|
Allen Formation
The Allen Formation is a geological formation in Argentina whose strata date back to the Late Cretaceous (middle Campanian to early Maastrichtian.Salgado et al., 2007 Dinosaur remains are among the fossils that have been recovered from the formation.Weishampel, David B; et al. (2004). "Dinosaur distribution (Late Cretaceous, South America)." In: Weishampel, David B.; Dodson, Peter; and Osmólska, Halszka (eds.): The Dinosauria, 2nd, Berkeley: University of California Press. Pp. 600-604. . Indeterminate chelid remains and other vertebrates have also been discovered in this formation. Description Uliana and Dellapé defined the formation's stratotype in 1981 in the eastern area of the Bajo de Añelo, where the relation between the base and top is clearly exposed. The deposits are mostly clastic, interbedded with banks of limestone and layers of anhydrite, which were defined as continental and shallow marine facies associated with semiarid conditions.Armas & Sánchez, 2015, p.1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
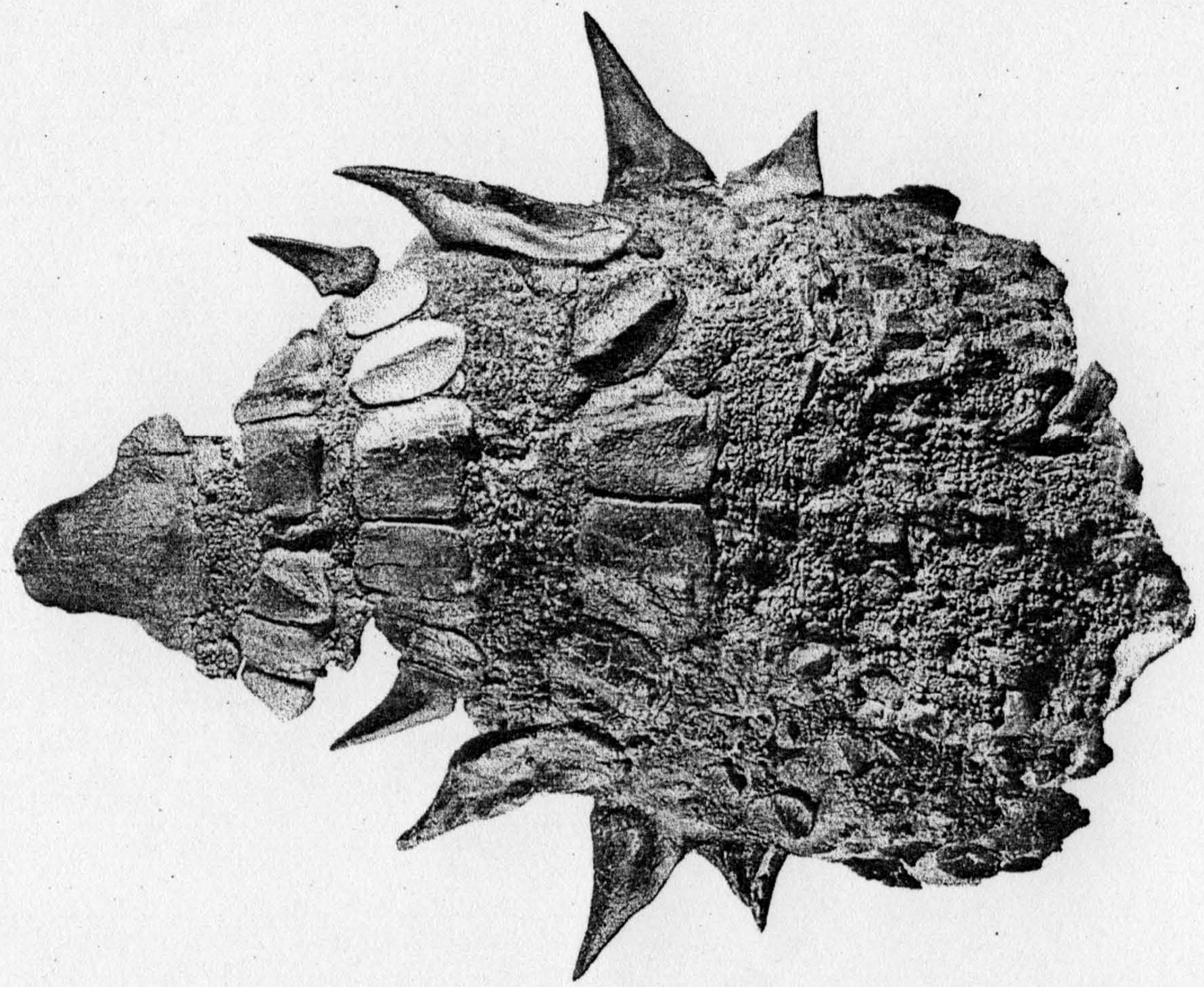
Patagopelta
''Patagopelta'' (meaning "Patagonian shield") is an extinct genus of ankylosaurian dinosaur from the Late Cretaceous (upper Campanian–lower Maastrichtian) Allen Formation of Argentina. The genus contains a Monotypic taxon, single species, ''P. cristata'', known from a partial skeleton. While originally described as a nodosaurine, later discoveries provided support for parankylosaurian affinities for the taxon. ''Patagopelta'' is a very small ankylosaur, comparable in size to the dwarf nodosaurid ''Struthiosaurus'', about long. Discovery and naming The ''Patagopelta'' fossil material was found in sediments of the Allen Formation (Salitral Moreno locality) near General Roca, Río Negro Province, Argentina. This locality is dated to the upper Campanian to lower Maastrichtian ages of the Late Cretaceous period. The first remains were described in 1996 and often appeared in the literature as the "Argentinian ankylosaur". The fossil material consists of various osteoderms, a tooth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Auca Mahuida
Auca Mahuida is a shield volcano in the Payenia Volcanic Province of Neuquén Province, Argentina. K–Ar dating of samples at the volcano indicated it formed between 1.8 and 1.0 million years ago, and is the only shield volcano in the province. The Volcanic crater, summit crater and andesitic volcanic plug are well-preserved. References {{reflist Volcanoes of Neuquén Province Geology of Neuquén Province Pleistocene shield volcanoes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chelid
Chelidae is one of three living families of the turtle suborder Pleurodira, and are commonly called Austro-South American side-neck turtles. The family is distributed in Australia, New Guinea, parts of Indonesia, and throughout most of South America. It is a large family of turtles with a significant fossil history dating back to the Cretaceous. The family is entirely Gondwanan in origin, with no members found outside Gondwana, either in the present day or as a fossil.Georges, A. & Thomson, S. (2006). "Evolution and Zoogeography of Australian freshwater turtles". In: Merrick, J. R.; Archer, M.; Hickey, G. & Lee, M. (eds.) ''Evolution and Zoogeography of Australasian Vertebrates''. Sydney: Australia. Description Like all pleurodirous turtles, the chelids withdraw their necks sideways into their shells, differing from cryptodires that fold their necks in the vertical plane. They are all highly aquatic species with webbed feet and the capacity to stay submerged for long periods of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ankylosauria
Ankylosauria is a group of herbivorous dinosaurs of the clade Ornithischia. It includes the great majority of dinosaurs with armor in the form of bony osteoderms, similar to turtles. Ankylosaurs were bulky quadrupeds, with short, powerful limbs. They are known to have first appeared in North Africa during the Middle Jurassic, and persisted until the end of the Late Cretaceous. The two main families of ankylosaurians, Nodosauridae and Ankylosauridae primarily originated from the Northern Hemisphere (North America, Europe and Asia), but the more basal Parankylosauria originated from southern Gondwana (South America, Australia and Antarctica) during the Cretaceous. Ankylosauria was first named by Henry Fairfield Osborn in 1923.Osborn, H. F. (1923). "Two Lower Cretaceous dinosaurs of Mongolia." ''American Museum Novitates'', 95: 1–1/ref> In the Linnaean classification system, the group is usually considered either a suborder or an infraorder. It is contained within the group ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quilmesaurus Hunting Bonapartesaurus Version 2
''Quilmesaurus'' is a genus of carnivorous Abelisauridae, abelisaurid theropod dinosaur from the Patagonian Upper Cretaceous (Campanian faunal stage, stage) of Argentina. It was a member of Abelisauridae, closely related to genera such as ''Carnotaurus''. The only known remains of this genus are leg bones which share certain similarities to a variety of abelisaurids. However, these bones lack unique features, which may render ''Quilmesaurus'' a ''nomen vanum'' (more commonly known as a ''nomen dubium'', or "dubious name"). Discovery and naming During the late 1980s, a field crew from the Universidad Nacional Tucumán, led by Jaime Powell, uncovered forty kilometres south of General Roca, Río Negro, Roca City, in Río Negro province, southern Argentina, the remains of a theropod near the Salitral Ojo de Agua. In 2001, Rodolfo Aníbal Coria named and described the type species ''Quilmesaurus curriei''. The genus name is derived from the Quilmes (tribe), Quilmes, a Indigenous peopl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Evaporite
An evaporite () is a water- soluble sedimentary mineral deposit that results from concentration and crystallization by evaporation from an aqueous solution. There are two types of evaporite deposits: marine, which can also be described as ocean deposits, and non-marine, which are found in standing bodies of water such as lakes. Evaporites are considered sedimentary rocks and are formed by chemical sediments. Formation Although all water bodies on the surface and in aquifers contain dissolved salts, the water must evaporate into the atmosphere for the minerals to precipitate. For this to happen, the water body must enter a restricted environment where water input into this environment remains below the net rate of evaporation. This is usually an arid environment with a small drainage basin fed by a limited input of water. When evaporation occurs, the remaining water is enriched in salts, and they precipitate after the water becomes saturated. Depositional environments ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tidal Flat
Mudflats or mud flats, also known as tidal flats or, in Ireland, slob or slobs, are coastal wetlands that form in intertidal areas where sediments have been deposited by tides or rivers. A global analysis published in 2019 suggested that tidal flat ecosystems are as extensive globally as mangroves, covering at least of the Earth's surface. / They are found in sheltered areas such as bays, bayous, lagoons, and estuaries; they are also seen in freshwater lakes and salty lakes (or inland seas) alike, wherein many rivers and creeks end. Mudflats may be viewed geologically as exposed layers of bay mud, resulting from deposition of estuarine silts, clays and aquatic animal detritus. Most of the sediment within a mudflat is within the intertidal zone, and thus the flat is submerged and exposed approximately twice daily. A recent global remote sensing analysis estimated that approximately 50% of the global extent of tidal flats occurs within eight countries (Indonesia, China, Aus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Estuary
An estuary is a partially enclosed coastal body of brackish water with one or more rivers or streams flowing into it, and with a free connection to the open sea. Estuaries form a transition zone between river environments and maritime environments and are an example of an ecotone. Estuaries are subject both to marine influences such as tides, waves, and the influx of saline water, and to fluvial influences such as flows of freshwater and sediment. The mixing of seawater and freshwater provides high levels of nutrients both in the water column and in sediment, making estuaries among the most productive natural habitats in the world. Most existing estuaries formed during the Holocene epoch with the flooding of river-eroded or glacially scoured valleys when the sea level began to rise about 10,000–12,000 years ago. Estuaries are typically classified according to their geomorphological features or to water-circulation patterns. They can have many different names, such as ba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fluvial
A river is a natural stream of fresh water that flows on land or inside caves towards another body of water at a lower elevation, such as an ocean, lake, or another river. A river may run dry before reaching the end of its course if it runs out of water, or only flow during certain seasons. Rivers are regulated by the water cycle, the processes by which water moves around the Earth. Water first enters rivers through precipitation, whether from rainfall, the runoff of water down a slope, the melting of glaciers or snow, or seepage from aquifers beneath the surface of the Earth. Rivers flow in channeled watercourses and merge in confluences to form drainage basins, or catchments, areas where surface water eventually flows to a common outlet. Rivers have a great effect on the landscape around them. They may regularly overflow their banks and flood the surrounding area, spreading nutrients to the surrounding area. Sediment or alluvium carried by rivers shapes the landscape a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aeolian Processes
Aeolian processes, also spelled eolian, pertain to wind activity in the study of geology and weather and specifically to the wind's ability to shape the surface of the Earth (or other planets). Winds may erosion, erode, transport, and deposit materials. They are effective agents in regions with sparse vegetation, a lack of soil moisture and a large supply of unconsolidated sediments. Although water is a much more powerful eroding force than wind, aeolian processes are important in arid environments such as deserts. The term is derived from the name of the Greek god Aeolus#Aeolus (son of Hippotes), Aeolus, the keeper of the winds. Definition and setting ''Aeolian processes'' are those processes of erosion, Sediment transport, transport, and Deposition (geology), deposition of sediments that are caused by wind at or near the surface of the earth. Sediment deposits produced by the action of wind and the sedimentary structures characteristic of these deposits are also described as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lacustrine
A lake is often a naturally occurring, relatively large and fixed body of water on or near the Earth's surface. It is localized in a basin or interconnected basins surrounded by dry land. Lakes lie completely on land and are separate from the ocean, although they may be connected with the ocean by rivers. Lakes, as with other bodies of water, are part of the water cycle, the processes by which water moves around the Earth. Most lakes are fresh water and account for almost all the world's surface freshwater, but some are salt lakes with salinities even higher than that of seawater. Lakes vary significantly in surface area and volume of water. Lakes are typically larger and deeper than ponds, which are also water-filled basins on land, although there are no official definitions or scientific criteria distinguishing the two. Lakes are also distinct from lagoons, which are generally shallow tidal pools dammed by sandbars or other material at coastal regions of oceans or large ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |