. CCN proteins have been shown to play important roles in m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NOV (gene)
NOV (nephroblastoma overexpressed) also known as CCN3 is a matricellular protein that in humans is encoded by the ''NOV'' gene. CCN family NOV is a member of the CCN family of secreted, extracellular matrix (ECM)-associated signaling proteins (see also CCN intercellular signaling protein). The CCN acronym is derived from the first three members of the family being identified, namely CYR61 (cysteine-rich angiogenic inducer 61, or CCN1), CTGF (connective tissue growth factor, or CCN2), and NOV. These proteins, together with WISP1 (CCN4), WISP2 (CCN5), and WISP3 (CCN6) comprise the six-member CCN family in vertebrates and have been renamed CCN1-6 in the order of their discovery by international consensus. Structure The human NOV protein contains 357 amino acids with an N-terminal secretory signal peptide followed by four structurally distinct domains with homologies to insulin-like growth factor binding protein (IGFBP), von Willebrand type C repeats ( vWC), thrombospondin type ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
WISP1
WNT1-inducible-signaling pathway protein 1 (WISP-1), also known as CCN4, is a matricellular protein that in humans is encoded by the ''WISP1'' gene In biology, the word gene (from , ; "... Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ''birth'' or ''gender'') can have several different meanings. The Mendelian gene is a b .... Structure WISP-1 is highly homologous to CYR61 (CCN1) and CTGF (CCN2), and is a member of the CCN family of secreted, extracellular matrix (ECM)-associated signaling proteins (CCN intercellular signaling protein). The CCN family of proteins shares a common molecular protein structure, characterized by an N-terminal secretory signal peptide followed by four distinct domains with homologies to insulin-like growth factor binding protein (insulin-like growth factor-binding protein, IGFBP), von Willebrand type C repeats (Von Willebrand factor type C domain, vWC), thrombospondin type 1 re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mir-155
MiR-155 is a microRNA that in humans is encoded by the ''MIR155'' host gene or ''MIR155HG''. MiR-155 plays a role in various physiological and pathological processes. Exogenous molecular control ''in vivo'' of miR-155 expression may inhibit malignant growth, viral infections, and enhance the progression of cardiovascular diseases. Discovery The ''MIR155HG'' was initially identified as a gene that was transcriptionally activated by promoter insertion at a common retroviral integration site in B-cell lymphomas and was formerly called BIC (B-cell Integration Cluster). The ''MIR155HG'' is transcribed by RNA polymerase II and the resulting ~1,500 nucleotide RNA is capped and polyadenylated. The 23 nucleotide single-stranded miR-155, which is harbored in exon 3, is subsequently processed from the parent RNA molecule. Biogenesis The MIR155HG RNA transcript does not contain a long open reading frame (ORF), however, it does include an imperfectly base-paired stem loop that is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Integrin
Integrins are transmembrane receptors that facilitate cell-cell and cell-extracellular matrix (ECM) adhesion. Upon ligand binding, integrins activate signal transduction pathways that mediate cellular signals such as regulation of the cell cycle, organization of the intracellular cytoskeleton, and movement of new receptors to the cell membrane. The presence of integrins allows rapid and flexible responses to events at the cell surface (''e.g''. signal platelets to initiate an interaction with coagulation factors). Several types of integrins exist, and one cell generally has multiple different types on its surface. Integrins are found in all animals while integrin-like receptors are found in plant cells. Integrins work alongside other proteins such as cadherins, the immunoglobulin superfamily cell adhesion molecules, selectins and syndecans, to mediate cell–cell and cell–matrix interaction. Ligands for integrins include fibronectin, vitronectin, collagen and laminin. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
WISP2
WNT1-inducible-signaling pathway protein 2, or WISP-2 (also named CCN5) is a matricellular protein that in humans is encoded by the ''WISP2'' gene. Function The CCN family of proteins regulates diverse cellular functions, including cell adhesion, migration, proliferation, differentiation. Structure WISP-2 is a member of the CCN family (CCN intercellular signaling protein) of secreted, extracellular matrix (ECM)-associated signaling matricellular proteins. The CCN acronym is derived from the first three members of the family identified, namely CYR61 (CCN1), CTGF (connective tissue growth factor, or CCN2), and NOV. These proteins, together with WISP1/CCN4, WISP2 (CCN5, this gene), and WISP3 (CCN6) comprise the six-member CCN family in vertebrates. CCN proteins characteristically contain an N-terminal secretory signal peptide followed by four structurally distinct domains with homologies to insulin-like growth factor binding protein (IGFBP), von Willebrand type C repeats ( vWC) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chromosome 1
Chromosome 1 is the designation for the largest human chromosome. Humans have two copies of chromosome 1, as they do with all of the autosomes, which are the non- sex chromosomes. Chromosome 1 spans about 249 million nucleotide base pairs, which are the basic units of information for DNA.http://vega.sanger.ac.uk/Homo_sapiens/mapview?chr=1 Chromosome size and number of genes derived from this database, retrieved 2012-03-11. It represents about 8% of the total DNA in human cells. It was the last completed chromosome, sequenced two decades after the beginning of the Human Genome Project. Genes Number of genes The following are some of the gene count estimates of human chromosome 1. Because researchers use different approaches to genome annotation their predictions of the number of genes on each chromosome varies (for technical details, see gene prediction). Among various projects, the collaborative consensus coding sequence project ( CCDS) takes an extremely conservative str ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CTGF
CTGF, also known as CCN2 or connective tissue growth factor, is a matricellular protein of the CCN family of extracellular matrix-associated heparin-binding proteins (see also CCN intercellular signaling protein). CTGF has important roles in many biological processes, including cell adhesion, migration, proliferation, angiogenesis, skeletal development, and tissue wound repair, and is critically involved in fibrotic disease and several forms of cancers. Structure and binding partners Members of the CCN protein family, including CTGF, are structurally characterized by having four conserved, cysteine-rich domains. These domains are, from N- to C-termini, the insulin-like growth factor binding protein ( IGFBP) domain, the von Willebrand type C repeats ( vWC) domain, the thrombospondin type 1 repeat (TSR) domain, and a C-terminal domain (CT) with a cysteine knot motif. CTGF exerts its functions by binding to various cell surface receptors in a context-dependent manner, including i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
WISP3
WNT1-inducible-signaling pathway protein 3 (WISP3, also named CCN6) is a matricellular protein that in humans is encoded by the ''WISP3'' gene. Structure It is a member of the CCN family ( CCN intercellular signaling protein) of secreted, extracellular matrix (ECM)-associated signaling matricellular proteins. The CCN acronym is derived from the first three members of the family identified, namely CYR61 (cysteine-rich angiogenic inducer 61, or CCN1), CTGF (connective tissue growth factor, or CCN2), and NOV (nephroblastoma overexpressed, or CCN3). These proteins, together with WISP1 WNT1-inducible-signaling pathway protein 1 (WISP-1), also known as CCN4, is a matricellular protein that in humans is encoded by the ''WISP1'' gene In biology, the word gene (from , ; "... Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe ... (CCN4), and WISP2 (CCN5) comprise the six-member CCN family in vertebrates. CCN proteins characteristically contain an N-terminal secretory signal pep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Promoter (genetics)
In genetics, a promoter is a sequence of DNA to which proteins bind to initiate transcription of a single RNA transcript from the DNA downstream of the promoter. The RNA transcript may encode a protein (mRNA), or can have a function in and of itself, such as tRNA or rRNA. Promoters are located near the transcription start sites of genes, upstream on the DNA (towards the 5' region of the sense strand). Promoters can be about 100–1000 base pairs long, the sequence of which is highly dependent on the gene and product of transcription, type or class of RNA polymerase recruited to the site, and species of organism. Promoters control gene expression in bacteria and eukaryotes. RNA polymerase must attach to DNA near a gene for transcription to occur. Promoter DNA sequences provide an enzyme binding site. The -10 sequence is TATAAT. -35 sequences are conserved on average, but not in most promoters. Artificial promoters with conserved -10 and -35 elements transcribe more slowly. All ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
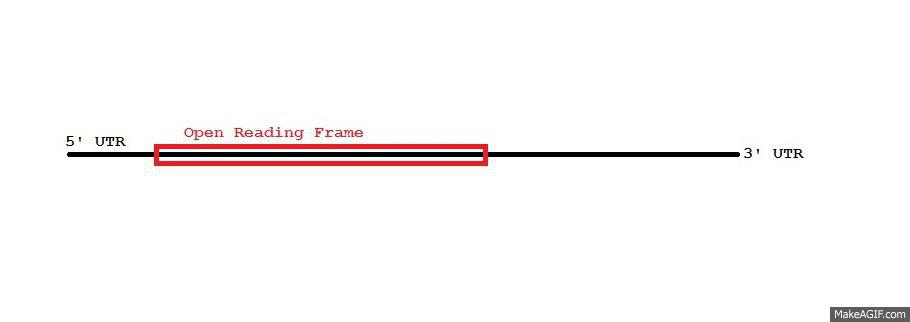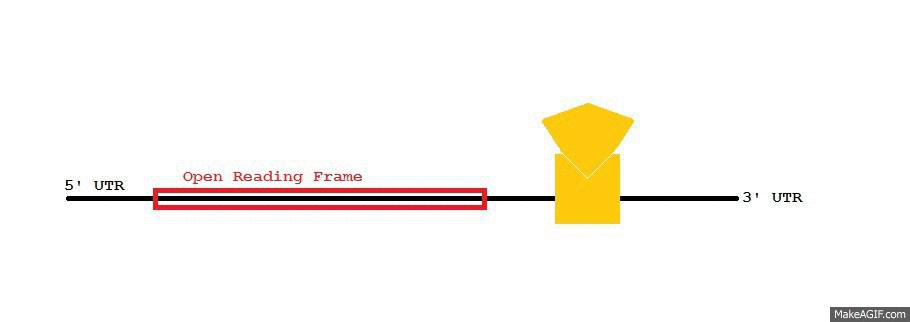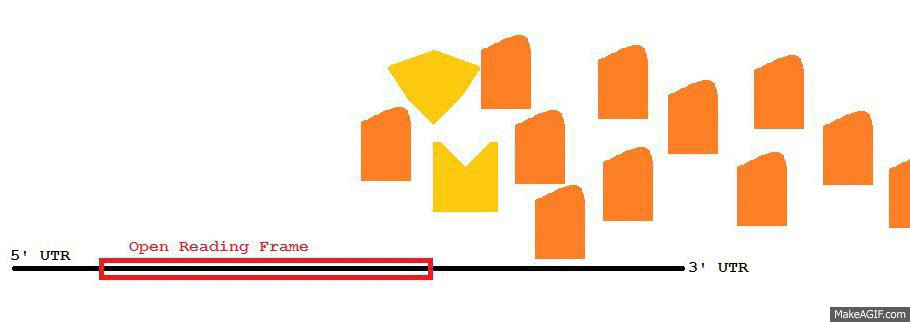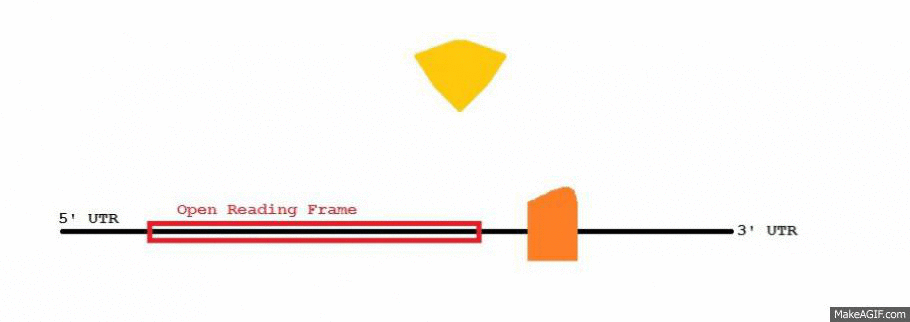
MRNA
In molecular biology, messenger ribonucleic acid (mRNA) is a single-stranded molecule of RNA that corresponds to the genetic sequence of a gene, and is read by a ribosome in the process of synthesizing a protein. mRNA is created during the process of transcription, where an enzyme ( RNA polymerase) converts the gene into primary transcript mRNA (also known as pre-mRNA). This pre-mRNA usually still contains introns, regions that will not go on to code for the final amino acid sequence. These are removed in the process of RNA splicing, leaving only exons, regions that will encode the protein. This exon sequence constitutes mature mRNA. Mature mRNA is then read by the ribosome, and, utilising amino acids carried by transfer RNA (tRNA), the ribosome creates the protein. This process is known as translation. All of these processes form part of the central dogma of molecular biology, which describes the flow of genetic information in a biological system. As in DNA, gen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
AU-rich Element
Adenylate-uridylate-rich elements (AU-rich elements; AREs) are found in the 3' untranslated region (UTR) of many messenger RNAs (mRNAs) that code for proto- oncogenes, nuclear transcription factors, and cytokines. AREs are one of the most common determinants of RNA stability in mammalian cells. AREs are defined as a region with frequent adenine and uridine bases in a mRNA. They usually target the mRNA for rapid degradation. ARE-directed mRNA degradation is influenced by many exogenous factors, including phorbol esters, calcium ionophores, cytokines, and transcription inhibitors. These observations suggest that AREs play a critical role in the regulation of gene transcription during cell growth and differentiation, and the immune response. AREs have been divided into three classes with different sequences. The best characterised adenylate uridylate (AU)-rich Elements have a core sequence of AUUUA within U-rich sequences (for example WWWU(AUUUA)UUUW where W is A or U). This lies ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |