|
Ankle
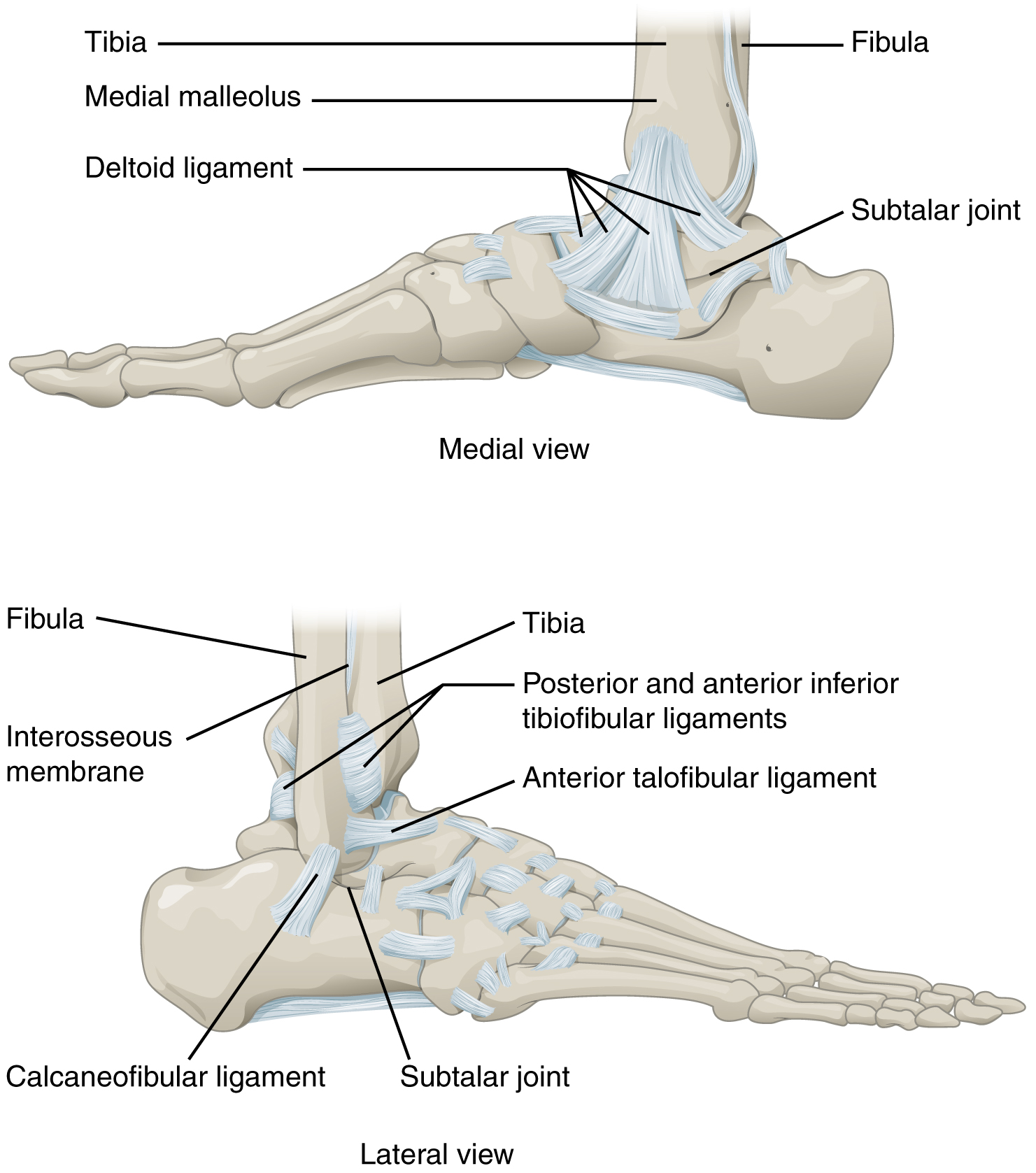
The ankle, the talocrural region or the jumping bone (informal) is the area where the foot and the leg meet. The ankle includes three joints: the ankle joint proper or talocrural joint, the subtalar joint, and the inferior tibiofibular joint. The movements produced at this joint are dorsiflexion and plantarflexion of the foot. In common usage, the term ankle refers exclusively to the ankle region. In medical terminology, "ankle" (without qualifiers) can refer broadly to the region or specifically to the talocrural joint. The main bones of the ankle region are the talus bone, talus (in the foot), the tibia, and fibula (both in the leg). The talocrural joint is a Synovial joint, synovial hinge joint that connects the distal ends of the tibia and fibula in the lower limb with the proximal end of the talus. The articulation between the tibia and the talus bears more weight than that between the smaller fibula and the talus. Structure Region The ankle region is found at the junction ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
High Ankle Sprain
A high ankle sprain, also known as a syndesmotic ankle sprain (SAS), is a sprain of the syndesmotic ligaments that connect the tibia and fibula in the lower leg, thereby creating a mortise and tenon joint for the ankle. High ankle sprains are described as high because they are located above the ankle. They comprise approximately 15% of all ankle sprains. Unlike the common lateral ankle sprains, when ligaments around the ankle are injured through an inward twisting, high ankle sprains are caused when the lower leg and foot externally rotates (twists out). Mechanism The ankle joint consists of the talus resting within the mortise created by the tibia and fibula as previously described. Since the talus is wider anteriorly (in the front) than posteriorly (at the back), as the front of the foot is raised (dorsiflexed) reducing the angle between the foot and lower leg to less than 90°, then the mortise is confronted with an increasingly wider talus. The force is heightened when the fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Human Leg
The leg is the entire lower limb (anatomy), limb of the human body, including the foot, thigh or sometimes even the hip or Gluteal muscles, buttock region. The major bones of the leg are the femur (thigh bone), tibia (shin bone), and adjacent fibula. There are 30 bones in each leg. The thigh is located in between the hip and knee. The calf (leg), calf (rear) and Tibia#Structure, shin (front), or shank, are located between the knee and ankle. Legs are used for standing, many forms of human movement, recreation such as dancing, and constitute a significant portion of a person's mass. Evolution has led to the human leg's development into a mechanism specifically adapted for efficient bipedalism, bipedal gait. While the capacity to walk upright is not unique to humans, other primates can only achieve this for short periods and at a great expenditure of energy. In humans, female legs generally have greater hip anteversion and tibiofemoral angles, while male legs have longer femur a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Talus Bone
The talus (; Latin for ankle or ankle bone; : tali), talus bone, astragalus (), or ankle bone is one of the group of Foot#Structure, foot bones known as the tarsus (skeleton), tarsus. The tarsus forms the lower part of the ankle joint. It transmits the entire weight of the body from the lower legs to the foot.Platzer (2004), p 216 The talus has joints with the two bones of the lower leg, the tibia and thinner fibula. These leg bones have two prominences (the Lateral malleolus, lateral and Medial malleolus, medial malleoli) that articulation (anatomy), articulate with the talus. At the foot end, within the tarsus, the talus articulates with the calcaneus (heel bone) below, and with the curved navicular bone in front; together, these foot articulations form the Ball-and-socket joint, ball-and-socket-shaped talocalcaneonavicular joint. The talus is the second largest of the Tarsus (skeleton), tarsal bones; it is also one of the bones in the human body with the highest percentage of i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Foot
The foot (: feet) is an anatomical structure found in many vertebrates. It is the terminal portion of a limb which bears weight and allows locomotion. In many animals with feet, the foot is an organ at the terminal part of the leg made up of one or more segments or bones, generally including claws and/or nails. Etymology The word "foot", in the sense of meaning the "terminal part of the leg of a vertebrate animal" comes from Old English ''fot'', from Proto-Germanic *''fot'' (source also of Old Frisian ''fot'', Old Saxon ''fot'', Old Norse ''fotr'', Danish ''fod'', Swedish ''fot'', Dutch ''voet'', Old High German ''fuoz'', German ''Fuß'', Gothic ''fotus'', all meaning "foot"), from PIE root *''ped-'' "foot". The plural form ''feet'' is an instance of i-mutation. Structure The human foot is a strong and complex mechanical structure containing 26 bones, 33 joints (20 of which are actively articulated), and more than a hundred muscles, tendons, and ligaments.Podiatry Chan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anterior Talofibular Ligament
The anterior talofibular ligament is a ligament in the ankle. It passes from the anterior margin of the fibular malleolus, passing anteromedially to insert at the lateral aspect of the talus at the talar neck , in front of its lateral articular facet. It is one of the lateral ligaments of the ankle and prevents the foot from sliding forward in relation to the shin. It is the most commonly injured ligament A ligament is a type of fibrous connective tissue in the body that connects bones to other bones. It also connects flight feathers to bones, in dinosaurs and birds. All 30,000 species of amniotes (land animals with internal bones) have liga ... in a sprained ankle—from an inversion injury—and will allow a positive anterior drawer test of the ankle if completely torn. See also * Sprained ankle * Posterior talofibular ligament References Further reading * External links * - "Lateral view of the ligaments of the ankle." * () Ligaments of the lower lim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tibia
The tibia (; : tibiae or tibias), also known as the shinbone or shankbone, is the larger, stronger, and anterior (frontal) of the two Leg bones, bones in the leg below the knee in vertebrates (the other being the fibula, behind and to the outside of the tibia); it connects the knee with the ankle bones, ankle. The tibia is found on the anatomical terms of location#Medial, medial side of the leg next to the fibula and closer to the median plane. The tibia is connected to the fibula by the interosseous membrane of leg, forming a type of fibrous joint called a syndesmosis with very little movement. The tibia is named for the flute ''aulos, tibia''. It is the second largest bone in the human body, after the femur. The leg bones are the strongest long bones as they support the rest of the body. Structure In human anatomy, the tibia is the second largest bone next to the femur. As in other vertebrates the tibia is one of two bones in the lower leg, the other being the fibula, and is a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lateral Malleolus
A malleolus is the bony prominence on each side of the human ankle. Each leg is supported by two bones, the tibia on the inner side (medial) of the leg and the fibula on the outer side (lateral) of the leg. The medial malleolus is the prominence on the inner side of the ankle, formed by the lower end of the tibia. The lateral malleolus is the prominence on the outer side of the ankle, formed by the lower end of the fibula. The word ''malleolus'' (), plural ''malleoli'' (), comes from Latin and means "small hammer". (It is cognate with ''mallet''.) Medial malleolus The medial malleolus is found at the foot end of the tibia. The medial surface of the lower extremity of tibia is prolonged downward to form a strong pyramidal process, flattened from without inward - the medial malleolus. * The ''medial surface'' of this process is convex and subcutaneous. * The ''lateral'' or ''articular surface'' is smooth and slightly concave, and articulates with the talus. * The ''anterior bo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medial Malleolus
A malleolus is the bony prominence on each side of the human ankle. Each leg is supported by two bones, the tibia on the inner side (medial) of the leg and the fibula on the outer side (lateral) of the leg. The medial malleolus is the prominence on the inner side of the ankle, formed by the lower end of the tibia. The lateral malleolus is the prominence on the outer side of the ankle, formed by the lower end of the fibula. The word ''malleolus'' (), plural ''malleoli'' (), comes from Latin and means "small hammer". (It is cognate with '' mallet''.) Medial malleolus The medial malleolus is found at the foot end of the tibia. The medial surface of the lower extremity of tibia is prolonged downward to form a strong pyramidal process, flattened from without inward - the medial malleolus. * The ''medial surface'' of this process is convex and subcutaneous. * The ''lateral'' or ''articular surface'' is smooth and slightly concave, and articulates with the talus. * The ''anterio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Osteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis is a type of degenerative joint disease that results from breakdown of articular cartilage, joint cartilage and underlying bone. A form of arthritis, it is believed to be the fourth leading cause of disability in the world, affecting 1 in 7 adults in the United States alone. The most common symptoms are joint pain and Joint stiffness, stiffness. Usually the symptoms progress slowly over years. Other symptoms may include joint effusion, joint swelling, decreased range of motion, and, when the back is affected, weakness or numbness of the arms and legs. The most commonly involved joints are the two near the ends of the fingers and the joint at the base of the thumbs, the knee and hip joints, and the joints of the neck and lower back. The symptoms can interfere with work and normal daily activities. Unlike some other types of arthritis, only the joints, not internal organs, are affected. Possible causes include previous joint injury, abnormal joint or limb development ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deltoid Ligament
The deltoid ligament (or medial ligament of talocrural joint) is a strong, flat, triangular band, attached, above, to the apex and anterior and posterior borders of the medial malleolus. The deltoid ligament supports the ankle joint and also resists excessive eversion of the foot. The deltoid ligament is composed of 4 fibers: # Anterior tibiotalar ligament # Tibiocalcaneal ligament # Posterior tibiotalar ligament # Tibionavicular ligament. It consists of two sets of fibers, superficial and deep. Superficial fibres Of the superficial fibres, * ''tibionavicular'' pass forward to be inserted into the tuberosity of the navicular bone, and immediately behind this they blend with the medial margin of the plantar calcaneonavicular ligament; * ''tibiocalcaneal'' descend almost perpendicularly to be inserted into the whole length of the sustentaculum tali of the calcaneus In humans and many other primates, the calcaneus (; from the Latin ''calcaneus'' or ''calcaneum'', meaning heel; ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anatomical Terms Of Motion
Motion, the process of movement, is described using specific anatomical terms. Motion includes movement of organs, joints, limbs, and specific sections of the body. The terminology used describes this motion according to its direction relative to the anatomical position of the body parts involved. Anatomists and others use a unified set of terms to describe most of the movements, although other, more specialized terms are necessary for describing unique movements such as those of the hands, feet, and eyes. In general, motion is classified according to the anatomical plane it occurs in. ''Flexion'' and ''extension'' are examples of ''angular'' motions, in which two axes of a joint are brought closer together or moved further apart. ''Rotational'' motion may occur at other joints, for example the shoulder, and are described as ''internal'' or ''external''. Other terms, such as ''elevation'' and ''depression'', describe movement above or below the horizontal plane. Many anatom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plantarflexion
Motion, the process of movement, is described using specific anatomical terms. Motion includes movement of organs, joints, limbs, and specific sections of the body. The terminology used describes this motion according to its direction relative to the anatomical position of the body parts involved. Anatomists and others use a unified set of terms to describe most of the movements, although other, more specialized terms are necessary for describing unique movements such as those of the hands, feet, and eyes. In general, motion is classified according to the anatomical plane it occurs in. ''Flexion'' and ''extension'' are examples of ''angular'' motions, in which two axes of a joint are brought closer together or moved further apart. ''Rotational'' motion may occur at other joints, for example the shoulder, and are described as ''internal'' or ''external''. Other terms, such as ''elevation'' and ''depression'', describe movement above or below the horizontal plane. Many anatomical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |