|
Alcoa
Alcoa Corporation (an acronym for "Aluminum Company of America") is an American industrial corporation. It is the world's eighth-largest producer of aluminum. Alcoa conducts operations in 10 countries. Alcoa is a major producer of primary aluminum, fabricated aluminum, and alumina combined, through its active and growing participation in all major aspects of the industry: technology, mining, refining, smelting, fabricating, and recycling. Alcoa emerged in 1888 as the brainchild of Charles Martin Hall, with the funding of Alfred E. Hunt and Arthur Vining Davis. Alcoa was the first mass producer of aluminum. Before Alcoa's formation, aluminum was difficult to refine and, as a result, was more expensive than silver or gold. In 1886, Hall discovered the Hall–Héroult process, the first inexpensive technique for refining aluminum, drastically reducing the price of aluminum while increasing its availability. Hall approached Hunt and Davis to form a company to bring his process to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Public Company
A public company is a company whose ownership is organized via shares of share capital, stock which are intended to be freely traded on a stock exchange or in over-the-counter (finance), over-the-counter markets. A public (publicly traded) company can be listed on a stock exchange (listing (finance), listed company), which facilitates the trade of shares, or not (unlisted public company). In some jurisdictions, public companies over a certain size must be listed on an exchange. In most cases, public companies are ''private'' enterprises in the ''private'' sector, and "public" emphasizes their reporting and trading on the public markets. Public companies are formed within the legal systems of particular states and so have associations and formal designations, which are distinct and separate in the polity in which they reside. In the United States, for example, a public company is usually a type of corporation, though a corporation need not be a public company. In the United Kin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
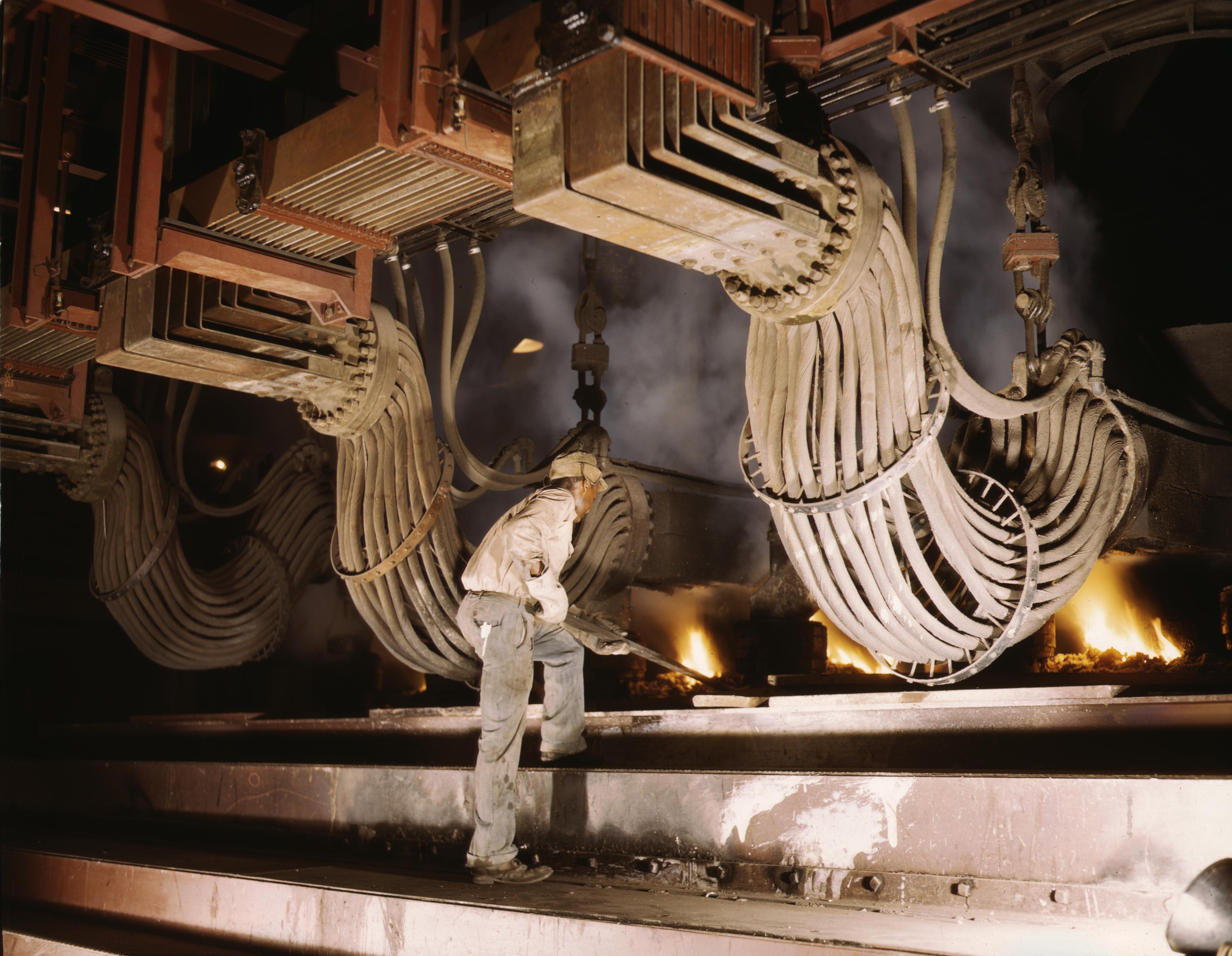
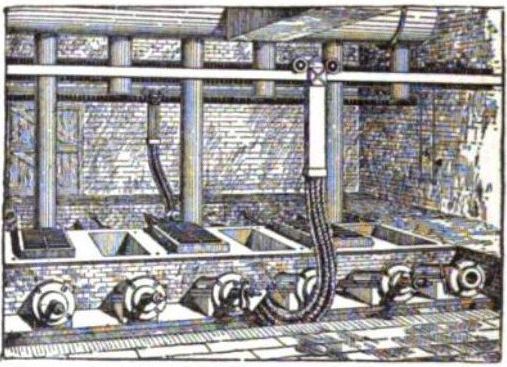
Hall–Héroult Process
The Hall–Héroult process is the major industrial process for smelting aluminium. It involves dissolving aluminium oxide (alumina) (obtained most often from bauxite, aluminium's chief ore, through the Bayer process) in molten cryolite and electrolyzing the molten salt bath, typically in a purpose-built cell. The process conducted at an industrial scale, happens at 940–980 °C (1700 to 1800°F) and produces aluminium with a purity of 99.5-99.8%. Recycling aluminum, which does not require electrolysis, is thus not treated using this method. The Hall–Héroult process consumes substantial electrical energy, and its electrolysis stage can produce significant amounts of carbon dioxide if the electricity is generated from high-emission sources. Furthermore, the process generates fluorocarbon compounds as byproducts, contributing to both air pollution and climate change. Process Difficulties faced Elemental aluminium cannot be produced by the electrolysis of an aqueous ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lockport (city), New York
Lockport is both a city and the Lockport (town), New York, town that surrounds it in Niagara County, New York, United States. The city is the Niagara county seat, with a population of 21,165 according to 2010 census figures, and an estimated population of 20,305 as of 2019. Its name derives from a set of Erie Canal Lock (water navigation), locks (Lock Numbers 34 and 35) within the city that were built to allow canal barges to traverse the of the Niagara Escarpment. It is part of the Buffalo–Niagara Falls metropolitan area. History The New York State Legislature authorized the Erie Canal's construction in April 1816. The route proposed by surveyors was to traverse an area in central Niagara County, New York, which was then "uncivilized" and free of White settlers. At the time, the nearest settlers were in nearby Cold Springs, Buffalo, New York, Cold Springs, New York. Following the announcement, land speculation, speculators began to buy large plots along and near the prop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electric Smelting And Aluminum Company
The Electric Smelting and Aluminum Company, founded as Cowles Electric Smelting and Aluminium Company, and Cowles Syndicate Company, Limited, was formed in the United States and England during the mid-1880s to extract and supply valuable metals. Founded by two brothers from Ohio, the Cowles companies are remembered for producing alloys in quantity sufficient for commerce. Their furnaces were electric arc smelters, one of the first viable methods for extracting metals. The businesses of the era dramatically increased the supply of aluminium, a valuable element not found in nature in pure form, and reduced its price. The Cowles process was the immediate predecessor to the Hall-Héroult process—today in nearly universal use more than a century after it was discovered by Charles Martin Hall and Paul Héroult and adapted by others including Carl Josef Bayer. Because of the patent landscape, the Cowles companies found themselves in court. Judges eventually acknowledged their innov ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Birthplace Of The Aluminum Industry (Pittsburgh, PA) (6038538949)
The place of birth (POB) or birthplace is the place where a person was born. This place is often used in legal documents, together with name and date of birth, to uniquely identify a person. Practice regarding whether this place should be a country, a territory or a city/town/locality differs in different countries, but often city or territory is used for native-born citizen passports and countries for foreign-born ones. As a general rule with respect to passports, if the place of birth is to be a country, it's determined to be the country that currently has ''sovereignty'' over the actual place of birth, regardless of when the birth actually occurred. The place of birth is not necessarily the place where the parents of the new baby live. If the baby is born in a hospital in another place, that place is the place of birth. In many countries, this also means that the government requires that the birth of the new baby is registered in the place of birth. Some countries place less ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bauxite
Bauxite () is a sedimentary rock with a relatively high aluminium content. It is the world's main source of aluminium and gallium. Bauxite consists mostly of the aluminium minerals gibbsite (), boehmite (γ-AlO(OH)), and diaspore (α-AlO(OH)), Mixture, mixed with the two iron oxides goethite (FeO(OH)) and haematite (), the aluminium Clay minerals, clay mineral kaolinite () and small amounts of anatase () and ilmenite ( or ). Bauxite appears dull in Lustre (mineralogy), luster and is reddish-brown, white, or tan. In 1821, the French people, French geologist Pierre Berthier discovered bauxite near the village of Les Baux-de-Provence, Les Baux in Provence, southern France. Formation Numerous classification schemes have been proposed for bauxite but, , there was no consensus. Vadász (1951) distinguished Laterite, lateritic bauxites (silicate bauxites) from karst bauxite ores (carbonate bauxites): * The carbonate bauxites occur predominantly in Europe, Guyana, Suriname, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bayer Process
The Bayer process is the principal industrial means of refining bauxite to produce alumina (aluminium oxide) and was developed by Carl Josef Bayer. Bauxite, the most important ore of aluminium, contains only 30–60% aluminium oxide (Al2O3), the rest being a mixture of silica, various iron oxides, and titanium dioxide. The aluminium oxide must be further purified before it can be refined into aluminium. The Bayer process is also the main source of gallium as a byproduct despite low extraction yields. Process Bauxite ore is a mixture of hydrated aluminium oxides and compounds of other elements such as iron. The aluminium compounds in the bauxite may be present as gibbsite (Al(OH)3), böhmite (γ-AlO(OH)) or diaspore (α-AlO(OH)); the different forms of the aluminium component and the impurities dictate the extraction conditions. Aluminium oxides and hydroxides are amphoteric, meaning that they are both acidic and basic. The solubility of Al(III) in water is very low but in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aluminum Oxide
Aluminium oxide (or aluminium(III) oxide) is a chemical compound of aluminium and oxygen with the chemical formula . It is the most commonly occurring of several aluminium oxides, and specifically identified as aluminium oxide. It is commonly called alumina and may also be called aloxide, aloxite, ALOX or alundum in various forms and applications and alumina is refined from bauxite. It occurs naturally in its crystalline polymorphic phase α-Al2O3 as the mineral corundum, varieties of which form the precious gemstones ruby and sapphire,which have an alumina content approaching 100%. Al2O3 is used as feedstock to produce aluminium metal, as an abrasive owing to its hardness, and as a refractory material owing to its high melting point. Natural occurrence Corundum is the most common naturally occurring crystalline form of aluminium oxide. Rubies and sapphires are gem-quality forms of corundum, which owe their characteristic colours to trace impurities. Rubies are given their ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cryolite
Cryolite ( Na3 Al F6, sodium hexafluoroaluminate) is a rare mineral identified with the once-large deposit at Ivittuut on the west coast of Greenland, mined commercially until 1987. It is used in the reduction ("smelting") of aluminium, in pest control, and as a dye. History Cryolite was first described in 1798 by Danish veterinarian and physician (1740–1801), from rock samples obtained from local Inuit who used the mineral for washing their hides; the actual source of the ore was later discovered in 1806 by the explorer Karl Ludwig Giesecke. who found the deposit at Ivigtut (old spelling) and nearby Arsuk Fjord, Southwest Greenland, where it was extracted by Øresund Chemical Industries. The name is derived from the Greek words (), and (). The Pennsylvania Salt Manufacturing Company used large amounts of cryolite to make caustic soda and fluorine compounds, including hydrofluoric acid at its Natrona, Pennsylvania, works, and at its integrated chemical plant in Cor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paul Héroult
Paul (Louis-Toussaint) Héroult (10 April 1863 – 9 May 1914) was a French scientist. He was one of the inventors of the Hall-Héroult process for smelting aluminium, and developed the first successful commercial electric arc furnace. He lived in Thury-Harcourt, Normandy. Life and career Paul Héroult read Henri Sainte-Claire Deville's treatise on aluminium, when he was 15 years old. At that time, aluminium was as expensive as silver and was used mostly for luxury items and jewellery. Héroult wanted to make it cheaper. He succeeded in doing so when he discovered the electrolytic aluminium process in 1886. The same year, in the United States, Charles Martin Hall (1863–1914) was discovering the same process. Because of this, the process was called the Hall–Heroult process. Héroult's second most important contribution is the first commercially successful electric arc furnace (EAF) for steel in 1900. The Héroult furnace gradually replaced the giant smelters for the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Smelting
Smelting is a process of applying heat and a chemical reducing agent to an ore to extract a desired base metal product. It is a form of extractive metallurgy that is used to obtain many metals such as iron-making, iron, copper extraction, copper, silver mining#Ore processing, silver, tin, lead smelting, lead and zinc smelting, zinc. Smelting uses heat and a chemical reducing agent to decompose the ore, driving off other elements as gases or slag and leaving the metal behind. The reducing agent is commonly a fossil-fuel source of carbon, such as carbon monoxide from incomplete combustion of coke (fuel), coke—or, in earlier times, of charcoal. The oxygen in the ore binds to carbon at high temperatures, as the Chemical energy, chemical potential energy of the bonds in carbon dioxide () is lower than that of the bonds in the ore. Sulfide ores such as those commonly used to obtain copper, zinc or lead, are roasting (metallurgy), roasted before smelting in order to convert the sulfid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oberlin College
Oberlin College is a Private university, private Liberal arts colleges in the United States, liberal arts college and conservatory of music in Oberlin, Ohio, United States. Founded in 1833, it is the oldest Mixed-sex education, coeducational liberal arts college in the United States and the second-oldest continuously operating List of coeducational colleges and universities in the United States, coeducational institute of higher learning in the world. The Oberlin Conservatory of Music is the oldest continuously operating conservatory in the United States. In 1835, Oberlin became one of the first colleges in the United States to admit African Americans, and in 1837, the first to admit women (other than Franklin & Marshall College, Franklin College's brief experiment in the 1780s). It has been known since its founding for progressive student activism. The College of Arts & Sciences offers more than 60 majors, minors, and concentrations. Oberlin is a member of the Great Lakes Colle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |