|
1623 In Science
The year 1623 in science and technology involved some significant events. Astronomy * July 16 – Great conjunction of Jupiter and Saturn, the closest together the two planets come until 2020. Biology * Apple orchard at Grönsö Manor in Sweden planted; it will still be productive into the 21st century. Psychology * Erotomania is first mentioned in a psychiatric treatise. Technology * Wilhelm Schickard draws a calculating clock on a letter to Kepler. This will be the first of five unsuccessful attempts at designing a ''direct entry'' Mechanical calculator, calculating clock in the 17th century (including the designs of Tito Livio Burattini, Tito Burattini, Samuel Morland and René Grillet de Roven, René Grillet). Births * June 19 – Blaise Pascal, French people, French mathematician and physicist (died 1662 in science, 1662) * July 12 – Elizabeth Walker (pharmacist), Elizabeth Walker, English people, English pharmacist (died 1690 in science, 1690) * August 26 – Johann ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Physicist
A physicist is a scientist who specializes in the field of physics, which encompasses the interactions of matter and energy at all length and time scales in the physical universe. Physicists generally are interested in the root or ultimate causes of Phenomenon, phenomena, and usually frame their understanding in mathematical terms. They work across a wide range of Physics#Research fields, research fields, spanning all length scales: from atom, sub-atomic and particle physics, through biological physics, to physical cosmology, cosmological length scales encompassing the universe as a whole. The field generally includes two types of physicists: Experimental physics, experimental physicists who specialize in the observation of natural phenomena and the development and analysis of experiments, and Theoretical physics, theoretical physicists who specialize in mathematical modeling of physical systems to rationalize, explain and predict natural phenomena. Physicists can apply their k ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jesuit
The Society of Jesus (; abbreviation: S.J. or SJ), also known as the Jesuit Order or the Jesuits ( ; ), is a religious order (Catholic), religious order of clerics regular of pontifical right for men in the Catholic Church headquartered in Rome. It was founded in 1540 by Ignatius of Loyola and six companions, with the approval of Pope Paul III. The Society of Jesus is the largest religious order in the Catholic Church and has played significant role in education, charity, humanitarian acts and global policies. The Society of Jesus is engaged in evangelization and apostolic ministry in 112 countries. Jesuits work in education, research, and cultural pursuits. They also conduct retreats, minister in hospitals and parishes, sponsor direct social and humanitarian works, and promote Ecumenism, ecumenical dialogue. The Society of Jesus is consecrated under the patron saint, patronage of Madonna della Strada, a title of the Blessed Virgin Mary, and it is led by a Superior General of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
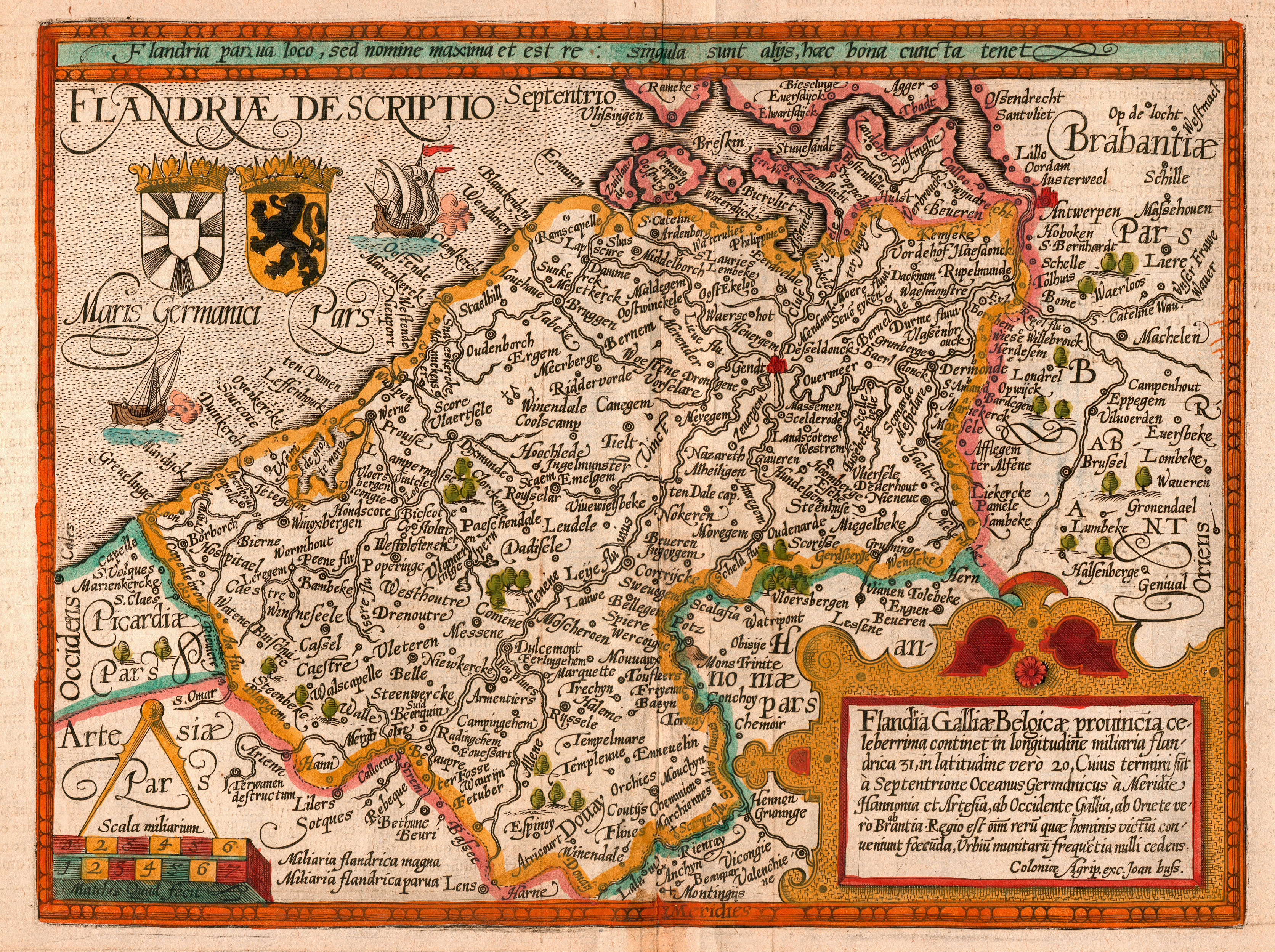
Flemish People
Flemish people or Flemings ( ) are a Germanic peoples, Germanic ethnic group native to Flanders, Belgium, who speak Flemish Dutch. Flemish people make up the majority of Belgians, at about 60%. ''Flemish'' was historically a geographical term, as all inhabitants of the medieval County of Flanders in modern-day Belgium, France and the Netherlands were referred to as "Flemings" irrespective of their ethnicity or language. The contemporary region of Flanders comprises a part of this historical county, as well as parts of the medieval Duchy of Brabant and the medieval County of Loon, where the modern national identity and Flemish culture, culture gradually formed. History The sense of "Flemish" identity increased significantly after the Belgian Revolution. Prior to this, the term "" in the Dutch language was in first place used for the inhabitants of the former County of Flanders. Flemish, however, had been used since the 14th century to refer to the language and dialects of both ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ferdinand Verbiest
Ferdinand Verbiest, (9 October 1623 – 28 January 1688) was a Flemish Jesuit missionary in China during the Qing dynasty. He was born in Pittem near Tielt in the County of Flanders (now part of Belgium). He is known as Nan Huairen () in Chinese. He was an accomplished mathematician and astronomer and proved to the court of the Kangxi Emperor that European astronomy was more accurate than Chinese astronomy. He then corrected the Chinese calendar and was later asked to rebuild and re-equip the Beijing Ancient Observatory, being given the roles of Head of the Mathematical Board and Director of the Observatory. He became close friends with the Kangxi Emperor, who frequently requested his instruction in geometry, philosophy and music. Verbiest worked as a diplomat, cartographer, and translator; he spoke Latin, German, Dutch, Spanish, Hebrew, Italian and Manchu. He wrote more than thirty books. During the 1670s, Verbiest designed what some claim to be the first ever self-propell ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1687 In Science
{{Science year nav, 1687 The year 1687 in science and technology involved some significant events. Astronomy * The constellation ''Triangulum Minus'' is named by Johannes Hevelius. Biology * Alida Withoos at the house of Agnes Block makes a painting of the first pineapple bred in Europe. Medicine * Dutch physician Willem ten Rhijne publishes ''Verhandelinge van de Asiatise Melaatsheid na een naaukeuriger ondersoek ten dienste van het gemeen'' in Amsterdam, explaining Asian leprosy to the West. Physics * July 5 – Isaac Newton's ''Philosophiæ Naturalis Principia Mathematica'', known as the ''Principia'', is published by the Royal Society of London. In it, Newton describes his theory of universal gravitation, explains the laws of mechanics (including Newton's laws of motion), gives a formula for the speed of sound and demonstrates that Earth is an oblate spheroid. The concepts in the ''Principia'' become the foundations of modern physics. Births * October 14 – Robert Simso ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Georg Balthasar Metzger
Georg Balthasar Metzger (23 September 1623 – 9 October 1687) was a German physician and scientist notable as one of the four founding members of the Academy of Sciences Leopoldina in Schweinfurt. Biography He was born in Schweinfurt. In 1646 Metzger obtained the Magister Artium degree from the University of Jena under Gottfried Möbius with a thesis entitled: ''Suppressionem mensium''. In 1650, he obtained his medical doctorate from the University of Basel under Johann Jakob von Brunn with a thesis entitled: Disputatio medica inauguralis de catarrho suffocativo'' In 1661 Metzger was appointed to the University of Tübingen by Eberhard III, Duke of Württemberg (1614–74) to improve its teaching of anatomy Anatomy () is the branch of morphology concerned with the study of the internal structure of organisms and their parts. Anatomy is a branch of natural science that deals with the structural organization of living things. It is an old scien ... and surgery. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1706 In Science
The year 1706 in science and technology involved some significant events. Mathematics * William Jones publishe''Synopsis palmariorum matheseos or, A New Introduction to the Mathematics, Containing the Principles of Arithmetic and Geometry Demonstrated in a Short and Easie Method ... Designed for ... Beginners''in which he ** proposes using the symbol π (the Greek letter '' pi'', as an abbreviation for ''perimeter'') to represent the ratio of the circumference of a circle to its diameter. ** introduces John Machin's quickly converging inverse-tangent series for π ( pi), enabling it to be computed to 100 decimal places. Technology * Francis Hauksbee produces his 'Influence machine' to generate static electricity. Publications * Johann Jakob Scheuchzer begins publication in Zürich of his ''Beschreibung der Naturgeschichten des Schweitzerlands'' giving an account of the natural history and geology of Switzerland. * Giovanni Battista Morgagni publishe''Adversaria anatomica''O ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caspar Schamberger
Caspar Schamberger (1 September 1623 in Leipzig, Germany – 8 April 1706) was a German surgeon. His name represents the first school of Western medicine in Japan and the beginning of ''rangaku'', or Dutch studies. Schamberger grew up in war-torn Saxony. In 1637 he started studying surgery under the master surgeon of the surgeons guild in his native town of Leipzig. Three years late he finished his education and started traveling through Northern Germany, Denmark, Sweden, and the Netherlands. In 1643 he joined the Dutch East India Company (VOC), signing a contract for four years of service. Schamberger left Europe in the same year aboard the ''Eiland Mauritius'', but the ship wrecked four months later near the Cape of Good Hope. In July 1644 Schamberger finally arrived in Batavia, the administrative center of the expanding Dutch colonial empire. The next few years he worked as a ship surgeon, visiting Portuguese Goa, Ceylon, Gamron and Kismis (Persia), to return to Batavia agai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1688 In Science
The year 1688 in science and technology included a number of events, some of which are listed here. Astronomy * The constellation '' Sceptrum Brandenburgicum'' is named by Gottfried Kirch. Exploration * A French Jesuit scientific mission led by Jean de Fontaney arrives in China. Mathematics * Simon de la Loubère introduces the Siamese method for constructing any size of ''n''-odd magic square to Western Europe. Technology * Earliest known mention of the balalaika. Births * January 29 – Emanuel Swedenborg, Swedish scientist and theologian (died 1772) * April 4 – Joseph-Nicolas Delisle, French astronomer (died 1768) * August 14 – Johann Leonhard Rost, German astronomer (died 1727) * September 26 – Willem 's Gravesande, Dutch polymath (died 1742) * November 15 – Louis Bertrand Castel, French Jesuit mathematician and physicist (died 1757) Deaths * January 28 – Ferdinand Verbiest, Flemish Jesuit astronomer in China (born 1623) * October 9 – Claude Perrault, Fren ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Johann Sigismund Elsholtz
Johann Sigismund Elsholtz (26 August 1623 – 28 February 1688), (some sources mention his day of birth as 28 August, and his death on 19 February) was a German naturalist who was a native of Frankfurt an der Oder. Biography Johann Sigismund Elsholtz studied at the Universities of Wittenberg, Königsberg and Padua, where he received his doctorate in 1653. He was appointed court botanist, alchemist and physician to Elector Friedrich Wilhelm of Brandenburg (1620-1688), and in 1657 was put in charge of Friedrich Wilhelm's botanical gardens at Berlin, Potsdam and Oranienburg. In 1654, he published ''Anthropometria'', an early study of anthropometry. This book was written for the benefit of artists and astrologers, as well as for students of medicine and physiognomy. It examines the perceived relationship between proportions of the human body and the incidence of disease. Elsholtz was a pioneer in the fields of hygiene and nutrition, and in his writings on holistic health, he ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1690 In Science
The year 1690 in science and technology involved some significant events. Astronomy * Giovanni Cassini observes differential rotation within Jupiter's atmosphere. * December – Earliest recorded sightings of the planet Uranus, by John Flamsteed, who mistakenly catalogues it as the star 34 Tauri. Geography * Franciscan Vincenzo Coronelli publishes the first folio of his atlas '' Atlante Veneto''. Botany * French horticulturalist Jean-Baptiste de La Quintinie's ''Instruction pour les jardins fruitiers et potagers'' is published posthumously. Mathematics * of Osaka publishes ''Sampo-Hakki'' (算法発揮), in which he gives the resultant and the Laplace expansion of the determinant for the ''n''×''n'' case. At about this date, {{nihongo, Tanaka Yoshizane, 田中 由真 also describes and applies the resultant, in ''Sampo-Funkai'' (算法紛解). * Michel Rolle publishes ''Traité d'Algebre'', in which he gives the first published description in Europe of Gaussian eliminati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |