|
Brennisteinsfjöll Volcanic System
Brennisteinsfjöll (, "Sulfur mountains" Brennisteinsfjöll. Detailed description. In: Catalogue of Icelandic Volcanoes. Retrieved 27 July 2020) is a minor Volcanism of Iceland, volcanic system, with crater rows and small es on the in southwest |
Road 417 In Iceland 03
A road is a thoroughfare used primarily for movement of traffic. Roads differ from streets, whose primary use is local access. They also differ from stroads, which combine the features of streets and roads. Most modern roads are Road surface, paved. The words "road" and "street" are commonly considered to be interchangeable, but the distinction is important in urban design. There are road hierarchy, many types of roads, including parkways, avenue (landscape), avenues, controlled-access highways (freeways, motorways, and expressways), tollways, interstates, highways, and local roads. The primary features of roads include lanes, sidewalks (pavement), roadways (carriageways), median strip, medians, shoulder (road), shoulders, road verge, verges, bike paths (cycle paths), and shared-use paths. Definitions Historically, many roads were simply recognizable routes without any formal construction or some maintenance. The Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development, Organi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
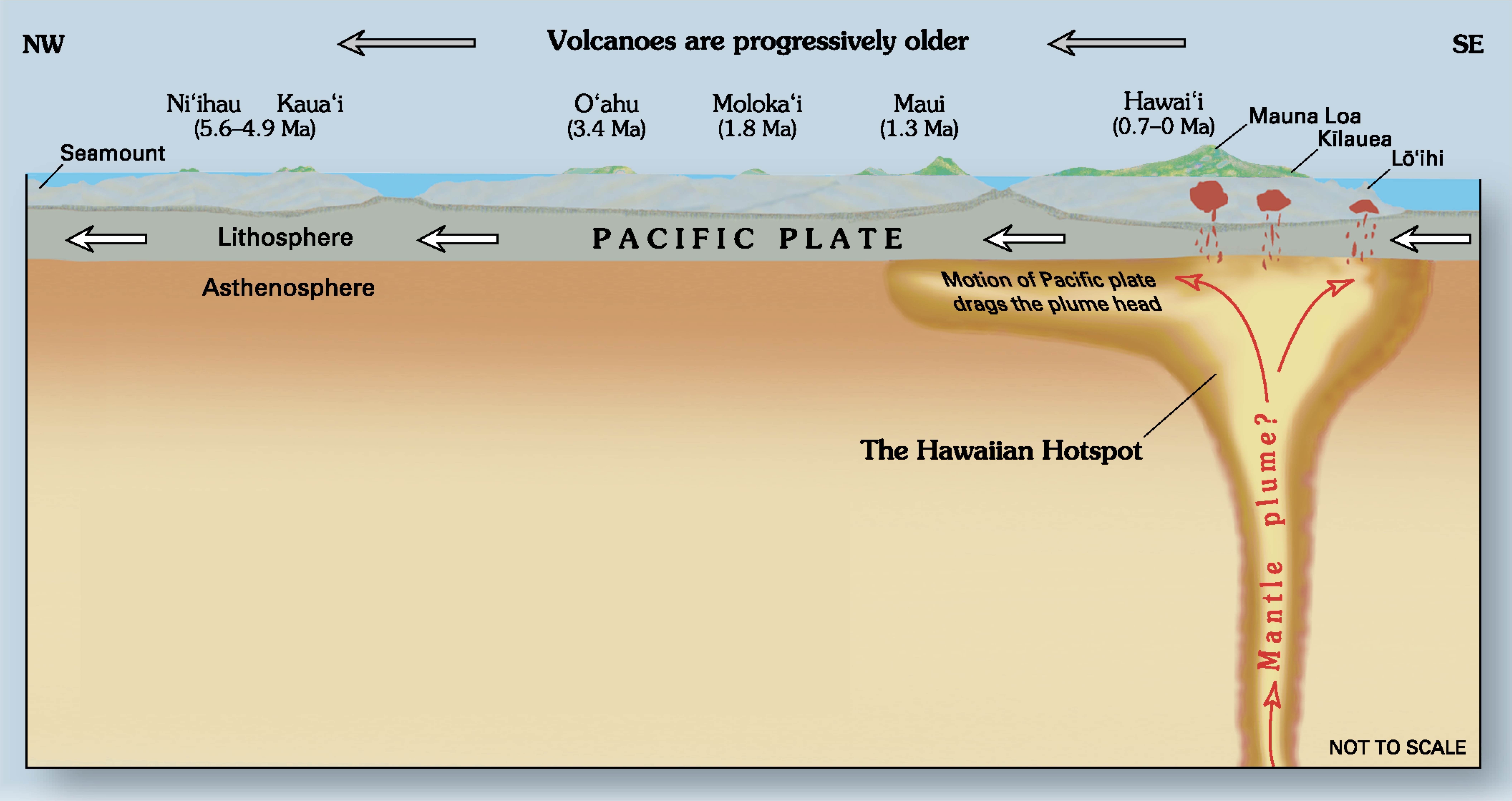
Hotspot (geology)
In geology, hotspots (or hot spots) are volcanic locales thought to be fed by underlying Mantle (geology), mantle that is anomalously hot compared with the surrounding mantle. Examples include the Hawaii hotspot, Hawaii, Iceland hotspot, Iceland, and Yellowstone hotspots. A hotspot's position on the Earth's surface is independent of plate boundary, tectonic plate boundaries, and so hotspots may create a chain of volcanoes as the plates move above them. There are two hypotheses that attempt to explain their origins. One suggests that hotspots are due to mantle plumes that rise as thermal diapirs from the core–mantle boundary. The alternative plate theory (volcanism), plate theory is that the mantle source beneath a hotspot is not anomalously hot, rather the crust above is unusually weak or thin, so that lithospheric extension permits the passive rising of melt from shallow depths. Origin The origins of the concept of hotspots lie in the work of J. Tuzo Wilson, who postulated ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Þingvellir
Þingvellir (, anglicised as ThingvellirThe spelling ''Pingvellir'' is sometimes seen, although the letter "p" is unrelated to the letter thorn (letter), "þ" (thorn), which is pronounced as "th".) was the site of the Althing, Alþing, the annual parliament of Iceland from the year 930 until the last session held at in 1798. Since 1881, the parliament has been located within Alþingishúsið in Reykjavík. is now a national park in the municipality of in southwestern Iceland, about 40 km (25 miles) northeast of Iceland's capital, . is a site of historical, cultural, and geological significance, and is one of the most popular tourist destinations in Iceland. The park lies in a rift valley that marks the crest of the Mid-Atlantic Ridge and the boundary between the North American Plate, North American and Eurasian Plate, Eurasian tectonic plates. To its south lies , the largest natural lake in Iceland. National Park ( ) was founded in 1930, marking the 1000th anniversary o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Þingvallavatn
Þingvallavatn (, ), anglicised as Thingvallavatn, is a rift valley lake in southwestern Iceland. With a surface of 84 km2 it is the largest natural lake in Iceland. Its greatest depth is 114 m. At the northern shore of the lake, at Þingvellir (after which the lake is named), the Alþingi, the national parliament, was founded in the year 930, and held its sessions there until 1799 and still as of today the name Alþingi Íslendinga is carried by the parliament of Iceland. The lake lies partially within Þingvellir National Park. The volcanic origin of the islands in the lake is clearly visible. The cracks and faults around it, of which the Almannagjá ravine is the largest, is where the Eurasian and North American tectonic plates meet. Silfra fissure is a popular scuba and snorkeling site. The only outflow from lake Þingvallavatn is the river Sog. One of the noted features of the lake is the presence of four morphs of the Arctic charr.Malmquist, H. J., Snorrason, S. S. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hengill
Hengill () is a volcanic table mountain situated in the south-west of Iceland, to the south of Þingvellir. The volcano is still active, as evidenced by its numerous hot springs and fumaroles, but the last eruption occurred approximately 2,000 years ago, before the settlement of Iceland. Geography The mountain is south of Lake Thingvallavatn (Þingvallavatn in Icelandic), south-west of the Nesjavellir geothermal area, south of Þingvellir National Park and is the most prominent part of a volcanic region that extends to the coast. South of the mountain towards the coast is the Hellisheiði geothermal area to its south-west, and the town of Hveragerði on Iceland's main ringroad, Route 1 about east of Reykjavík. At the coast is the port of Þorlákshöfn. Geology The mountain is part of the long Hengill volcanic system, which is part of the Reykjanes volcanic belt, and is a hyaloclastite massif of tuyas and tindars. The dominant lava in the Hengill volcanic system is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kleifarvatn
Kleifarvatn () is the largest lake on the Reykjanesskagi, Reykjanes Peninsula in Iceland, situated in the southern part of the peninsula. It is located on the Fissure vent, fissure zone of the Mid-Atlantic Ridge. The lake has no visible water coming in or going out as most of its water comes and leaves underground. The lake can be reached via a track, and there are two areas with high temperature that can be found not far from it: Seltún/Krýsuvík and another to the east. A 2012 survey demonstrated one definite geothermal vent under the lake and suggested two others in a linear line trending as for most of the faults in the area. Kleifarvatn was first surveyed in 1964 and studied at greater resolution later. The lake's greatest recorded depth was in 1975 with height above sea level of . After the 2000 Iceland earthquakes, the lake began to diminish, so that at least 20% of its surface has since disappeared and the serial surveys suggest there has been some material deposition ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |