|
Alkylating Antineoplastic Agents
An alkylating antineoplastic agent is an alkylating agent used in cancer treatment that attaches an alkyl group (CnH2n+1) to DNA. Since cancer cells, in general, proliferate faster and with less error-correcting than healthy cells, cancer cells are more sensitive to DNA damage—such as being alkylated. Alkylating agents are used to treat several cancers. However, they are also toxic to normal cells (cytotoxic), particularly Labile cell, cells that divide frequently, such as those in the gastrointestinal tract, bone marrow, testicles and ovaries, which can cause loss of fertility. Most of the alkylating agents are also carcinogenic. History Before their use in chemotherapy, alkylating agents were better known for their use as sulfur mustard, ("mustard gas") and related chemical weapons in World War I. The nitrogen mustards were the first alkylating agents used medically, as well as the first modern cancer chemotherapies. Goodman, Gilman, and others began studying nitrogen mustar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Triaziquone
Triaziquone is a drug used in chemotherapy. It is aziridinylbenzoquinone-based, and may have potential antineoplastic activity. It is an alkylating agent. It can react with DNA to form intrastrand crosslinks. It is a member of aziridines as well. References 1-Aziridinyl compounds Alkylating antineoplastic agents 1,4-Benzoquinones {{antineoplastic-drug-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
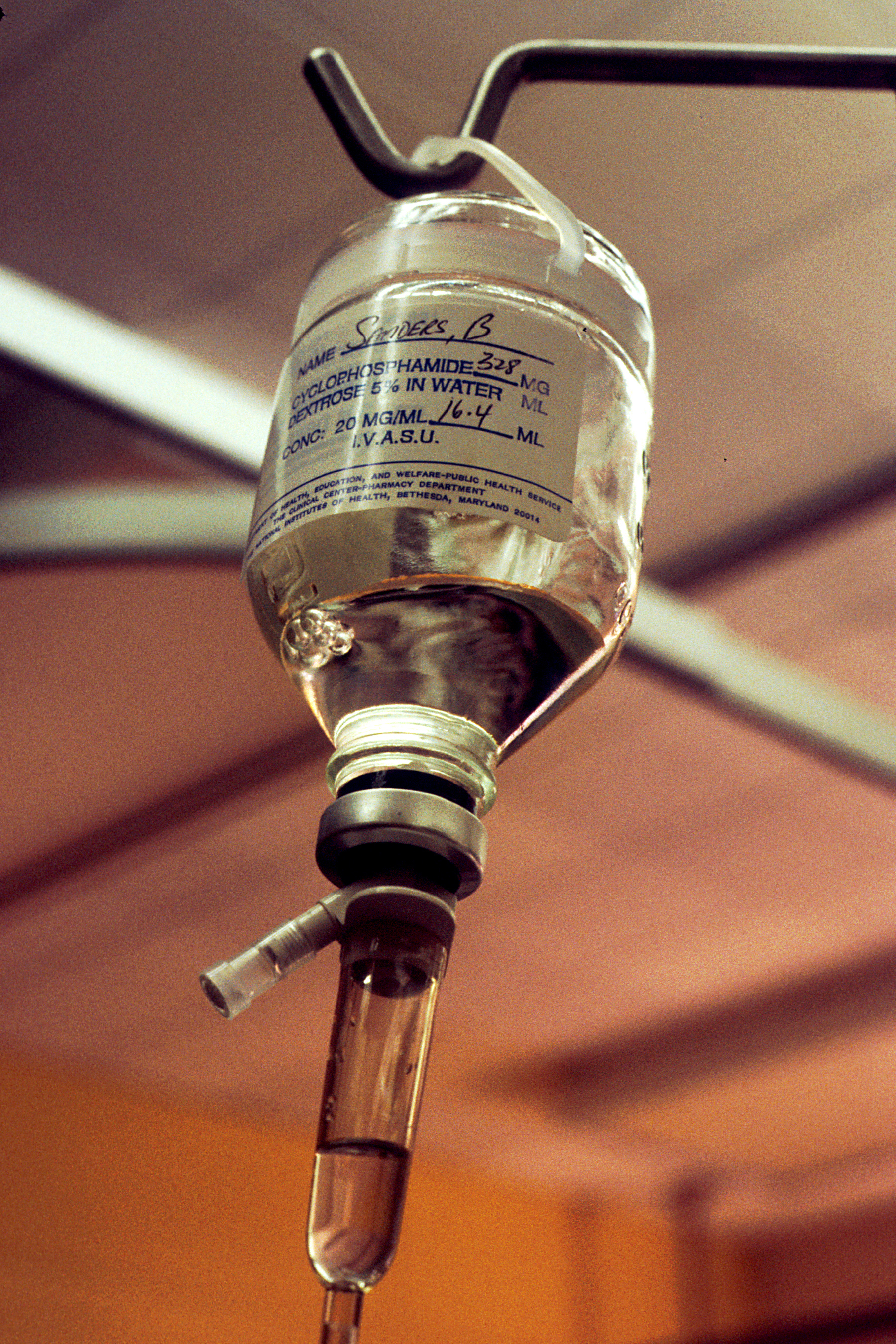
Cyclophosphamide
Cyclophosphamide (CP), also known as cytophosphane among other names, is a medication used as chemotherapy and to suppress the immune system. As chemotherapy it is used to treat lymphoma, multiple myeloma, leukemia, ovarian cancer, breast cancer, small cell lung cancer, neuroblastoma, and sarcoma. As an immune suppressor it is used in nephrotic syndrome, ANCA-associated vasculitis, and following organ transplant, among other conditions. It is taken by mouth or injection into a vein. Most people develop side effects. Common side effects include low white blood cell counts, loss of appetite, vomiting, hair loss, and bleeding from the bladder. Other severe side effects include an increased future risk of cancer, infertility, allergic reactions, and pulmonary fibrosis. Cyclophosphamide is in the alkylating agent and nitrogen mustard family of medications. It is believed to work by interfering with the duplication of DNA and the creation of RNA. Cyclophosphamide was approved ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enzyme
An enzyme () is a protein that acts as a biological catalyst by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrate (chemistry), substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different molecules known as product (chemistry), products. Almost all metabolism, metabolic processes in the cell (biology), cell need enzyme catalysis in order to occur at rates fast enough to sustain life. Metabolic pathways depend upon enzymes to catalyze individual steps. The study of enzymes is called ''enzymology'' and the field of pseudoenzyme, pseudoenzyme analysis recognizes that during evolution, some enzymes have lost the ability to carry out biological catalysis, which is often reflected in their amino acid sequences and unusual 'pseudocatalytic' properties. Enzymes are known to catalyze more than 5,000 biochemical reaction types. Other biocatalysts include Ribozyme, catalytic RNA molecules, also called ribozymes. They are sometimes descr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
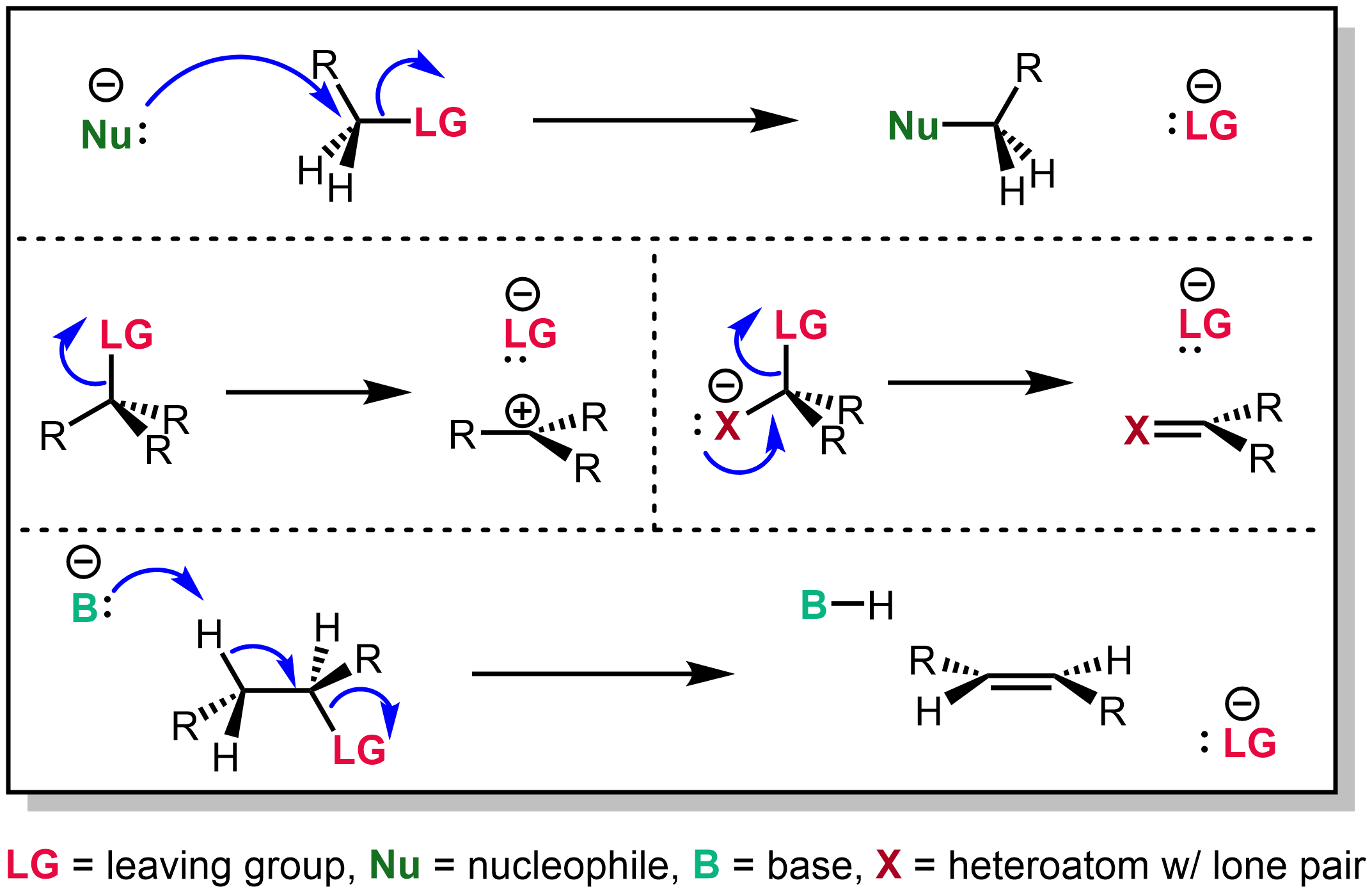
Leaving Group
In organic chemistry, a leaving group typically means a Chemical species, molecular fragment that departs with an electron, electron pair during a reaction step with heterolysis (chemistry), heterolytic bond cleavage. In this usage, a ''leaving group'' is a less formal but more commonly used synonym of the term ''nucleofuge''; although IUPAC gives the term a broader definition. A species' ability to serve as a leaving group can affect whether a reaction is viable, as well as what mechanism the reaction takes. Leaving group ability depends strongly on context, but often correlates with ability to stabilize additional electron density from bond heterolysis. Common anionic leaving groups are , and halides and sulfonate esters such as tosylate (). Water (), alcohols (), and amines () are common neutral leaving groups, although they often require activating catalysts. Some moieties, such as hydride (H−) serve as leaving groups only extremely rarely. Nomenclature IUPAC ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diester
In chemistry, an ester is a compound derived from an acid (either organic or inorganic) in which the hydrogen atom (H) of at least one acidic hydroxyl group () of that acid is replaced by an organyl group (R). These compounds contain a distinctive functional group. Analogues derived from oxygen replaced by other chalcogens belong to the ester category as well. According to some authors, organyl derivatives of acidic hydrogen of other acids are esters as well (e.g. amides), but not according to the IUPAC. Glycerides are fatty acid esters of glycerol; they are important in biology, being one of the main classes of lipids and comprising the bulk of animal fats and vegetable oils. Lactones are cyclic carboxylic esters; naturally occurring lactones are mainly 5- and 6-membered ring lactones. Lactones contribute to the aroma of fruits, butter, cheese, vegetables like celery and other foods. Esters can be formed from oxoacids (e.g. esters of acetic acid, carbonic acid, sulfuri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Methanesulfonate
In organosulfur chemistry, a mesylate is any salt or ester of methanesulfonic acid (). In salts, the mesylate is present as the anion. When modifying the international nonproprietary name of a pharmaceutical substance containing the group or anion, the spelling used is sometimes mesilate (as in ''imatinib mesilate'', the mesylate salt of imatinib). Mesylate esters are a group of organic compounds that share a common functional group with the general structure , abbreviated , where R is an organic substituent. Mesylate is considered a leaving group in nucleophilic substitution reactions. Preparation Mesylate esters are generally prepared by treating an alcohol and methanesulfonyl chloride in the presence of a base, such as triethylamine. Mesyl Related to mesylate is the mesyl (Ms) or methanesulfonyl () functional group. The shortened term itself was coined by Helferich et al. in 1938 similarly to tosyl adopted earlier. Methanesulfonyl chloride is often referred to as mesy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Busulfan
Busulfan (Myleran, GlaxoSmithKline, Busulfex IV, Otsuka America Pharmaceutical, Inc.) is a chemotherapy drug in use since 1959. It is a cell cycle non-specific alkylating antineoplastic agent, in the class of alkyl sulfonates. Its chemical designation is 1,4-butanediol dimethanesulfonate. History Busulfan was approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for treatment of chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) in 1999. Busulfan was the mainstay of the chemotherapeutic treatment of chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) until it was displaced by the new gold standard, imatinib, though it is still in use to a degree as a result of the drug's relative low cost. Indications Busulfan is used in pediatrics and adults in combination with cyclophosphamide or fludarabine/clofarabine as a conditioning agent prior to bone marrow transplantation, especially in chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML) and other leukemias, lymphomas, and myeloproliferative disorders. Busulfan can control t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cross-link
In chemistry and biology, a cross-link is a bond or a short sequence of bonds that links one polymer chain to another. These links may take the form of covalent bonds or ionic bonds and the polymers can be either synthetic polymers or natural polymers (such as proteins). In polymer chemistry "cross-linking" usually refers to the use of cross-links to promote a change in the polymers' physical properties. When "crosslinking" is used in the biological field, it refers to the use of a probe to link proteins together to check for protein–protein interactions, as well as other creative cross-linking methodologies. Although the term is used to refer to the "linking of polymer chains" for both sciences, the extent of crosslinking and specificities of the crosslinking agents vary greatly. Synthetic polymers : 260px, left, Chemical reactions associated with crosslinking of drying oils, the process that produces curing'' refers to the crosslinking of thermosetting">linoleum. Cros ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cystitis
A urinary tract infection (UTI) is an infection that affects a part of the urinary tract. Lower urinary tract infections may involve the bladder (cystitis) or urethra ( urethritis) while upper urinary tract infections affect the kidney (pyelonephritis). Symptoms from a lower urinary tract infection include suprapubic pain, painful urination (dysuria), frequency and urgency of urination despite having an empty bladder. Symptoms of a kidney infection, on the other hand, are more systemic and include fever or flank pain usually in addition to the symptoms of a lower UTI. Rarely, the urine may appear bloody. Symptoms may be vague or non-specific at the extremities of age (i.e. in patients who are very young or old). The most common cause of infection is ''Escherichia coli'', though other bacteria or fungi may sometimes be the cause. Risk factors include female anatomy, sexual intercourse, diabetes, obesity, catheterisation, and family history. Although sexual intercourse is a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pancytopenia
Pancytopenia is a medical condition in which there is significant reduction in the number of almost all blood cells (red blood cells, white blood cells, platelets, monocytes, lymphocytes, etc.). If only two parameters from the complete blood count are low, the term bicytopenia can be used. The diagnostic approach is the same as for pancytopenia. Causes Iatrogenic causes of pancytopenia include chemotherapy for malignancies if the drug or drugs used cause bone marrow suppression. Rarely, drugs (antibiotics, blood pressure medication, heart medication) can cause pancytopenia. For example, the antibiotic chloramphenicol can cause pancytopenia in some individuals. Rarely, pancytopenia may have other causes, such as mononucleosis or other viral diseases. Increasingly, HIV is itself a cause of pancytopenia. * Familial hemophagocytic syndrome * Aplastic anemia * Gaucher's disease * Metastatic carcinoma of bone * Multiple Myeloma * Overwhelming infections * Lymphoma * Myelofibro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Autoimmune Disease
An autoimmune disease is a condition that results from an anomalous response of the adaptive immune system, wherein it mistakenly targets and attacks healthy, functioning parts of the body as if they were foreign organisms. It is estimated that there are more than 80 recognized autoimmune diseases, with recent scientific evidence suggesting the existence of potentially more than 100 distinct conditions. Nearly any body part can be involved. Autoimmune diseases are a separate class from autoinflammatory diseases. Both are characterized by an immune system malfunction which may cause similar symptoms, such as rash, swelling, or fatigue, but the cardinal cause or mechanism of the diseases is different. A key difference is a malfunction of the innate immune system in autoinflammatory diseases, whereas in autoimmune diseases there is a malfunction of the adaptive immune system. Symptoms of autoimmune diseases can significantly vary, primarily based on the specific type of the d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |