|
2017 In Spaceflight
Notable spaceflight activities in 2017 included the maiden flight, maiden orbital flight of India's Geosynchronous Satellite Launch Vehicle Mark III (also called LVM3) on 5 June and the first suborbital test of Rocket Lab's Electron rocket, inaugurating the Mahia spaceport in New Zealand. The rocket is named for its innovative Rutherford (rocket engine), Rutherford engine which feeds propellants via Electric pump-fed engine, battery-powered electric motors instead of the usual gas generator and turbopumps. Overview China launched its new missile-derived Kaituozhe-2 variant on 2 March. The Japanese S-Series (rocket family)#SS-520-4, SS-520, a suborbital sounding rocket modified for orbital flight, failed to reach orbit in January. If successful, it would have become the smallest and lightest vehicle to ever put an object in orbit. The venerable Russian Soyuz-U workhorse was retired after its 786th mission on 22 February. On 30 March, the SES-10 mission was launched with a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electron (rocket)
Electron is a two-stage, partially reusable orbital launch vehicle developed by Rocket Lab, an American aerospace company with a wholly owned New Zealand subsidiary. Servicing the commercial small satellite launch market, it is the third most launched small-lift launch vehicle in history. Its Rutherford engines are the first electric-pump-fed engine to power an orbital-class rocket. Electron is often flown with a kickstage or Rocket Lab's Photon spacecraft. Although the rocket was designed to be expendable, Rocket Lab has recovered the first stage twice and is working towards the capability of reusing the booster. The Flight 26 (F26) booster has featured the first helicopter catch recovery attempt. Rocket Lab has, however, abandoned the idea of catching Electron. In December 2016, Electron completed flight qualification. The first rocket was launched on 25 May 2017, reaching space but not achieving orbit due to a glitch in communication equipment on the ground. During its s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rocket Lab
Rocket Lab Corporation is a Public company, publicly traded aerospace manufacturer and List of launch service providers, launch service provider. Its Rocket Lab Electron, Electron orbital rocket launches Small satellite, small satellites, and has launched 63 times as of April 2025. A Sub-orbital spaceflight, sub-orbital Electron variant called HASTE (Hypersonic Accelerator Suborbital Test Electron) serves other needs. The company also supplies satellite components including Star tracker, star trackers, Reaction wheel, reaction wheels, Solar cell, solar cells and arrays, Satellite radio, satellite radios, separation systems, as well as flight and ground software. The Expendable launch system, expendable Electron rocket first Rocket, launched in May 2017. In August 2020, the company launched its first Rocket Lab Photon, Photon satellite. The company built and operates satellites for the Space Development Agency, part of the United States Space Force. In May 2022, the company attemp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
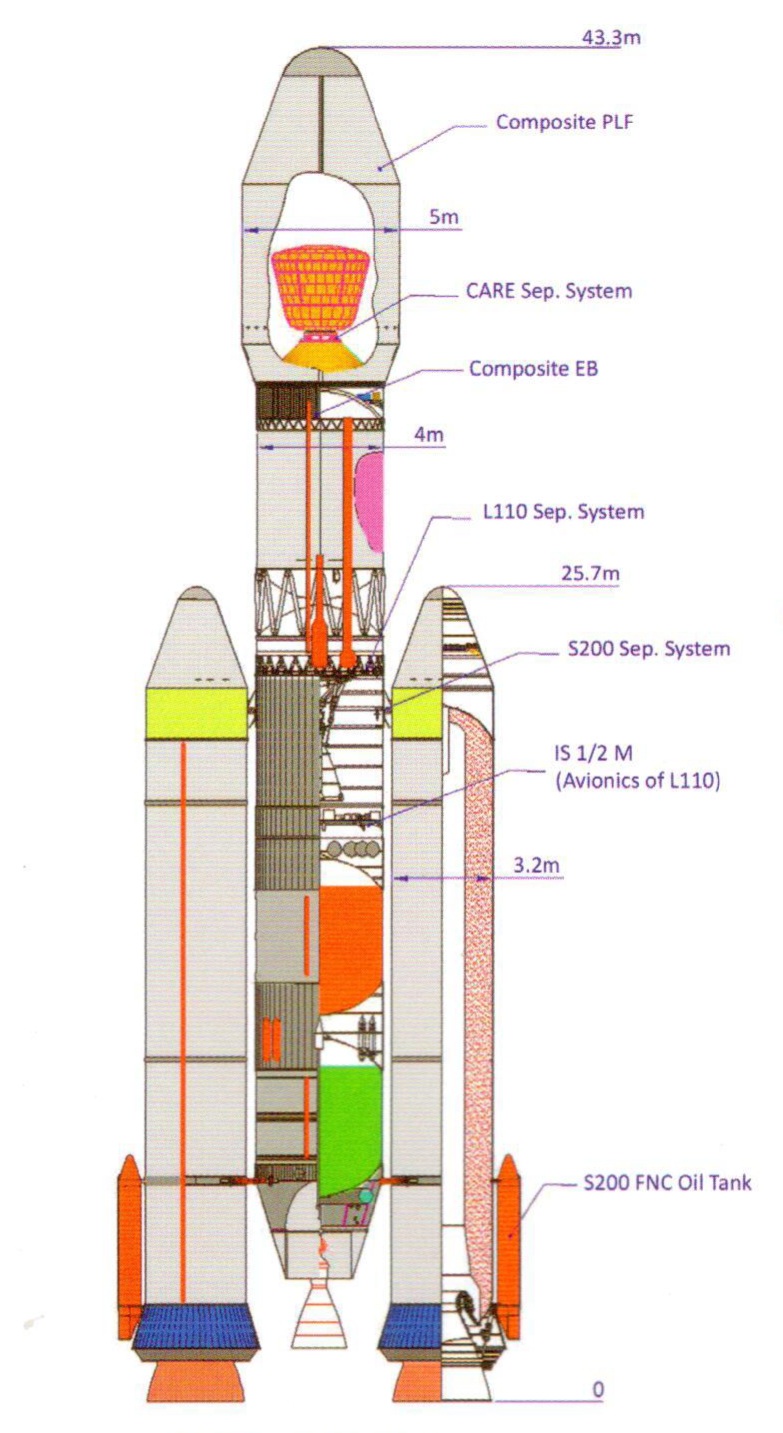
Geosynchronous Satellite Launch Vehicle Mark III
The Launch Vehicle Mark-3 or LVM3 (previously referred as the Geosynchronous Satellite Launch Vehicle Mark III or GSLV Mk III) is a three-stage medium-lift launch vehicle developed by the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO). Primarily designed to launch communication satellites into geostationary orbit, it is also due to launch crewed missions under the Indian Human Spaceflight Programme. LVM3 has a higher payload capacity than its predecessor, GSLV. After several delays and a sub-orbital test flight on 18 December 2014, ISRO successfully conducted the first orbital test launch of LVM3 on 5 June 2017 from the Satish Dhawan Space Centre. Total development cost of project was . In June 2018, the Union Cabinet approved to build 10 LVM3 rockets over a five-year period. The LVM3 has launched CARE, India's space capsule recovery experiment module, Chandrayaan-2 and Chandrayaan-3, India's second and third lunar missions, and will be used to carry Gaganyaan, the first crewed m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maiden Flight
The maiden flight, also known as first flight, of an aircraft is the first occasion on which it leaves the ground under its own power. The same term is also used for the first launch of rockets. In the early days of aviation it could be dangerous, because the exact handling characteristics of the aircraft were generally unknown. The maiden flight of a new type is almost invariably flown by a highly experienced test pilot. Maiden flights are usually accompanied by a chase plane, to verify items like altitude, airspeed, and general airworthiness. A maiden flight is only one stage in the development of an aircraft type. Unless the type is a pure research aircraft (such as the X-15), the aircraft must be tested extensively to ensure that it delivers the desired performance with an acceptable margin of safety. In the case of civilian aircraft, a new type must be certified by a governing agency (such as the Federal Aviation Administration in the United States) before it can enter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2018 In Spaceflight
This article documents notable spaceflight events during the year 2018. For the first time since 1990 in spaceflight, 1990, more than 100 orbital launches were performed globally. Overview Planetary exploration The NASA InSight seismology probe was launched in May 2018 and landed on Mars in November. The Parker Solar Probe was launched to explore the Sun in August 2018, and reached its first perihelion in November, traveling faster than any prior spacecraft. On 20 October the ESA and JAXA launched BepiColombo to Mercury (planet), Mercury, on a 10-year mission featuring several flybys and eventually deploying two orbiters in 2025 for local study. The asteroid sampling mission Hayabusa2 reached its target 162173 Ryugu, Ryugu in June, and the similar OSIRIS-REx probe reached 101955 Bennu, Bennu in December. China launched its Chang'e 4 lander/rover in December which performed the first ever soft landing on the far side of the Moon in January 2019; a communications relay wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2016 In Spaceflight
Several new rockets and spaceports began operations in 2016. Overview Russia inaugurated the far-Eastern Vostochny Cosmodrome on 28 April 2016 with a traditional Soyuz-2.1a flight, before expanding it for the Angara (rocket family), Angara rocket family in the following years. The Chinese Long March 7 flew its maiden flight from the new Wenchang Satellite Launch Center on Hainan Island on 25 June, and the maiden flight of the Long March 5 took place on 3 November. Two years after its Cygnus CRS Orb-3, 2014 accident, the Antares rocket returned to flight on 17 October with its upgraded Antares 230, 230 version featuring the Russian RD-181 engine. After Falcon 9 first-stage landing tests, many failed attempts, SpaceX began landing its Falcon 9 first stages on autonomous spaceport drone ships, edging closer to their long-stated goal of SpaceX reusable launch system development program, developing reusable launch vehicles. The company indicated that the recovered engines and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Timeline Of Spaceflight
This is a timeline of known spaceflights, both crewed and uncrewed, sorted chronologically by launch date. Due to its large size, the timeline has been split into smaller articles, one for each year since 1951. There is a separate list for all flights that occurred before 1951. The list for the year and for its subsequent years may contain planned launches, but the statistics will only include past launches. For the purpose of these lists, a spaceflight is defined as any flight that crosses the Kármán line, the Fédération Aéronautique Internationale, FAI-recognized edge of space, which is Above mean sea level, above mean sea level (AMSL). The timeline contains all the flights which have either crossed the edge of space, were intended to do so but failed, or are planned in the near future. Notable test flights of spaceflight systems may be listed even if they were not planned to reach space. Some lists are further divided into orbital launches (sending a payload into ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zenit (rocket Family)
Zenit (, ; meaning ''Zenith'') was a family of space launch vehicles designed by the Yuzhnoye Design Bureau in Dnipro, Ukraine, which was then part of the Soviet Union. Zenit was originally built in the 1980s for two purposes: as a liquid rocket booster for the Energia (rocket), Energia rocket and, equipped with a second stage, as a stand-alone middle-weight launcher with a payload greater than the 7 tonnes of the Soyuz (rocket), Soyuz but smaller than the 20 tonnes payload of the Proton (rocket family), Proton. The last rocket family developed in the USSR, the Zenit was intended as an eventual replacement for the dated Soyuz and Proton families, and it would employ propellants which were safer and less toxic than the Proton's nitrogen tetroxide/UDMH mix. Zenit was planned to take over crewed spaceship launches from Soyuz, but these plans were abandoned after the dissolution of the Soviet Union in 1991. Many of components of the Zenit rockets were produced in Russia. The Ukraini ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Delta II
Delta II was an expendable launch system, originally designed and built by McDonnell Douglas, and sometimes known as the Thorad Delta 1. Delta II was part of the Delta rocket family, derived directly from the Delta 3000, and entered service in 1989. There were two main variants, the Delta 6000 and Delta 7000, with the latter also having "Light" and "Heavy" subvariants. During its career, Delta II flew several notable payloads, including 24 Global Positioning System (GPS) GPS satellite blocks, Block II satellites, several dozen NASA payloads, and 60 Iridium communication satellites. The rocket flew its final mission, ICESat-2, on 15 September 2018, earning the launch vehicle a streak of 100 successful missions in a row, with the last failure being GPS IIR-1 in 1997. In the late 1990s, Delta II was developed further into the unsuccessful Delta III, which was in turn developed into the more capable and successful Delta IV, though the latter shares little heritage with the original ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soyuz-U
Soyuz-U ( GRAU index: 11A511U) was a Soviet and later Russian expendable medium-lift launch vehicle designed by the TsSKB design bureau and constructed at the Progress factory in Samara, Russia. The ''U'' designation stands for ''unified'', as the launch vehicle was the replacement for both the Voskhod rocket and the original Soyuz rocket. The Soyuz-U is part of the R-7 rocket family, which evolved from the R-7 Semyorka, an intercontinental ballistic missile. The first Soyuz-U flight took place on 18 May 1973, carrying as its payload Kosmos 559, a Zenit military surveillance satellite. The final flight of a Soyuz-U rocket took place on 22 February 2017, carrying Progress MS-05 to the International Space Station. Soyuz-U was in use continuously for almost 44 years. Production of R-7 derived launch vehicles peaked in the late 1970s-early 1980s at 55–60 a year. Soyuz-U held the world record of highest launch rate in a year in 1979 with 47 flights until this was bea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |