|
155mm Artillery Shells
The 155 mm calibre is widely used for artillery guns. Land warfare Historic calibres France - 1874 The caliber originated in France after the Franco-Prussian War, Franco-Prussian War (1870–1871). A French artillery committee met on 2 February 1874 to discuss new models for French fortress and siege artillery, among which there was a weapon in the calibre range. After several meetings, on 16 April 1874 the committee settled on the calibre, and led to the De Bange 155 mm cannon. NATO standard Among the existing and the former 155 mm artillery shells, there is one that has been standardised by NATO under both the AOP-29 part 1 (in reference to STANAG 4425), and under the (Joint Ballistics Memorandum of Understanding). This standard defines a standard 155mm projectile with a 23 litre combustion chamber volume. NATO is now pushing from standardised artillery shell to sharable ammunition. The standard described above enables the use of NATO shells in all NATO guns. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cannon-launched Guided Projectile
Cannon-launched guided projectiles (CLGP) are precision-guided munitions launched by howitzers, mortar (weapon), mortars, tank guns, and naval guns. Those projectile main propulsion system is the initial kinetic shoot, directed as much as possible toward the target. A secondary GPS or geocoordinates-based system then corrects the trajectory to increase target accuracy and fall closer to the target. This system relies on electronic guidance and pre-programmed coordinates, submitted to the round before its launch. Systems capable of firing CLGPs *120×570mm NATO ** ** *120 mm mortar ** * 125 mm smoothbore ammunition ** ** ** ** *152 mm ** ** ** *155 mm ** List of CLGPs Tank * 105×617mm, 105x617mm NATO ** ** Falarick 105 – (Belgium/Ukraine) * 120×570mm NATO ** ** ** (planned to also support 125 mm smoothbore) * 125 mm smoothbore ammunition ** ** * 152 mm ** Naval * 5-inch, US naval (mainly Mark 45) ** (abandoned) ** (cancelled) **Excal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Type 99 155 mm Self-propelled Howitzer
The is a 155 mm self-propelled howitzer of the Japanese Ground Self-Defense Force, which was developed as the successor to the Type 75 155 mm self-propelled howitzer. History Research and development for a successor to the Type 75 155 mm self-propelled howitzer started in 1985. The new weapon would have a 155 mm gun barrel 52 calibers long (L52) instead of the 30 calibers (L30) barrel of the Type 75, and would mount the latest fire-control system. Japan Steel Works was the primary contractor, developing and manufacturing the main gun and turret. Mitsubishi Heavy Industries was tasked to design the chassis. The designing stage cost 5 billion yen and was completed in 1992. After various technical and practical tests, the first vehicle was delivered to the training division of Japan Ground Self-Defense Force in 1999.99式自走155m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palmaria (artillery)
The Palmaria is an Italian self-propelled howitzer using the 155 mm (6.1″) NATO-standard artillery calibre. History Developed by OTO Melara for the export market, the development of the Palmaria began in 1977, with the first prototype appearing in 1981. Design The Palmaria's chassis is based on the OF-40 main battle tank. The primary armament is a 155 mm howitzer, with a secondary 7.62 mm machine gun or 12.7 mm machine gun on anti-aircraft mount and four 76 mm forward-facing smoke grenade dischargers on either side of the turret. The howitzer has an automatic loading system, providing a rate of fire of one round every 15 seconds or a burst-fire rate of three rounds every 25 seconds. The loader has 23 ready rounds, with seven more rounds stored in the hull. Including manual reloading of the charge, the overall firing rate is normally one round per minute for one hour. Intense firing is four rounds in one minute. Sustained fire is one round every three minu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soltam M-71
The M-71 is a 155 mm 39 caliber towed howitzer manufactured by Israeli company Soltam Systems. Design The weapon was based on the earlier Soltam M-68 and uses the same recoil system, breech and carriage but had a longer gun barrel (39 calibre versus 33 calibre of M-68). It is fitted with a compressed air-driven rammer to permit rapid and easy loading at all angles of elevation as well as having a rechargeable battery mounted on the right trail for auxiliary power. It can fire a high-explosive shell up to a maximum range of at a muzzle velocity of . Deployment In addition to Israel, this weapon is in service with Chile, Singapore, Thailand, Philippines, South Africa, Slovenia and Myanmar. A version of this weapon was developed to mount on a modified Centurion chassis (M-72), but this vehicle never reached production. Operators * *: 18 *: 60 howitzers used by the Chilean Army, 36 Soltam M-68s acquired in the 1970s later upgraded to Soltam M-71 standard and 24 Soltam M- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ATMOS 2000
ATMOS (Autonomous Truck Mounted howitzer System) is a 155 mm/52 calibre self-propelled gun system manufactured by Israeli military manufacturer Soltam Systems. The system is long range, fast moving, truck mounted with high firepower and mobility, rapid deployment, short response time, operable in all terrain areas. The system is integrated with a fully computerized system, providing an automatic control, accurate navigation and target acquisition, the system is offered with various gun barrel lengths, ranging from 39 to 52 calibre, in order to meet different customer requirements. Overview The ATMOS is fitted with a 155 mm/52 calibre ordnance which conforms to NATO Joint Ballistic Memorandum of Understanding (JBMoU), and is mounted on a 6 × 6 cross-country truck chassis. The breech mechanism is horizontal sliding which automatically opens to the right with a self-sealing metal obturating ring. The buffer is a hydraulic cylinder with a Hydraulic recoil mechanism, hydro-pne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
FH70
The FH70 (field howitzer for the 1970s) is a towed 155 mm howitzer used by several nations. History In 1963, NATO agreed a NATO Basic Military Requirement 39 for close support artillery, either towed or tracked. Subsequently, Germany and UK started discussions and design studies and in 1968 established agreed operational characteristics for a towed 155 mm close support gun. Italy became a party to the agreement in 1970. Key requirements were: * A detachable auxiliary power unit (APU) * An unassisted range of ; an assisted range of * A burst capability of three rounds in 15–20 seconds, six rounds per minute for a short period and two rounds per minute sustained * The ability to fire all 155 mm munitions in NATO service, plus a new range of ammunition The two national authorities had overall responsibility for R&D, and Vickers Ltd was the co-ordinating design authority. They were also the design authority for the carriage and Rheinmetall GmbH was the authority f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PzH 2000
The Panzerhaubitze 2000 (), meaning "armoured howitzer 2000" and abbreviated PzH 2000, is a German 155 mm Self-propelled gun, self-propelled howitzer developed by KNDS Deutschland (formerly Krauss-Maffei Wegmann (KMW)) and Rheinmetall in the 1980s and 1990s for the German Army. The PzH 2000 has automatic support for up to five rounds of Artillery#Multiple round simultaneous impact, multiple round simultaneous impact. Replenishment of shells is automated. Two operators can load 60 shells and propelling charges in less than 12 minutes. The PzH 2000 equips the armies of German Army, Germany, Italian Army, Italy, Ukrainian Ground Forces, Ukraine, Royal Netherlands Army, Netherlands, Hellenic Army, Greece, Lithuanian Armed Forces, Lithuania, Hungarian Defence Forces, Hungary, Qatar Armed Forces, Qatar, and Croatian Army, Croatia, mostly replacing older systems such as the M109 howitzer. In November 2019, a PzH 2000 L52 gun fired a shell a distance of almost . Rheinmetall started ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GCT 155mm
The AMX-30 AuF1 is a French self-propelled gun vehicle currently in use by the armies of France and Saudi Arabia. It replaced the former Mk F3 155mm in French Army service. The AuF1 primary advantage is that it incorporates full armor and nuclear-biological-chemical (NBC) protection for its crew of four, while the former Mk F3 155mm offered no protection and could carry only two of its four crew members. The AuF1 saw combat with the Iraqi Army in the Iran–Iraq War. AuF1 The CN 155 AuF1 (Canon de 155 Automoteur Modèle F1, meaning "155 mm self-propelled gun model F1") is based on the AMX-30 main battle tank (MBT) chassis and equipped with a NATO-standard 155mm 39-caliber (L/39) gun with a bustle-mounted autoloader, giving a rate of fire of 8 rounds per minute. It is also equipped with a roof-mounted 12.7mm anti-aircraft gun. The AUF1 has an effective range of 23,000 meters firing conventional rounds and 28,000 meters using Rocket Assisted Projectiles (RAPs). Variants and upg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CAESAR Self-propelled Howitzer
The ''Camion Équipé d'un Système d'Artillerie'' (English: "Truck equipped with an artillery system") or CAESAR is a French 155 mm, 52-caliber self-propelled gun that can fire 39/52 caliber NATO-standard shells. It is installed on a 6x6 or 8x8 truck chassis. Equipped with an autonomous weapon network incorporating an inertial navigation system and ballistic computer, the CAESAR can accurately strike targets more than away using "Extended Range, Full Bore" (ERFB) ammunition with base bleed, or targets over away using rocket-assisted or smart ammunition. The CAESAR was developed by French defense contractor GIAT Industries (now KNDS France) and has been exported to various countries. Units manufactured for the French Army use a 6x6 Renault Sherpa 5 chassis, while some export customers have opted for systems integrated on a 6x6 Unimog U2450L or 8x8 Tatra 817 chassis. In February 2022, the French government awarded Nexter a contract for the development of a new generation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
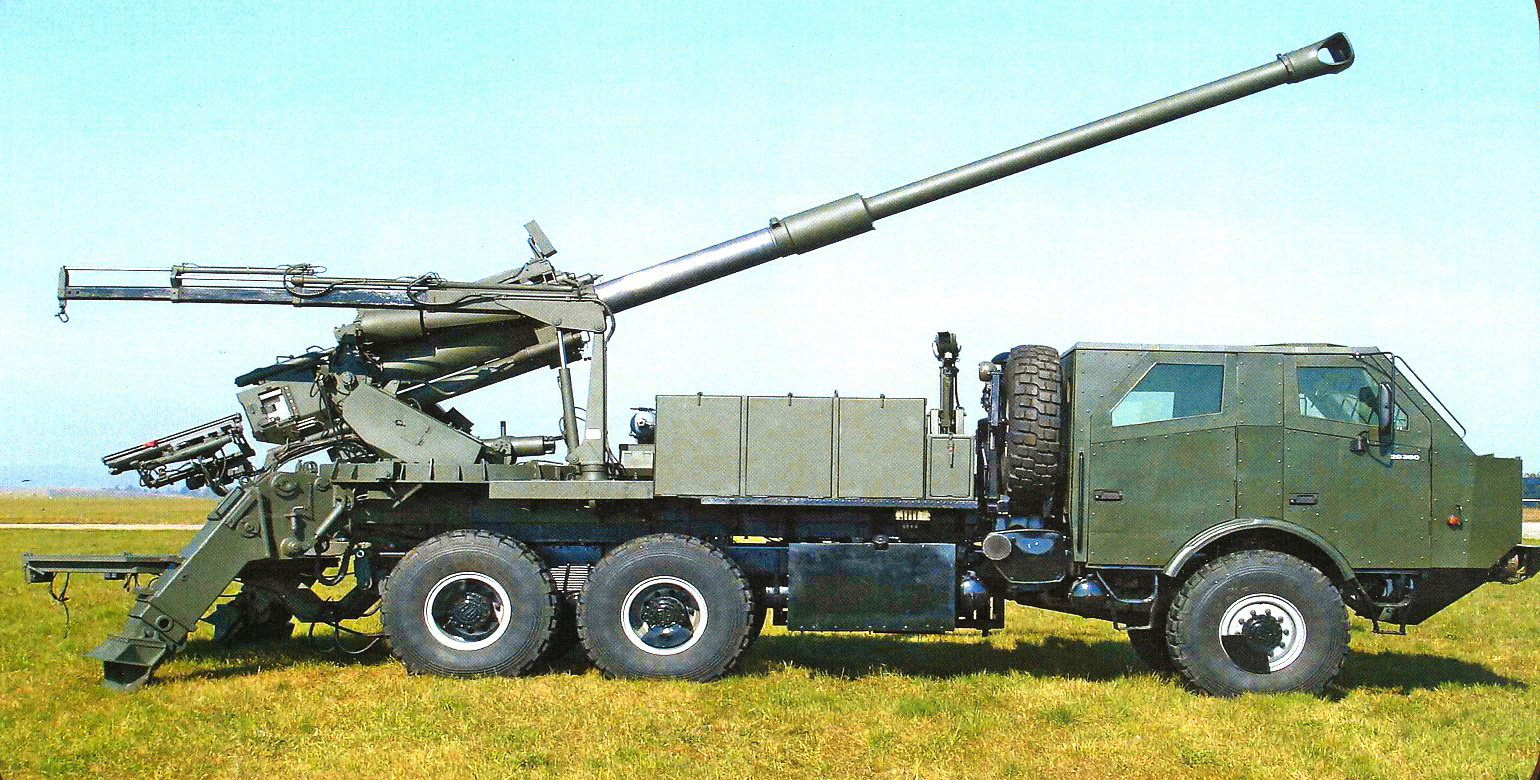
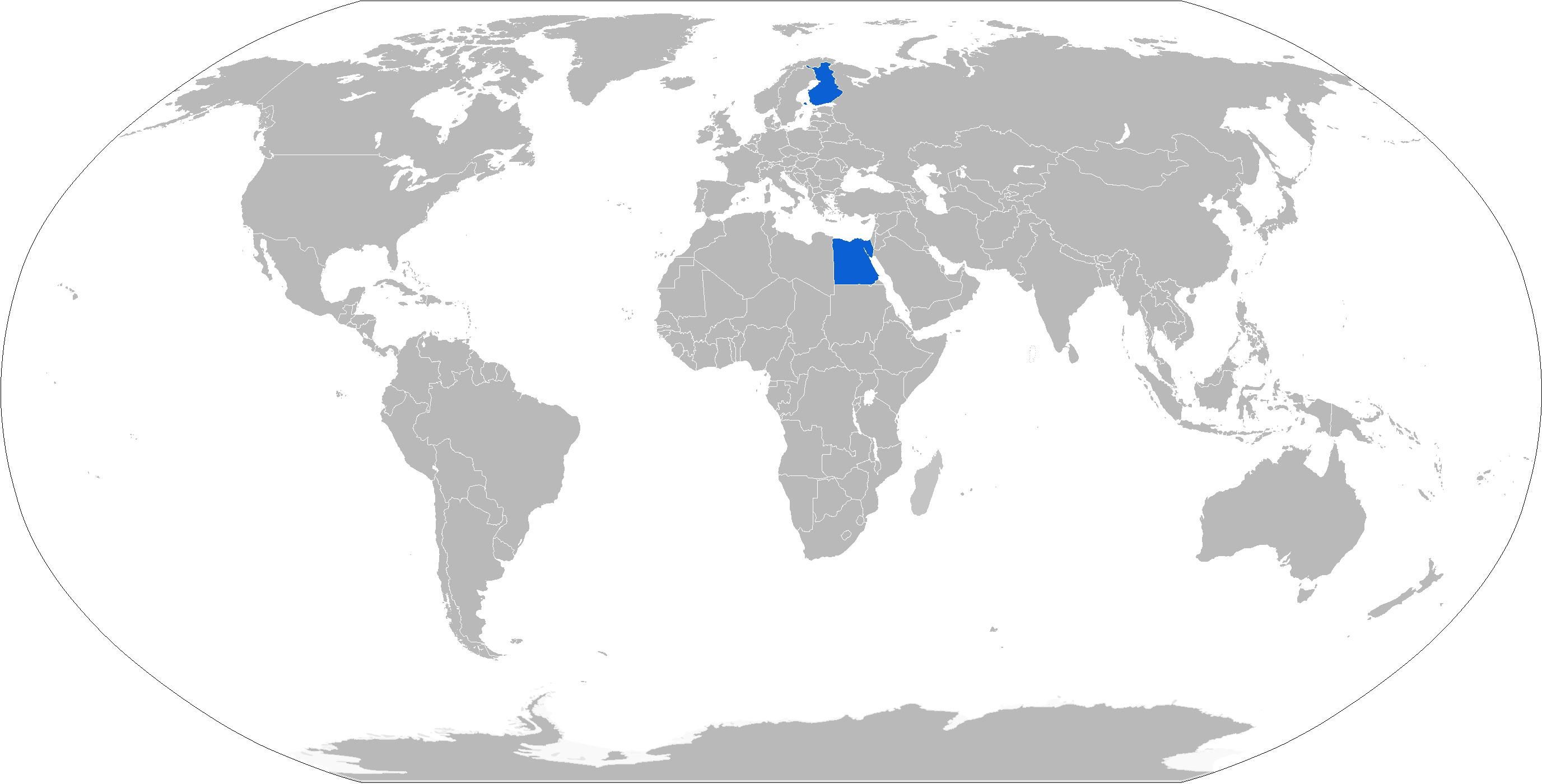
155 GH 52 APU
The 155 GH 52 APU (which stands for ''155 mm gun-howitzer, 52 Caliber (artillery), calibers, auxiliary power unit''), Finnish designation 155 K 98 (''155 mm kenttäkanuuna 1998'' or "155 mm field gun 1998"; Finnish Defence Forces, FDF terminology does not recognise gun-howitzers), is a Finnish towed artillery piece developed in 1998. It is largely based on the 155 K 83 with some major enhancements. It can be moved on the field short distances with its own auxiliary diesel engine, which is used in all 56 units used by the Finnish defence forces, is a 78-kilowatt Deutz AG, Deutz diesel engine. The Egyptian units are not equipped with the APU. The 155 GH 52 is considered to be one of the most modern field artillery cannons to date and was originally manufactured by Oy Tampella AB industries (today a part of Patria (company), Patria, Patria Vammas Systems Oy). It has a high rate of fire (6 rounds per minute) and can fire all types of 155 mm ammunition. Domestic operators The Ka ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
155 K 83
The Tampella 155 K 83 is a Finnish towed 155 mm field gun (Finnish designation; technically it is a gun-howitzer), manufactured in the 1980s by Tampella. History The development process for the 155 K 83 began in 1960 when Tampella presented their concept of a new 122 mm gun for the Finnish Army. It was a sound concept, but quite a heavy gun. It was only ordered in small numbers and designated 122 K 60 in Finnish nomenclature. In order to take advantage of the design, a decision was made to further develop this into a 155 mm gun. Through a number of development stages the 155 K 83 was born. Tampella cooperated with the Israeli group Soltam. The Tampella drawings for the never realized Finnish 122mm 35 K 68 were used to develop the Israeli Soltam M-68, which, after improvements, became the Soltam M-71 (designated the G4 in South Africa). Tampella went on to design and prototype successive models (155): K 68, K 74, K 74–82, K 74–83. The last with a barrel lengt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |