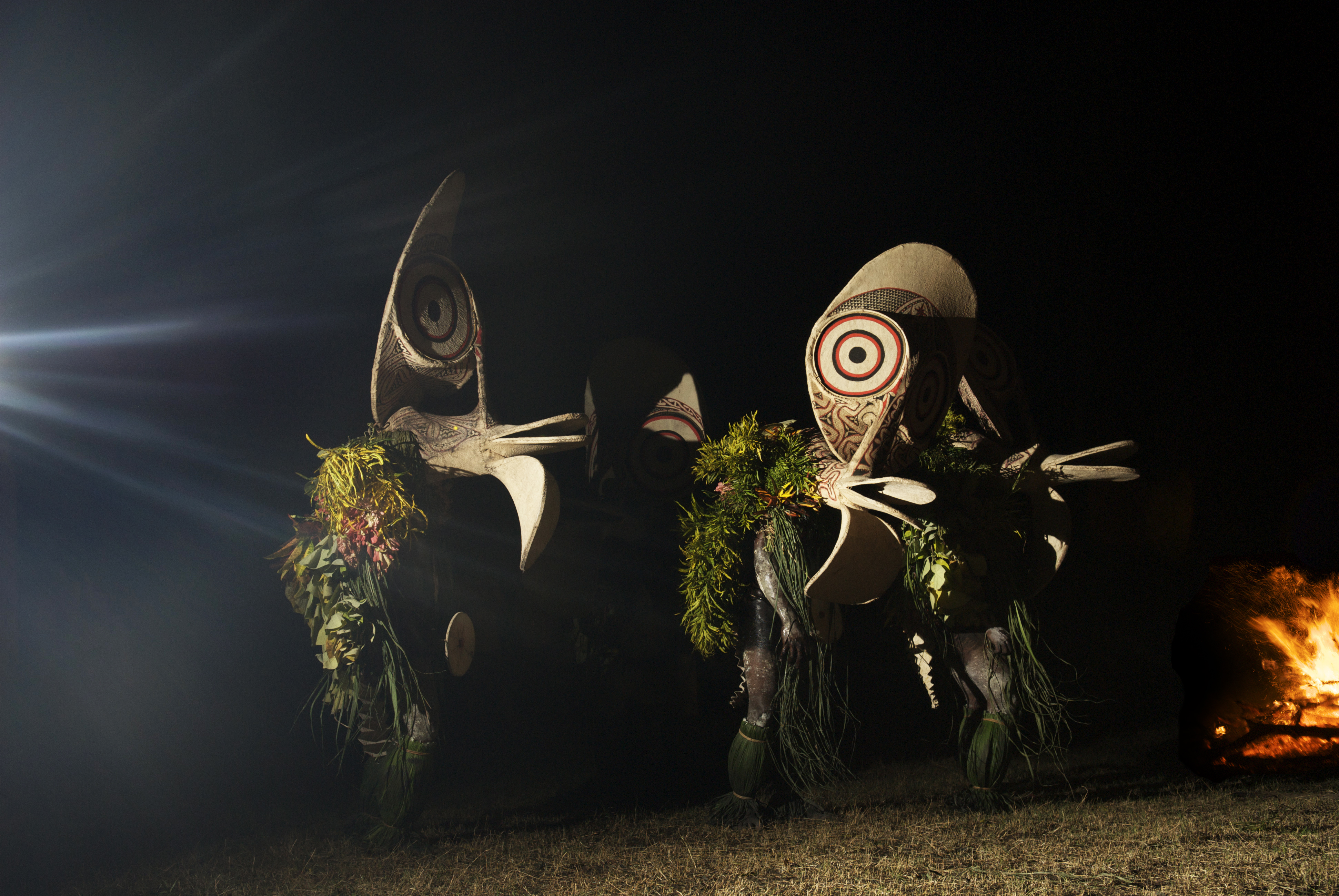|
Baining Languages
The Baining languages are a small language family spoken by the Baining people on the Gazelle Peninsula of New Britain in Papua New Guinea. They appear to be related to the neighboring Taulil–Butam languages, which diffused from New Ireland. Languages The languages are: *Mali Mali, officially the Republic of Mali, is a landlocked country in West Africa. It is the List of African countries by area, eighth-largest country in Africa, with an area of over . The country is bordered to the north by Algeria, to the east b ... (2,200 speakers) * Qaqet (6,400 speakers) * Kairak (900 speakers) * Simbali (450 speakers) * Ura (1,900 speakers) Extinct Makolkol neighbored the (other) Baining languages to their southwest but is unattested. Vocabulary comparison The following basic vocabulary words are from SIL field notes (1970, 1971, 1975), as cited in the Trans-New Guinea database. The words cited constitute translation equivalents, whether they are cognate (e.g. ''sʌdᶺm'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gazelle Peninsula
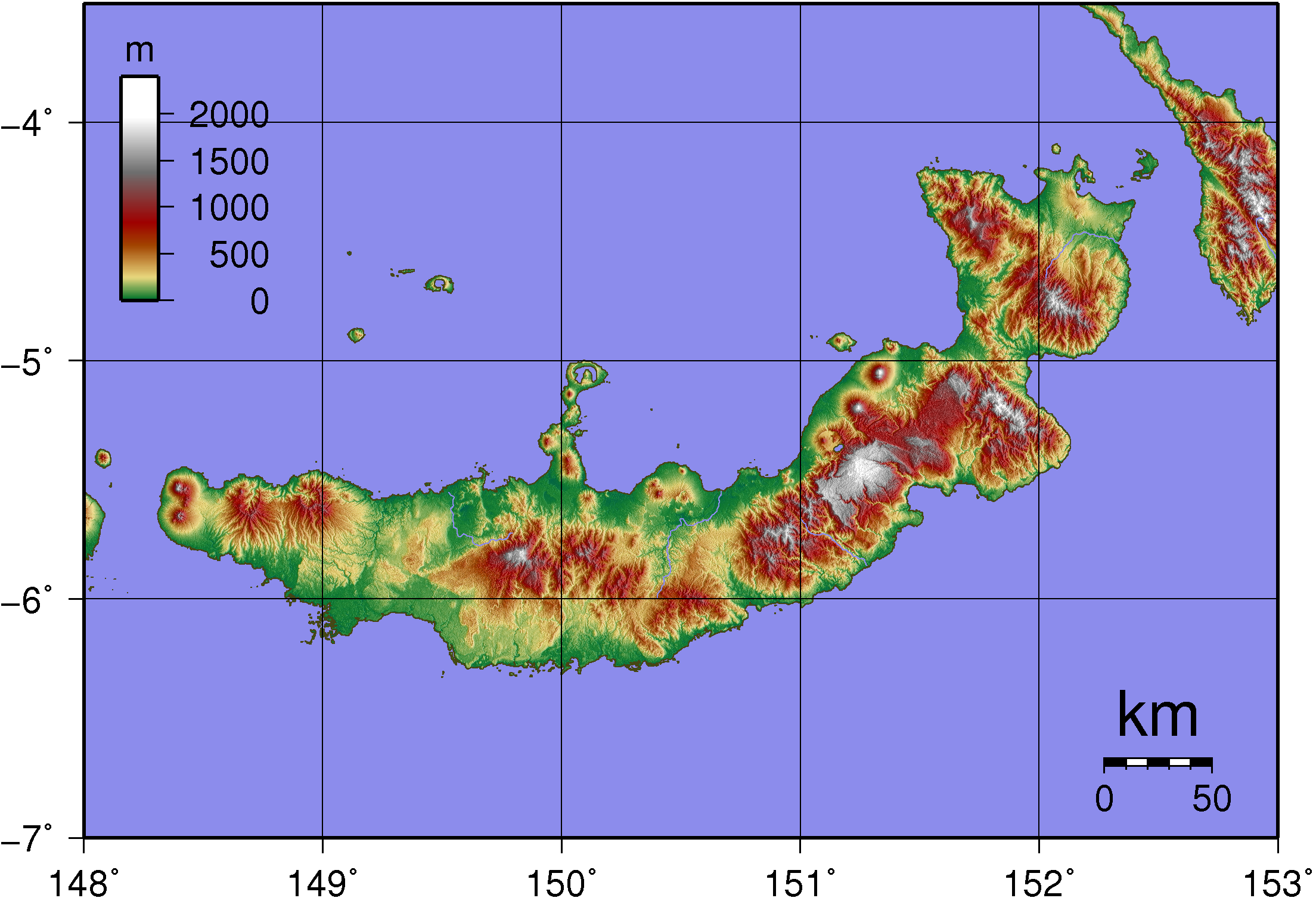
The Gazelle Peninsula is a large peninsula in northeastern East New Britain, Papua New Guinea located on the island of New Britain within the Bismarck Archipelago, situated in the southwestern Pacific Ocean. The Rabaul caldera is located on the northern tip of the peninsula. Upon the Gazelle Peninsula are the Baining Mountains, of which the highest point is Mount Sinewit at . The Gazelle Peninsula houses Vulcan Crater and Mount Tavurvur, both of which conducted volcanic activity in the 20th and 21st centuries and have provided extremely fertile soils. The body of the Gazelle Peninsula is about . The southern isthmus upon which the Gazelle Peninsula is connected to the main body of East New Britain is reduced to about . The Editors of Encyclopædia Britannica, (2015). Gazelle peninsula. Retrieved April 23, 2019 from https://www.britannica.com/place/Gazelle-Peninsula History The Tolai people of the peninsula probably colonised the peninsula from New Ireland not long befo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Britain
New Britain () is the largest island in the Bismarck Archipelago, part of the Islands Region of Papua New Guinea. It is separated from New Guinea by a northwest corner of the Solomon Sea (or with an island hop of Umboi Island, Umboi the Dampier Strait (Papua New Guinea), Dampier and Vitiaz Straits) and from New Ireland (island), New Ireland by St. George's Channel (Papua New Guinea), St. George's Channel. The main towns of New Britain are Rabaul/Kokopo and Kimbe. The island is roughly the size of Taiwan. When the island was part of German New Guinea, its name was Neupommern ("New Pomerania"). In common with most of the Bismarcks it was largely formed by volcanic processes, and has active volcanoes including Ulawun (highest volcano nationally), Langila, the Garbuna Group, the Sulu Range, and the volcanoes Tavurvur and Vulcan (volcano), Vulcan of the Rabaul caldera. A major eruption of Tavurvur in 1994 destroyed the East New Britain provincial capital of Rabaul. Most of the to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baining People
The Baining people are among the earliest continuously located inhabitants of the Gazelle Peninsula of East New Britain, Papua New Guinea; they currently live in the Baining Mountains, from which they take their name. The Baining are thought to have been driven to this area in comparatively recent times by the Tolai people, Tolai tribes who migrated to the coastal areas. The Baining migration inland may also have been influenced by major volcanic activity taking place over the centuries around the present day town of Rabaul on the north-east coast. Baining languages The Baining languages are a distinct language family spoken by the Baining. They are possibly related to the Taulil–Butam languages as well as to extinct Makolkol language, Makolkol. The languages, which correspond to clan groups, are: *Mali language, Mali (2,200 speakers) *Qaqet language, Qaqet (6,400 speakers) *Kairak language, Kairak (900 speakers) *Simbali language, Simbali (450 speakers) *Ura language (Papua Ne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
East New Britain Languages
The East New Britain languages are a possible small language family spoken on the Gazelle Peninsula of New Britain in Papua New Guinea. They were classified as East Papuan languages by Wurm, but this does not now seem tenable. The only comparative work that has been done between the two branches of the proposed family is Ross (2001), which shows similarities in the pronouns. Languages The languages are: *Baining: Mali, Qaqet, Kairak, Simbali, Ura, ? Makolkol (extinct?) * Taulil–Butam: Taulil, Butam (extinct) Makolkol is unattested. ''Glottolog'' does not accept that a connection between the two branches has been demonstrated. Stebbins et al. (2018) note that further work needs to be done, and are uncertain how to explain the similarity in pronouns between the two families with the fact that the ancestors of the Taulil and Butam people had migrated from New Ireland and so presumably would have their closest relatives there. Pronouns The pronouns Ross (2001) compares fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Language Family
A language family is a group of languages related through descent from a common ancestor, called the proto-language of that family. The term ''family'' is a metaphor borrowed from biology, with the tree model used in historical linguistics analogous to a family tree, or to phylogenetic trees of taxa used in evolutionary taxonomy. Linguists thus describe the ''daughter languages'' within a language family as being ''genetically related''. The divergence of a proto-language into daughter languages typically occurs through geographical separation, with different regional dialects of the proto-language undergoing different language changes and thus becoming distinct languages over time. One well-known example of a language family is the Romance languages, including Spanish, French, Italian, Portuguese, Romanian, Catalan, and many others, all of which are descended from Vulgar Latin.Lewis, M. Paul, Gary F. Simons, and Charles D. Fennig (eds.)''Ethnologue: Languages ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Papua New Guinea
Papua New Guinea, officially the Independent State of Papua New Guinea, is an island country in Oceania that comprises the eastern half of the island of New Guinea and offshore islands in Melanesia, a region of the southwestern Pacific Ocean north of Australia. It has Indonesia–Papua New Guinea border, a land border with Indonesia to the west and neighbours Australia to the south and the Solomon Islands to the east. Its capital, on its southern coast, is Port Moresby. The country is the world's third largest list of island countries, island country, with an area of . The nation was split in the 1880s between German New Guinea in the North and the Territory of Papua, British Territory of Papua in the South, the latter of which was ceded to Australia in 1902. All of present-day Papua New Guinea came under Australian control following World War I, with the legally distinct Territory of New Guinea being established out of the former German colony as a League of Nations mandate. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taulil–Butam Languages
The Taulil–Butam or Butam–Taulil languages are a small language family spoken in East New Britain Province, Papua New Guinea. They may be related to the Baining languages. Speakers consistently report that their ancestors came from New Ireland. Classification The languages are: * Taulil * Butam (extinct) The languages are not close but are clearly related. They are classified with the Baining languages in an East New Britain family by Ross (2001, 2005), based on similarities in their pronominal paradigms, but so far no other work has been done to support such a connection. The Austronesian impact on the languages, or at least on Taulil, is small. See also *Baining languages *Papuan languages The Papuan languages are the non- Austronesian languages spoken on the western Pacific island of New Guinea, as well as neighbouring islands in Indonesia, Solomon Islands, and East Timor. It is a strictly geographical grouping, and does not imply ... References * Ross, Malcolm (20 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Ireland (island)
New Ireland (Tok Pisin: ''Niu Ailan''), or Latangai, is a large island in Papua New Guinea, approximately in area with 120,000 people. It is named after the island of Ireland. It is the largest island of New Ireland Province, lying northeast of the island of New Britain. Both islands are part of the Bismarck Archipelago, named after Otto von Bismarck, and they are separated by Saint George's Channel (Papua New Guinea), Saint George's Channel. The administrative centre of the island and of New Ireland province is the town of Kavieng located at the northern end of the island. While the island was part of German New Guinea, it was named Neumecklenburg ("New Mecklenburg"). Geography The island is part of the Bismarck Archipelago and is often described as having the shape of a musket. New Ireland is surrounded by the Bismarck Sea in the southwest and by the Pacific Ocean in the northeast. For much of its in length, the island's width varies between less than to , yet the c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mali Language
Mali or Gaktai is a Papuan language spoken in East New Britain Province on the island of New Britain, Papua New Guinea. Dialects There are two dialects of Mali: *''Arongda'' dialect (standard dialect; with two groups), spoken in the mountains, including in Marunga village () in Sinivit Rural LLG, East New Britain Province East New Britain is a province of Papua New Guinea, consisting of the north-eastern part of the island of New Britain and the Duke of York Islands. The capital of the province is Kokopo, not far from the old capital of Rabaul, which was largely ... *''Abilta'' dialect, spoken along the coast Phonology The phonology of the Mali language: Consonants Vowels Noun classes Mali makes use of noun classes. Below are some Mali noun class paradigms, using the noun root ''amēng'' ‘tree’ as an example: : Bibliography * * References {{Languages of Papua New Guinea Languages of East New Britain Province Baining languages ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Qaqet Language
Qaqet (Kakat, Makakat, Maqaqet), or Baining, is a non- Austronesian language from the Baining family spoken in East New Britain Province on the island of New Britain, Papua New Guinea. Overview Qaqet is spoken by some 15,000 people in the Gazelle Peninsula in the East New Britain Province of Papua New Guinea. Historically, the Qaqet used to lead highly mobile lives, subsisting of horticulture and hunting. Rather recently, colonial administrators have created permanent settlements. Today, villages with major Qaqet-speaking populations are:Marley, Alexandra. 2013. ''Language Use amongst the Qaqet Baining: A sociolinguistic study of language choices in an ethnolinguistic minority in Papua New Guinea''. MA thesis, La Trobe University. *Raunsepna () in Inland Baining Rural LLG *Kamanakam () in Inland Baining Rural LLG *Walmetki () in Lassul Baining Rural LLG Raunsepna is located in the mountainous interior, while the other two villages are located near the coast. Raunsepna's rela ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kairak Language
Kairak is a Papuan language spoken in East New Britain Province on the island of New Britain, Papua New Guinea Papua New Guinea, officially the Independent State of Papua New Guinea, is an island country in Oceania that comprises the eastern half of the island of New Guinea and offshore islands in Melanesia, a region of the southwestern Pacific Ocean n .... It is spoken in Ivere () and Malabunga () villages of Inland Baining Rural LLG. References Languages of East New Britain Province Baining languages {{papuan-lang-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Simbali Language
Simbali is a poorly-documented Baining language spoken in the southern Gazelle Peninsula on New Britain, Papua New Guinea Papua New Guinea, officially the Independent State of Papua New Guinea, is an island country in Oceania that comprises the eastern half of the island of New Guinea and offshore islands in Melanesia, a region of the southwestern Pacific Ocean n .... Names Simbali is alternatively known as Asimbali or Neu-Pommern. Location In 2012, the language was described as being strongest in the villages of Alingirka, Avungi () and Kavudemki (). Status A 2012 SIL report described the language as vigorous and used across all ages, with speakers having a strong ethno-linguistic identity and a desire to maintain the language. This is seemingly no longer true; the Simbali have since lost most of their land to palm oil and logging companies, a large risk factor for language death. External links * A collection of mostly open-access Simbali material is availab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |