|
Box Hill, Surrey
Box Hill is a summit of the North Downs in Surrey, approximately south-west of London. It is named after the ancient Buxus sempervirens, box woodland found on the steepest west-facing chalk slopes overlooking the River Mole. The western part of the hill is owned and managed by the National Trust for Places of Historic Interest or Natural Beauty, National Trust, whilst the village of Box Hill lies on higher ground to the east. The highest point is Betchworth Clump at Ordnance Datum, above OD, although the Salomons Memorial (at 172 metres) overlooking the town of Dorking is the most popular viewpoint. Box Hill is part of the Surrey Hills National Landscape and forms part of the Mole Gap to Reigate Escarpment Site of Special Scientific Interest. The north- and south-facing slopes support an area of chalk downland, noted for its orchids and other rare plant species. The hill provides a habitat for 38 species of butterfly, and has given its name to a species of Coreidae, squash bu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
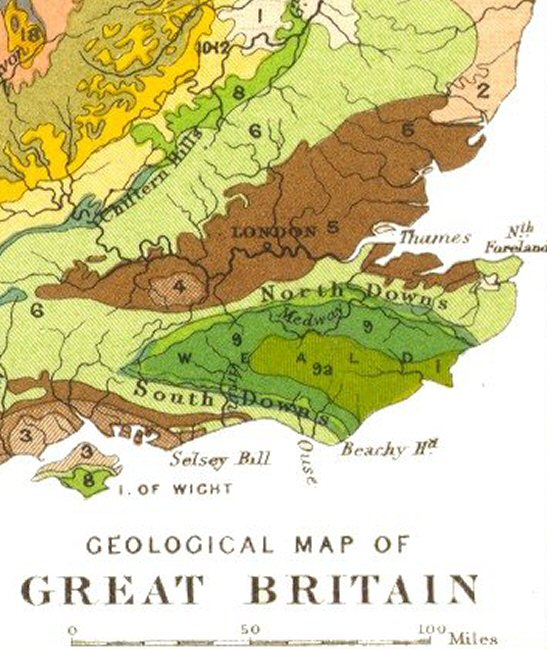
North Downs
The North Downs are a ridge of chalk hills in south east England that stretch from Farnham in Surrey to the White Cliffs of Dover in Kent. Much of the North Downs comprises two Area of Outstanding Natural Beauty, Areas of Outstanding Natural Beauty (AONBs): the Surrey Hills AONB, Surrey Hills and the Kent Downs AONB, Kent Downs. The North Downs Way National Trail runs along the North Downs from Farnham to Dover. The highest point in the North Downs is Botley Hill, Surrey ( above sea level). The ''County Top'' of Kent is Betsom's Hill ( above sea level), which is less than 1 km from Westerham Heights, Bromley, the highest point in Greater London at an elevation of . Etymology 'Downs' is from Old English ''dun'', meaning, amongst other things, "hill". The word acquired the sense of "elevated rolling grassland" around the 14th century. The name contains "North" to distinguish them from a similar range of hills – the South Downs – which runs roughly parallel to them but s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mole Gap To Reigate Escarpment
Mole Gap to Reigate Escarpment is a biological and geological Site of Special Scientific Interest west of Reigate in Surrey. It is a Geological Conservation Review site and a Special Area of Conservation. Part of it is a Nature Conservation Review site, Grade I. Two small private nature reserves in the site are managed by the Surrey Wildlife Trust, Dawcombe and Fraser Down. This eight mile long site on the North Downs contains an outstanding range of wildlife habitats, including large areas of woodland and chalk grassland. Mole Gap has a variety of Quaternary landforms and there are well developed river cliffs where alluvial fan An alluvial fan is an accumulation of sediments that fans outwards from a concentrated source of sediments, such as a narrow canyon emerging from an escarpment. They are characteristic of mountainous terrain in arid to Semi-arid climate, semiar ...s have diverted the River Mole against the valley sides. References External linksSurrey County C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Escarpment
An escarpment is a steep slope or long cliff that forms as a result of faulting or erosion and separates two relatively level areas having different elevations. Due to the similarity, the term '' scarp'' may mistakenly be incorrectly used interchangeably with ''escarpment.'' ''Escarpment'' referring to the margin between two landforms, and ''scarp'' referring to a cliff or a steep slope. In this usage an escarpment is a ridge which has a gentle slope on one side and a steep scarp on the other side. More loosely, the term ''scarp'' also describes a zone between a coastal lowland and a continental plateau which shows a marked, abrupt change in elevation caused by coastal erosion at the base of the plateau. Formation and description Scarps are generally formed by one of two processes: either by differential erosion of sedimentary rocks, or by movement of the Earth's crust at a geologic fault. The first process is the more common type: the escarpment is a transition from one seri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Field System
The study of field systems (collections of fields) in landscape history is concerned with the size, shape and orientation of a number of fields. These are often adjacent, but may be separated by a later feature. Field systems by region Czech Republic In the Czech Republic (ancient Bohemia, Moravia and Czech Silesia), Ervín Černý undertook a study of medieval field systems. England Although agriculture was practised earlier, the earliest recognisable field systems in England are neolithic. Cairnfields, which are pre-historic in date, are found in upland areas. They contain scattered stones and boulders and originated in surface clearance for agriculture.''Field Systems'', English Heritage, May, 2011 So called Celtic fields can date from the Bronze Age through to the early Middle Ages. These fields are typically small and rectangular. They are frequently coaxial - that is they form a system in which the boundaries of adjacent fields make a series of long, roughly parallel line ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mickleham, Surrey
Mickleham is a village in South East England, south east England, between the towns of Dorking and Leatherhead in Surrey. The civil parishes in England, civil parish covers and includes the hamlet of Fredley. The larger parish, ecclesiastical parish includes the majority of the neighbouring village of Westhumble, from which Mickleham is separated by the River Mole. History Mickleham lies near to the old Roman road known as Stane Street (Chichester), Stane Street, which ran from London to Chichester. It acquired its Old English based name in Anglo-Saxon England, Anglo-Saxon times, when it was a small settlement lying within the Copthorne (hundred), Copthorne hundred (division), hundred. Mickleham appears in the Domesday Book of 1086 as ''Michelham'' and ''Micleham''. It was partly held by Nigel from the Bishop of Bayeux and partly by Oswald from (under) Richard de Tonbridge. Its Domesday assets were: 7 hide (unit), hides; 1 church, 7 ploughs, of meadow, woodland worth 4 hog (s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boundary Marker
A boundary marker, border marker, boundary stone, or border stone is a robust physical marker that identifies the start of a land Border, boundary or the change in a boundary, especially a change in direction of a boundary. There are several other types of named border markers, known as boundary trees, pillars, monuments, obelisks, and corners. Border markers can also be markers through which a border line runs in a straight line to determine that border. They can also be the markers from which a border marker has been fixed. Purpose According to Josiah Ober, boundary markers are "a way of imposing human, cultural, social meanings upon a once-undifferentiated natural environment." Boundary markers are linked to social hierarchies, since they derive their meaning from the authority of a person or group to declare the limits of a given space of land for political, social or religious reasons. Ober notes that "determining who can use parcels of arable land and for what purpose, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Round Barrow
A round barrow is a type of tumulus and is one of the most common types of archaeological monuments. Although concentrated in Europe, they are found in many parts of the world, probably because of their simple construction and universal purpose. In Britain, most of them were built between 2200BC and 1100BC. This was the Late Neolithic period to the Late Bronze Age. Later Iron Age barrows were mostly different, and sometimes square. Description At its simplest, a round barrow is a hemispherical mound of earth and/or stone raised over a burial placed in the middle. Beyond this there are numerous variations which may employ surrounding ditches, stone kerbs or flat berms between ditch and mound. Construction methods range from a single creation process of heaped material to a complex depositional sequence involving alternating layers of stone, soil and turf with timbers or wattle used to help hold the structure together. The center may be placed a stone chamber or cist or in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beech Pollard - Box Hill, Surrey
Beech (genus ''Fagus'') is a genus of deciduous trees in the family Fagaceae, native to subtropical (accessory forest element) and temperate (as dominant element of mesophytic forests) Eurasia and North America. There are 14 accepted species in two distinct subgenera, ''Englerianae'' and ''Fagus''. The subgenus ''Englerianae'' is found only in East Asia, distinctive for its low branches, often made up of several major trunks with yellowish bark. The better known species of subgenus ''Fagus'' are native to Europe, western and eastern Asia and eastern North America. They are high-branching trees with tall, stout trunks and smooth silver-grey bark. The European beech ''Fagus sylvatica'' is the most commonly cultivated species, yielding a utility timber used for furniture construction, flooring and engineering purposes, in plywood, and household items. The timber can be used to build homes. Beechwood makes excellent firewood. Slats of washed beech wood are spread around the bottom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ecclesiastical Parish
A parish is a territorial entity in many Christianity, Christian denominations, constituting a division within a diocese. A parish is under the pastoral care and clerical jurisdiction of a priest#Christianity, priest, often termed a parish priest, who might be assisted by one or more curates, and who operates from a parish church. Historically, a parish often covered the same geographical area as a Manorialism, manor. Its association with the parish church remains paramount. By extension the term ''parish'' refers not only to the territorial entity but to the people of its community or congregation as well as to church property within it. In England this church property was technically in ownership of the parish priest ''Ex officio member, ex officio'', vested in him on his institution to that parish. Etymology and use First attested in English in the late 13th century, the word ''parish'' comes from the Old French , in turn from , the Romanization of Greek, Romanisation of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dorking And Horley (UK Parliament Constituency)
Dorking and Horley is a new constituency of the House of Commons in the UK Parliament. Further to the completion of the 2023 periodic review of Westminster constituencies, it was first contested in the 2024 general election, since when it has been represented by Chris Coghlan of the Liberal Democrats. The constituency is named for the towns of Dorking and Horley in Surrey. Boundaries The constituency is defined as being composed of the following as they existed on 1 December 2020: * The District of Mole Valley wards of: Beare Green; Bookham North; Bookham South; Box Hill and Headley; Brockham, Betchworth and Buckland; Capel, Leigh and Newdigate; Charlwood; Dorking North; Dorking South; Fetcham East; Fetcham West; Holmwoods; Leith Hill; Mickleham, Westhumble and Pixham; Okewood; Westcott. * The Borough of Reigate and Banstead wards of: Horley Central & South; Horley East & Salfords; Horley West & Sidlow. *The Borough of Waverley ward of Ewhurst Following local government bou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mole Valley
Mole Valley is a local government district in Surrey, England. Its council is based in Dorking, and the district's other town is Leatherhead. The largest villages are Ashtead, Fetcham and Great Bookham, in the northern third of the district. Most of the district is on the escarpments of or adjoins the Surrey Hills, a designated Area of Outstanding Natural Beauty, which cover parts of the North Downs and Greensand Ridge, including locally Leith Hill, Polesden Lacey and Box Hill. Denbies Wine Estate, the largest vineyard in the country, is on the hills north-west of Dorking. The Pilgrims' Way footpath runs along the North Downs. There are stations on the London–Worthing and Reading–Gatwick Airport railways, and in the northern third, a commuter stopping-service pattern line, London–Guildford (via Epsom) line. The A24 road and the M25 motorway are the main thoroughfares and relative to London the incidence of car ownership is high. Between 2011 and its final iteratio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |