|
Anglo-Norman Folklore
Anglo-Norman may refer to: *Anglo-Normans, the medieval ruling class in England following the Norman conquest of 1066 *Anglo-Norman language **Anglo-Norman literature *Anglo-Norman England, or Norman England, the period in English history from 1066 till 1154 *Anglo-Norman horse, a breed from Normandy, France *Anglo-Norman Isles, or Channel Islands, an archipelago in the English Channel * CSS ''Anglo-Norman'', a gunboat of the Confederate Navy See also *Cambro-Normans *Normans in Ireland *Scoto-Norman The term Scoto-Norman (also Franco-Scottish or Franco-Gaelic) is used to describe people, families, institutions and archaeological artifacts that are partly Scottish (in some sense) and partly Anglo-Norman (in some sense), after the Norman Conq ... {{disamb Language and nationality disambiguation pages ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anglo-Normans
The Anglo-Normans (, ) were the medieval ruling class in the Kingdom of England following the Norman Conquest. They were primarily a combination of Normans, Bretons, Flemings, French people, Frenchmen, Anglo-Saxons and Celtic Britons. After the conquest the victorious Normans formed a ruling class in England, distinct from (although intermarrying with) the native Anglo-Saxon and Celtic populations. Over time, their language evolved from the continental Old Norman to the distinct Anglo-Norman language. Anglo-Normans quickly established control over all of England, as well as Norman invasion of Wales, parts of Wales (the Cambro-Normans, Welsh-Normans). After 1130, parts of southern and eastern Scotland came under Anglo-Norman rule (the Scoto-Norman, Scots-Normans), in return for their support of David I of Scotland#Government and feudalism, David I's conquest. The Anglo-Norman invasion of Ireland from 1169 saw Anglo-Normans and Cambro-Normans conquer swaths of Ireland, becomi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anglo-Norman Language
Anglo-Norman (; ), also known as Anglo-Norman French, was a dialect of Old Norman that was used in Kingdom of England, England and, to a lesser extent, other places in Great Britain and Ireland during the Anglo-Normans, Anglo-Norman period. Origin The term "Anglo-Norman" harks back to the time when the language was regarded as being primarily the regional dialect of the Norman settlers. Today the generic term "Anglo-French" is used instead to reflect not only the broader origin of the settlers who came with William the Conqueror, but also the continued influence of Parisian French from the House of Plantagenet, Plantagenet period onwards. According to some linguists, the name Insular French might be more suitable, because "Anglo-Norman" is constantly associated with the notion of a mixed language based on English and Norman. According to some, such a mixed language never existed. Other sources, however, indicate that such a language did exist, and that it was the language desc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anglo-Norman Literature
Anglo-Norman literature is literature composed in the Anglo-Norman language and developed during the period of 1066–1204, as the Duchy of Normandy and the Kingdom of England were united in the Anglo-Norman realm. Introduction The Norman language was introduced to England during the rule of William the Conqueror. Following the Norman Conquest, the Norman language was spoken by England's nobility. Similar to Latin, the Anglo-Norman language (the variety of Norman used in England) was deemed the literary language of England in the 12th century, and it was in use at the court until the 14th century. During the reign of Henry IV, English became the native tongue of the kings of England. The language underwent specific changes which distinguished it from the Old Norman spoken in Normandy, from which specific pronunciation rules are inferred. An Anglo-Norman variety of French continued to exist into the early 15th century, though it was in decline from at least the 1360s when it wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anglo-Norman England
The territory today known as England became inhabited more than 800,000 years ago, as the discovery of stone tools and footprints at Happisburgh in Norfolk have indicated.; "Earliest footprints outside Africa discovered in Norfolk" (2014). BBC News. Retrieved 7 February 2014. The earliest evidence for early modern humans in Northwestern Europe, a jawbone discovered in Devon at Kents Cavern in 1927, was re-dated in 2011 to between 41,000 and 44,000 years old. Continuous human habitation in England dates to around 13,000 years ago (see Creswellian), at the end of the Last Glacial Period. The region has numerous remains from the Mesolithic, Neolithic and Bronze Age, such as Stonehenge and Avebury. In the Iron Age, all of Britain south of the Firth of Forth was inhabited by the Celtic people known as the Britons, including some Belgic tribes (e.g. the Atrebates, the Catuvellauni, the Trinovantes, etc.) in the south east. In AD 43 the Roman conquest of Britain began; t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anglo-Norman Horse
The Anglo-Norman horse is a warmblood horse breed developed in Lower Normandy in northern France. A major center of horse breeding, the area had numerous regional types that were bred to one another and then crossed with Thoroughbreds to form the Anglo-Norman. Various body types developed within the Anglo-Norman breed, two of which were split off to form the Norman Cob and French Trotter. The remaining types were eventually standardized, although there remained some criticism of the "hybrid (biology), hybrid" nature of the breed's equine conformation, conformation. However, it is successful as an international sport horse, especially in the sport of show jumping. The Anglo-Norman also contributed to the development of several other breeds in Europe and Asia. The Anglo-Norman was developed in the early 19th century, and along with Thoroughbred and local Norman blood, influences were seen from other breeds, including British and Russian trotting horses. By the mid-19th century, th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anglo-Norman Isles
The Channel Islands are an archipelago in the English Channel, off the French coast of Normandy. They are divided into two Crown Dependencies: the Bailiwick of Jersey, which is the largest of the islands; and the Bailiwick of Guernsey, consisting of Guernsey, Alderney, Sark, Herm and some smaller islands. Historically, they are the remnants of the Duchy of Normandy. Although they are not part of the United Kingdom, the UK is responsible for the defence and international relations of the islands as it is for the other Crown Dependency, the Isle of Man, and the British Overseas Territories. The Crown Dependencies are neither members of the Commonwealth of Nations, nor part of the European Union. They have a total population of about , and the bailiwicks' capitals, Saint Helier and Saint Peter Port, have populations of 33,500 and 18,207 respectively. "Channel Islands" is a geographical term, not a political unit. The two bailiwicks have been administered separately since the late ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CSS Anglo-Norman
CSS ''Anglo-Norman'' was a side-wheel steam gunboat of the Confederate States of America. Built at Algiers, Louisiana in 1850 and thereafter employed as a towboat by the Southern Steamship Company in New Orleans New Orleans (commonly known as NOLA or The Big Easy among other nicknames) is a Consolidated city-county, consolidated city-parish located along the Mississippi River in the U.S. state of Louisiana. With a population of 383,997 at the 2020 ..., ''Anglo-Norman'' was seized by Confederate forces on January 16, 1862. The steamer was one of fourteen ships acquired by Brigadier General Mansfield Lovell with the backing of the Confederate Secretary of War, for possible conversion to gunboats and rams in the Mississippi River Defense Fleet. At the time of the action at Ports Jackson and St. Philip, April 1862, ''Anglo-Norman'' was not mentioned as one of the River Defense Fleet. The steamer is recorded as burning on April 27, but nevertheless appears as one of the 22 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cambro-Normans
Cambro-Normans (; "Wales", ; ) were Normans who settled in southern Wales and the Welsh Marches after the Norman invasion of Wales. Cambro-Norman knights were also the leading force in the Cambro-Norman invasion of Ireland, led by Richard de Clare, 2nd Earl of Pembroke in 1170. In Wales Following the Norman conquest of England, Norman forces would invade South Wales, where William FitzOsbern, 1st Earl of Hereford overran the Kingdom of Gwent and the Earl of Shrewsbury invaded the Kingdom of Deheubarth. Despite a number of Welsh revolts against Norman rule, these areas (along with the Gower), would become the main focus of Norman settlement in Wales. Although Welsh forces would retake much of the Norman territories following their crushing victory at the Battle of Crug Mawr in 1136, the Norman King of England would control much of the Welsh borders and southern agricultural land by the 12th century. This led to Wales being split in two, with one area becoming the Marcher ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
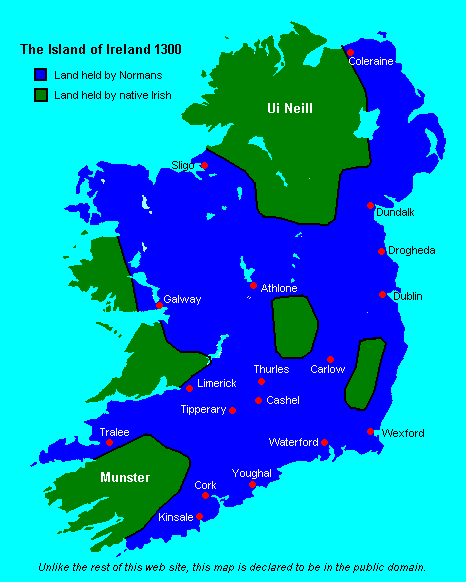
Normans In Ireland
Norman Irish or Hiberno-Normans (; ) is a modern term for the descendants of Norman settlers who arrived during the Anglo-Norman invasion of Ireland in the 12th century. Most came from England and Wales. They are distinguished from the native Gaelic Irish; although some Normans eventually became Gaelicised. The Hiberno-Normans were a feudal aristocracy and merchant oligarchy who controlled the Lordship of Ireland. The Hiberno-Normans were associated with the Gregorian Reform of the Catholic Church in Ireland and contributed to the emergence of a Hiberno-English dialect. Some of the most prominent Hiberno-Norman families were the Burkes (de Burghs), Butlers, and FitzGeralds. One of the most common Irish surnames, Walsh, derives from Welsh Normans who arrived in Ireland as part of this group. Some Norman families were said to have become " more Irish than the Irish themselves" by merging culturally and intermarrying with the Gaels. The dominance of the Catholic Hiberno-N ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scoto-Norman
The term Scoto-Norman (also Franco-Scottish or Franco-Gaelic) is used to describe people, families, institutions and archaeological artifacts that are partly Scottish (in some sense) and partly Anglo-Norman (in some sense), after the Norman Conquest. It is used to refer to people or things of Norman, Anglo-Norman, French or even Flemish or Breton origin, but who are associated with Scotland in the Middle Ages like Scoto-Anglo-Saxon. It is also used for any of these things where they exhibit syncretism between French or Anglo-French culture on the one hand and Gaelic culture on the other. For instance, the Kings of Scotland between the reign of the David I and the Stewart period are often described as Scoto-Norman. A classic case of Gaelic and French cultural syncretism would be Lochlann, Lord of Galloway, who used both a Gaelic (''Lochlann'') and French name (''Roland''), and kept followers of both languages. Another example of a Scoto-Norman would be Robert the Bruce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |