|
Bioethicists
Bioethics is both a field of study and professional practice, interested in ethical issues related to health (primarily focused on the human, but also increasingly includes animal ethics), including those emerging from advances in biology, medicine, and technologies. It proposes the discussion about moral discernment in society (what decisions are "good" or "bad" and why) and it is often related to medical policy and practice, but also to broader questions as environment, well-being and public health. Bioethics is concerned with the ethical questions that arise in the relationships among life sciences, biotechnology, medicine, politics, law, theology and philosophy. It includes the study of values relating to primary care, other branches of medicine (" the ethics of the ordinary"), ethical education in science, animal, and environmental ethics, and public health. Etymology The term ''bioethics'' (Greek , "life"; , "moral nature, behavior") was coined in 1927 by Fritz Jahr in a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fritz Jahr
Paul Max Fritz Jahr (January 18, 1895 in Halle (Saale) —October 1, 1953) was a German theologian, pastor and teacher in Halle. He is considered the founder of bioethics. See also * Van Rensselaer Potter Van Rensselaer Potter II (12 November, 1911 – September 6, 2001) was an American biochemist, oncologist, and bioethicist. Born in northeast South Dakota, Potter was professor of oncology at the McArdle Laboratory for Cancer Research at th ... References 1895 births 1953 deaths German theologians People from Halle (Saale) Bioethicists {{Germany-theologian-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ethics
Ethics is the philosophy, philosophical study of Morality, moral phenomena. Also called moral philosophy, it investigates Normativity, normative questions about what people ought to do or which behavior is morally right. Its main branches include normative ethics, applied ethics, and metaethics. Normative ethics aims to find general principles that govern how people should act. Applied ethics examines concrete ethical problems in real-life situations, such as abortion, treatment of animals, and Business ethics, business practices. Metaethics explores the underlying assumptions and concepts of ethics. It asks whether there are objective moral facts, how moral knowledge is possible, and how moral judgments motivate people. Influential normative theories are consequentialism, deontology, and virtue ethics. According to consequentialists, an act is right if it leads to the best consequences. Deontologists focus on acts themselves, saying that they must adhere to Duty, duties, like t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biosphere
The biosphere (), also called the ecosphere (), is the worldwide sum of all ecosystems. It can also be termed the zone of life on the Earth. The biosphere (which is technically a spherical shell) is virtually a closed system with regard to matter,"Biosphere" in ''The Columbia Encyclopedia'', 6th ed. (2004) Columbia University Press. with minimal inputs and outputs. Regarding , it is an open system, with capturing |
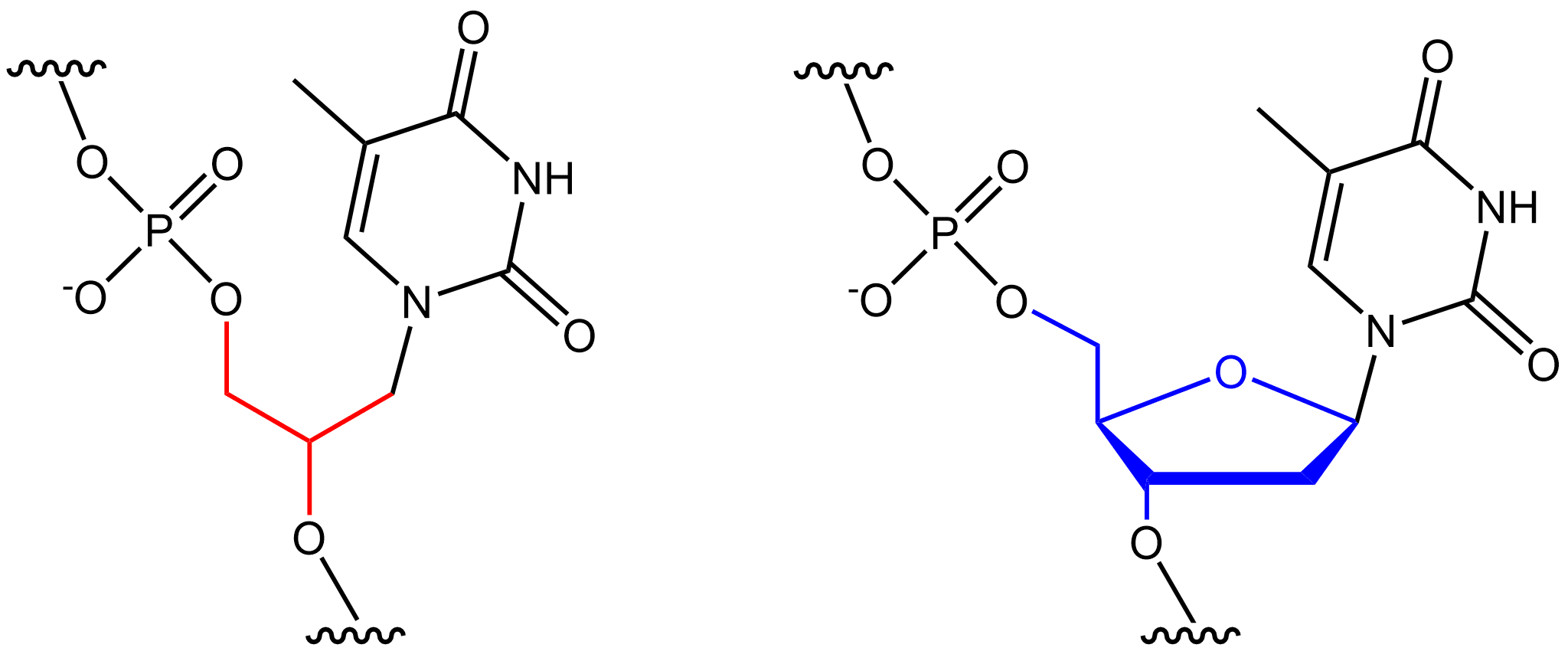
Xeno Nucleic Acid
Xenonucleic acids (XNAs) are synthetic nucleic acid analogues that are engineered with structurally distinct components, such as alternative nucleosides, sugars, or backbones. XNAs have fundamentally different properties from endogenous nucleic acids, enabling different specialized applications, such as therapeutics, probes, or functional molecules. For instance, peptide nucleic acids, the backbones of which are made up of repeating aminoethylglycine units, are extremely stable and resistant to degradation by nucleases because they are not recognised. The same nucleobases can be used to store genetic information and interact with DNA, RNA, or other XNA bases, but the different backbone gives the compound different properties. Their altered chemical structure means they cannot be processed by naturally occurring cellular processes. For instance, natural DNA polymerases cannot read and duplicate the alien information, thus the genetic information stored in XNA is invisible to DNA- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Human Genetic Engineering
Human genetic enhancement or human genetic engineering refers to human enhancement by means of a genetic modification. This could be done in order to cure diseases (gene therapy), prevent the possibility of getting a particular disease (similarly to vaccines), to improve athlete performance in sporting events (gene doping), or to change physical appearance, metabolism, and even improve physical capabilities and mental faculties such as memory and intelligence. These genetic enhancements may or may not be done in such a way that the change is heritable (which has raised concerns within the scientific community). Ethics Genetics is the study of genes and inherited traits and while the ongoing advancements in this field have resulted in the advancement of healthcare at multiple levels, ethical considerations have become increasingly crucial especially alongside. Genetic engineering has always been a topic of moral debate among bioethicists. Even though the technological advancem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Life Extension
Life extension is the concept of extending the human lifespan, either modestly through improvements in medicine or dramatically by increasing the maximum lifespan beyond its generally-settled biological limit of around 125 years. Several researchers in the area, along with "life extensionists", " immortalists", or " longevists" (those who wish to achieve longer lives themselves), postulate that future breakthroughs in tissue rejuvenation, stem cells, regenerative medicine, molecular repair, gene therapy, pharmaceuticals, and organ replacement (such as with artificial organs or xenotransplantations) will eventually enable humans to have indefinite lifespans through complete rejuvenation to a healthy youthful condition (agerasia). The ethical ramifications, if life extension becomes a possibility, are debated by bioethicists. The sale of purported anti-aging products such as supplements and hormone replacement is a lucrative global industry. For example, the industry that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gene Therapy
Gene therapy is Health technology, medical technology that aims to produce a therapeutic effect through the manipulation of gene expression or through altering the biological properties of living cells. The first attempt at modifying human DNA was performed in 1980, by Martin Cline, but the first successful nuclear gene transfer in humans, approved by the National Institutes of Health, was performed in May 1989. The first therapeutic use of gene transfer as well as the first direct insertion of human DNA into the nuclear genome was performed by French Anderson in a trial starting in September 1990. Between 1989 and December 2018, over 2,900 clinical trials were conducted, with more than half of them in Phases of clinical research, phase I. In 2003, Gendicine became the first gene therapy to receive regulatory approval. Since that time, further gene therapy drugs were approved, such as alipogene tiparvovec (2012), Strimvelis (2016), tisagenlecleucel (2017), voretigene neparvovec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cloning
Cloning is the process of producing individual organisms with identical genomes, either by natural or artificial means. In nature, some organisms produce clones through asexual reproduction; this reproduction of an organism by itself without a mate is known as parthenogenesis. In the field of biotechnology, cloning is the process of creating cloned organisms of Cell (biology), cells and of DNA fragments. The artificial cloning of organisms, sometimes known as reproductive cloning, is often accomplished via somatic-cell nuclear transfer (SCNT), a cloning method in which a viable embryo is created from a somatic cell and an egg cell. In 1996, Dolly (sheep), Dolly the sheep achieved notoriety for being the first mammal cloned from a somatic cell. Another example of artificial cloning is molecular cloning, a technique in molecular biology in which a single living cell is used to clone a large population of cells that contain identical DNA molecules. In bioethics, there are a vari ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Technology
Technology is the application of Conceptual model, conceptual knowledge to achieve practical goals, especially in a reproducible way. The word ''technology'' can also mean the products resulting from such efforts, including both tangible tools such as Kitchen utensil, utensils or machines, and intangible ones such as software. Technology plays a critical role in science, engineering, and everyday life. Technological advancements have led to significant changes in society. The earliest known technology is the stone tool, used during prehistory, followed by the control of fire—which in turn contributed to the Brain size, growth of the human brain and the development of language during the Pleistocene, Ice Age, according to the cooking hypothesis. The invention of the wheel in the Bronze Age allowed greater travel and the creation of more complex machines. More recent technological inventions, including the printing press, telephone, and the Internet, have lowered barriers to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Morality
Morality () is the categorization of intentions, Decision-making, decisions and Social actions, actions into those that are ''proper'', or ''right'', and those that are ''improper'', or ''wrong''. Morality can be a body of standards or principles derived from a code of conduct from a particular philosophy, religion or culture, or it can derive from a standard that is Universal morality, understood to be universal. Morality may also be specifically synonymous with "goodness", "appropriateness" or "rightness". Moral philosophy includes meta-ethics, which studies abstract issues such as moral ontology and moral epistemology, and normative ethics, which studies more concrete systems of moral decision-making such as deontological ethics and consequentialism. An example of normative Ethics, ethical philosophy is the Golden Rule, which states: "One should treat others as one would like others to treat oneself." Immorality is the active opposition to morality (i.e., opposition to that w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Health Care Rationing
Health care rationing refers to mechanisms that are used for resource allocation ('' viz.'' rationing) in health care. Overall health care United States Healthcare rationing in the United States of America is largely accomplished through market forces, though major government programs include Medicare, Medicaid, Veterans Affairs, and the Indian Health Service. Most Americans have private health insurance, and non-emergency health care rationing decisions are made based on what the insurance company or government insurance will pay for, what the patient is willing to pay for (though health care prices are often not transparent), and the ability and willingness of the provider to perform uncompensated care. The Emergency Medical Treatment and Active Labor Act of 1986 requires any properly equipped hospital receiving Medicare funds (nearly all private hospitals) to provide emergency healthcare regardless of citizenship, immigration status, or ability to pay. The government also r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organ Donation
Organ donation is the process when a person authorizes an organ (anatomy), organ of their own to be removed and organ transplantation, transplanted to another person, #Legislation and global perspectives, legally, either by consent while the donor is alive, through a Authorization, legal authorization for deceased donation made prior to death, or for deceased donations through the authorization by the De jure, legal next of Kinship, kin. Donation may be for research or, more commonly, healthy transplantable organs and tissues may be donated to be transplanted into another person. Common transplantations include kidney transplantation, kidneys, heart transplantation, heart, liver transplantation, liver, pancreas transplantation, pancreas, intestine transplantation, intestines, lung transplantation, lungs, bone transplantation, bones, bone marrow transplantation, bone marrow, skin transplantation, skin, and cornea transplantation, corneas. Some organs and tissues can be donated ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |