|
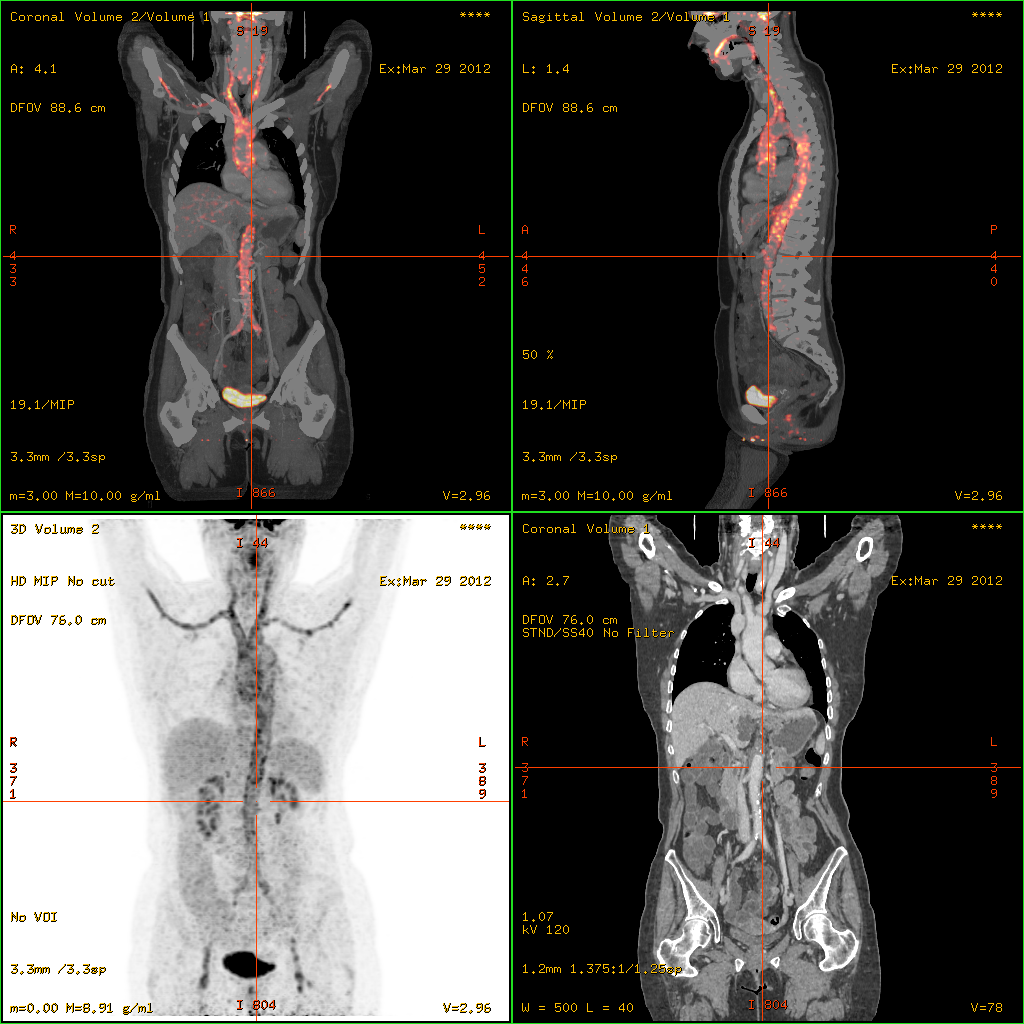
Buerger's Syndrome
Thromboangiitis obliterans, also known as Buerger disease (English ; ) or Winiwarter-Buerger disease, is a recurring progressive inflammation and thrombosis (clotting) of small and medium arteries and veins of the hands and feet. It is strongly associated with use of tobacco products, primarily from smoking, but is also associated with smokeless tobacco. Signs and symptoms There is a recurrent acute and chronic inflammation and thrombosis of arteries and veins of the hands and feet. The main symptom is pain in the affected areas, at rest and while walking (claudication). The impaired circulation increases sensitivity to cold. Peripheral pulses are diminished or absent. There are color changes in the extremities. The colour may range from cyanotic blue to reddish blue. Skin becomes thin and shiny. Hair growth is reduced. Ulcerations and gangrene in the extremities are common complications, often resulting in the need for amputation of the involved extremity. Pathophysiology The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Femoral Artery
The femoral artery is a large artery in the thigh and the main arterial supply to the thigh and leg. The femoral artery gives off the deep femoral artery or profunda femoris artery and descends along the anteromedial part of the thigh in the femoral triangle. It enters and passes through the adductor canal, and becomes the popliteal artery as it passes through the adductor hiatus in the adductor magnus near the junction of the middle and distal thirds of the thigh. Structure The femoral artery enters the thigh from behind the inguinal ligament as the continuation of the external iliac artery. Here, it lies midway between the anterior superior iliac spine and the symphysis pubis (Mid-inguinal point). Segments In clinical parlance, the femoral artery has the following segments: *The common femoral artery (CFA) is the segment of the femoral artery between the inferior margin of the inguinal ligament and the branching point of the deep femoral artery/profunda femoris artery. Its ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vasculitis
Vasculitis is a group of disorders that destroy blood vessels by inflammation. Both arteries and veins are affected. Lymphangitis (inflammation of lymphatic vessels) is sometimes considered a type of vasculitis. Vasculitis is primarily caused by leukocyte migration and resultant damage. Although both occur in vasculitis, inflammation of veins (phlebitis) or arteries (arteritis) on their own are separate entities. Signs and symptoms Possible signs and symptoms include: * General symptoms: Fever, unintentional weight loss * Skin: Palpable purpura, livedo reticularis * Muscles and joints: Muscle pain or inflammation, joint pain or joint swelling * Nervous system: Mononeuritis multiplex, headache, stroke, tinnitus, reduced visual acuity, acute visual loss * Heart and arteries: Heart attack, high blood pressure, gangrene * Respiratory tract: Nosebleeds, bloody cough, lung infiltrates * GI tract: Abdominal pain, bloody stool, perforations (hole in the GI tract) * Kidneys: Inflamma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
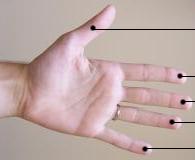
Digit (anatomy)
A digit is one of several most distal parts of a limb, such as fingers or toes, present in many vertebrates. Names Some languages have different names for hand and foot digits (English: respectively "finger" and "toe", German: "Finger" and "Zeh", French: "doigt" and "orteil"). In other languages, e.g. Arabic, Russian, Polish, Spanish, Portuguese, Italian, Czech, Tagalog, Turkish, Bulgarian, and Persian, there are no specific one-word names for fingers and toes; these are called "digit of the hand" or "digit of the foot" instead. In Japanese, yubi (指) can mean either, depending on context. Human digits Humans normally have five digits on each extremity. Each digit is formed by several bones called phalanges, surrounded by soft tissue. Human fingers normally have a nail at the distal phalanx. The phenomenon of polydactyly occurs when extra digits are present; fewer digits than normal are also possible, for instance in ectrodactyly. Whether such a mutation can be surgica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plethysmograph
A plethysmograph is an instrument for measuring changes in volume within an organ or whole body (usually resulting from fluctuations in the amount of blood or air it contains). The word is derived from the Greek "plethysmos" (increasing, enlarging, becoming full), and "graphein" (to write). Organs studied Lungs Pulmonary plethysmographs are commonly used to measure the functional residual capacity (FRC) of the lungs—the volume in the lungs when the muscles of respiration are relaxed—and total lung capacity. In a traditional plethysmograph (or "body box"), the test subject, or patient, is placed inside a sealed chamber the size of a small telephone booth with a single mouthpiece. At the end of normal expiration, the mouthpiece is closed. The patient is then asked to make an inspiratory effort. As the patient tries to inhale (a maneuver which looks and feels like panting), the lungs expand, decreasing pressure within the lungs and increasing lung volume. This, in turn, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thrombophilia
Thrombophilia (sometimes called hypercoagulability or a prothrombotic state) is an abnormality of blood coagulation that increases the risk of thrombosis (blood clots in blood vessels). Such abnormalities can be identified in 50% of people who have an episode of thrombosis (such as deep vein thrombosis in the leg) that was not provoked by other causes. A significant proportion of the population has a detectable thrombophilic abnormality, but most of these develop thrombosis only in the presence of an additional risk factor. There is no specific treatment for most thrombophilias, but recurrent episodes of thrombosis may be an indication for long-term preventive anticoagulation. The first major form of thrombophilia to be identified by medical science, antithrombin deficiency, was identified in 1965, while the most common abnormalities (including factor V Leiden) were described in the 1990s. Signs and symptoms The most common conditions associated with thrombophilia are deep ve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scleroderma
Scleroderma is a group of autoimmune diseases that may result in changes to the skin, blood vessels, muscles, and internal organs. The disease can be either localized to the skin or involve other organs, as well. Symptoms may include areas of thickened skin, stiffness, feeling tired, and poor blood flow to the fingers or toes with cold exposure. One form of the condition, known as CREST syndrome, classically results in calcium deposits, Raynaud's syndrome, esophageal problems, thickening of the skin of the fingers and toes, and areas of small, dilated blood vessels. The cause is unknown, but it may be due to an abnormal immune response. Risk factors include family history, certain genetic factors, and exposure to silica. The underlying mechanism involves the abnormal growth of connective tissue, which is believed to be the result of the immune system attacking healthy tissues. Diagnosis is based on symptoms, supported by a skin biopsy or blood tests. While no cure is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lupus
Lupus, technically known as systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), is an autoimmune disease in which the body's immune system mistakenly attacks healthy tissue in many parts of the body. Symptoms vary among people and may be mild to severe. Common symptoms include painful and swollen joints, fever, chest pain, hair loss, mouth ulcers, swollen lymph nodes, feeling tired, and a red rash which is most commonly on the face. Often there are periods of illness, called flares, and periods of remission during which there are few symptoms. The cause of SLE is not clear. It is thought to involve a mixture of genetics combined with environmental factors. Among identical twins, if one is affected there is a 24% chance the other one will also develop the disease. Female sex hormones, sunlight, smoking, vitamin D deficiency, and certain infections are also believed to increase a person's risk. The mechanism involves an immune response by autoantibodies against a person's own tissues. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Raynaud's Phenomenon
Raynaud syndrome, also known as Raynaud's phenomenon, eponymously named after the physician Auguste Gabriel Maurice Raynaud, who first described it in his doctoral thesis in 1862, is a medical condition in which the spasm of small arteries causes episodes of reduced blood flow to end arterioles. Typically, the fingers, and less commonly, the toes, are involved. Rarely, the nose, ears, or lips are affected. The episodes classically result in the affected part turning white and then blue. Often, numbness or pain occurs. As blood flow returns, the area turns red and burns. The episodes typically last minutes but can last several hours. Episodes are typically triggered by cold or emotional stress. Primary Raynaud's, also known as idiopathic, means that it is spontaneous, of unknown cause, and unrelated to another disease. Secondary Raynaud's occurs as a result of another condition and has an older age at onset; episodes are intensely painful and can be asymmetric and associated wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endocarditis
Endocarditis is an inflammation of the inner layer of the heart, the endocardium. It usually involves the heart valves. Other structures that may be involved include the interventricular septum, the chordae tendineae, the mural endocardium, or the surfaces of intracardiac devices. Endocarditis is characterized by lesions, known as '' vegetations'', which is a mass of platelets, fibrin, microcolonies of microorganisms, and scant inflammatory cells. In the subacute form of infective endocarditis, the vegetation may also include a center of granulomatous tissue, which may fibrose or calcify. There are several ways to classify endocarditis. The simplest classification is based on cause: either ''infective'' or ''non-infective'', depending on whether a microorganism is the source of the inflammation or not. Regardless, the diagnosis of endocarditis is based on clinical features, investigations such as an echocardiogram, and blood cultures demonstrating the presence of endocarditis-c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atherosclerosis
Atherosclerosis is a pattern of the disease arteriosclerosis in which the wall of the artery develops abnormalities, called lesions. These lesions may lead to narrowing due to the buildup of atheroma, atheromatous plaque. At onset there are usually no symptoms, but if they develop, symptoms generally begin around middle age. When severe, it can result in coronary artery disease, stroke, peripheral artery disease, or kidney problems, depending on which Artery, arteries are affected. The exact cause is not known and is proposed to be multifactorial. Risk factors include dyslipidemia, abnormal cholesterol levels, elevated levels of inflammatory markers, high blood pressure, diabetes, smoking, obesity, family history, genetic, and an unhealthy diet. Atheroma, Plaque is made up of fat, cholesterol, calcium, and other substances found in the blood. The narrowing of Artery, arteries limits the flow of oxygen-rich blood to parts of the body. Diagnosis is based upon a physical exam, ele ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ischemia
Ischemia or ischaemia is a restriction in blood supply to any tissue, muscle group, or organ of the body, causing a shortage of oxygen that is needed for cellular metabolism (to keep tissue alive). Ischemia is generally caused by problems with blood vessels, with resultant damage to or dysfunction of tissue i.e. hypoxia and microvascular dysfunction. It also implies local hypoxia in a part of a body resulting from constriction (such as vasoconstriction, thrombosis, or embolism). Ischemia causes not only insufficiency of oxygen, but also reduced availability of nutrients and inadequate removal of metabolic wastes. Ischemia can be partial (poor perfusion) or total blockage. The inadequate delivery of oxygenated blood to the organs must be resolved either by treating the cause of the inadequate delivery or reducing the oxygen demand of the system that needs it. For example, patients with myocardial ischemia have a decreased blood flow to the heart and are prescribed with medi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |