|
Bracken Fern
Bracken (''Pteridium'') is a genus of large, coarse ferns in the family (biology), family Dennstaedtiaceae. Ferns (Pteridophyta) are vascular plants that have alternating generations, large plants that produce spores and small plants that produce gamete, sex cells (eggs and sperm). Brackens are noted for their large, highly divided leaves. They are found on all continents except Antarctica and in all environments except deserts, though their typical habitat is moorland. The genus probably has the widest distribution of any fern in the world. The word ''bracken'' is of Old Norse origin, related to Swedish ''bräken'' and Danish ''bregne'', both meaning fern. In the past, the genus was commonly treated as having only one species, ''Pteridium aquilinum'', but the recent trend is to subdivide it into about ten species. Like other ferns, brackens do not have seeds or fruits, but the immature fronds, known as ''fiddleheads'', are sometimes eaten, although some are #Toxicity, thought ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pteridaceae
Pteridaceae is a family of ferns in the order Polypodiales, including some 1150 known species in ca 45 genera (depending on taxonomic opinions), divided over five subfamilies. The family includes four groups of genera that are sometimes recognized as separate families: the adiantoid, cheilanthoid, pteridoid, and hemionitidoid ferns. Relationships among these groups remain unclear, and although some recent genetic analyses of the Pteridales suggest that neither the family Pteridaceae nor the major groups within it are all monophyletic, as yet these analyses are insufficiently comprehensive and robust to provide good support for a revision of the order at the family level. Description Members of Pteridaceae have creeping or erect rhizomes. The leaves are almost always compound and have linear sori that are typically on the margins of the leaves and lack a true indusium, typically being protected by a false indusium formed from the reflexed margin of the leaf. Taxonomy Tradi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spores
In biology, a spore is a unit of sexual or asexual reproduction that may be adapted for dispersal and for survival, often for extended periods of time, in unfavourable conditions. Spores form part of the life cycles of many plants, algae, fungi and protozoa. Bacterial spores are not part of a sexual cycle, but are resistant structures used for survival under unfavourable conditions. Myxozoan spores release amoeboid infectious germs ("amoebulae") into their hosts for parasitic infection, but also reproduce within the hosts through the pairing of two nuclei within the plasmodium, which develops from the amoebula. In plants, spores are usually haploid and unicellular and are produced by meiosis in the sporangium of a diploid sporophyte. Under favourable conditions the spore can develop into a new organism using mitotic division, producing a multicellular gametophyte, which eventually goes on to produce gametes. Two gametes fuse to form a zygote which develops into a new s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pteridium Caudatum
Bracken (''Pteridium'') is a genus of large, coarse ferns in the family Dennstaedtiaceae. Ferns (Pteridophyta) are vascular plants that have alternating generations, large plants that produce spores and small plants that produce sex cells (eggs and sperm). Brackens are noted for their large, highly divided leaves. They are found on all continents except Antarctica and in all environments except deserts, though their typical habitat is moorland. The genus probably has the widest distribution of any fern in the world. The word ''bracken'' is of Old Norse origin, related to Swedish ''bräken'' and Danish ''bregne'', both meaning fern. In the past, the genus was commonly treated as having only one species, ''Pteridium aquilinum'', but the recent trend is to subdivide it into about ten species. Like other ferns, brackens do not have seeds or fruits, but the immature fronds, known as ''fiddleheads'', are sometimes eaten, although some are thought to be carcinogenic. Description and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pteridium Arachnoideum
Bracken (''Pteridium'') is a genus of large, coarse ferns in the family Dennstaedtiaceae. Ferns (Pteridophyta) are vascular plants that have alternating generations, large plants that produce spores and small plants that produce sex cells (eggs and sperm). Brackens are noted for their large, highly divided leaves. They are found on all continents except Antarctica and in all environments except deserts, though their typical habitat is moorland. The genus probably has the widest distribution of any fern in the world. The word ''bracken'' is of Old Norse origin, related to Swedish ''bräken'' and Danish ''bregne'', both meaning fern. In the past, the genus was commonly treated as having only one species, ''Pteridium aquilinum'', but the recent trend is to subdivide it into about ten species. Like other ferns, brackens do not have seeds or fruits, but the immature fronds, known as ''fiddleheads'', are sometimes eaten, although some are thought to be carcinogenic. Description and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2007 United Kingdom Foot-and-mouth Outbreak
The 2007 United Kingdom foot-and-mouth outbreak occurred when the discharge of infectious effluent from a laboratory in Surrey led to foot-and-mouth disease (FMD) infections at four nearby farms. The infections were detected via regular livestock testing by the Department for Environment, Food and Rural Affairs (Defra). The first diagnosis took place in a field of Normandy, Surrey; the second was three days later in a cattle-rotation field of a farm in Elstead, and the following day a third infection was found nearby within a quickly-established protection zone around the first detection. One month and ten days after the first diagnosis a final incidence of 2007 was identified and dealt with north of the first diseased animal. The source of the strain released and contained in Surrey in 2007 was the advanced effluent pipes from either the Institute for Animal Health or the similar vaccine researching and producing Merial Animal Health laboratory near to Pirbright villag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
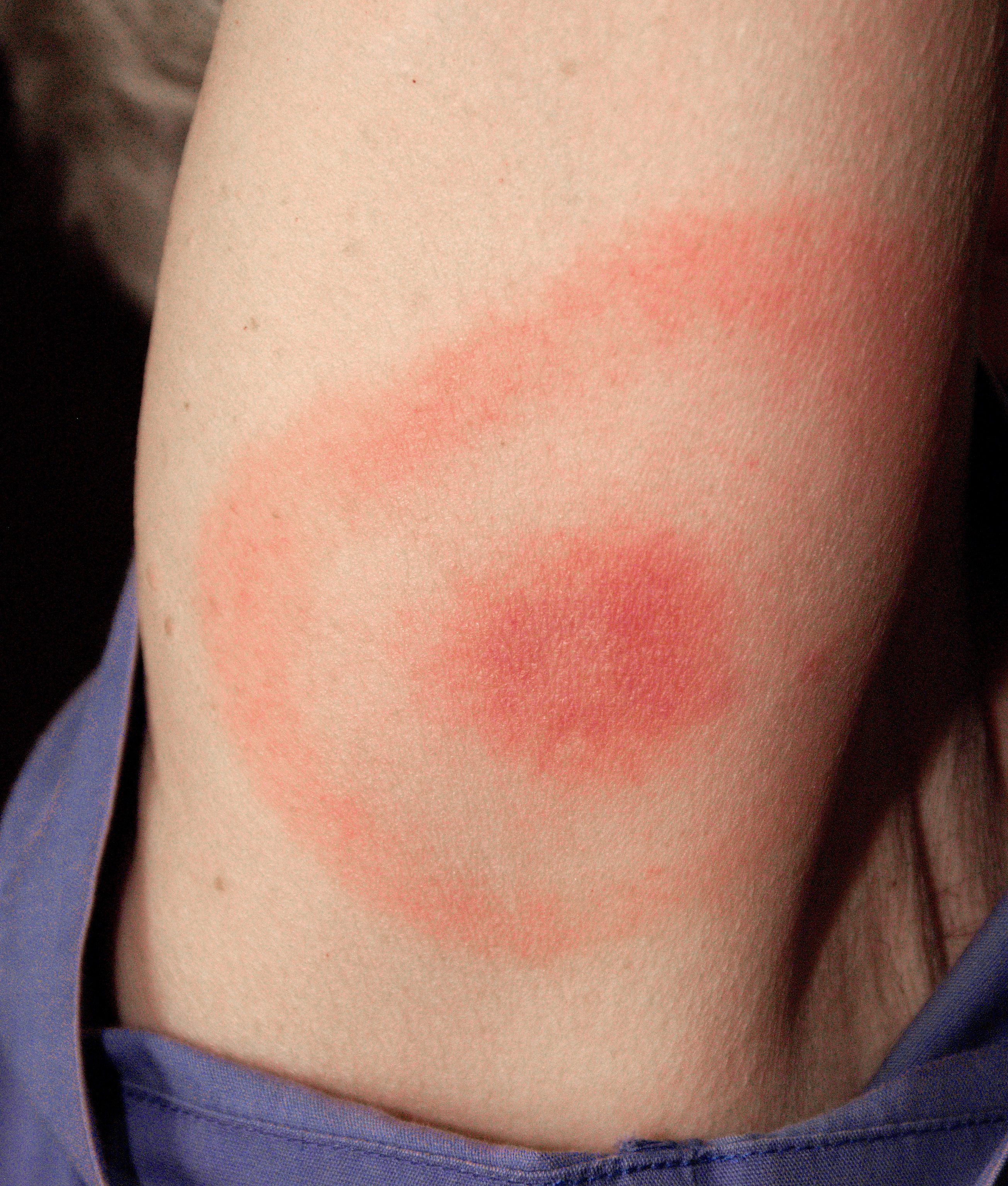
Lyme Disease
Lyme disease, also known as Lyme borreliosis, is a vector-borne disease caused by the ''Borrelia'' bacterium, which is spread by ticks in the genus ''Ixodes''. The most common sign of infection is an expanding red rash, known as erythema migrans (EM), which appears at the site of the tick bite about a week afterwards. The rash is typically neither itchy nor painful. Approximately 70–80% of infected people develop a rash. Early diagnosis can be difficult. Other early symptoms may include fever, headaches and tiredness. If untreated, symptoms may include loss of the ability to move one or both sides of the face, joint pains, severe headaches with neck stiffness or heart palpitations. Months to years later repeated episodes of joint pain and swelling may occur. Occasionally shooting pains or tingling in the arms and legs may develop. Despite appropriate treatment about 10 to 20% of those affected develop joint pains, memory problems and tiredness for at least six months. Lym ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ericaceae
The Ericaceae are a family of flowering plants, commonly known as the heath or heather family, found most commonly in acidic and infertile growing conditions. The family is large, with c.4250 known species spread across 124 genera, making it the 14th most species-rich family of flowering plants. The many well known and economically important members of the Ericaceae include the cranberry, blueberry, huckleberry, rhododendron (including azaleas), and various common heaths and heathers ('' Erica'', '' Cassiope'', '' Daboecia'', and ''Calluna'' for example). Description The Ericaceae contain a morphologically diverse range of taxa, including herbs, dwarf shrubs, shrubs, and trees. Their leaves are usually evergreen, alternate or whorled, simple and without stipules. Their flowers are hermaphrodite and show considerable variability. The petals are often fused ( sympetalous) with shapes ranging from narrowly tubular to funnelform or widely urn-shaped. The corollas are usually rad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
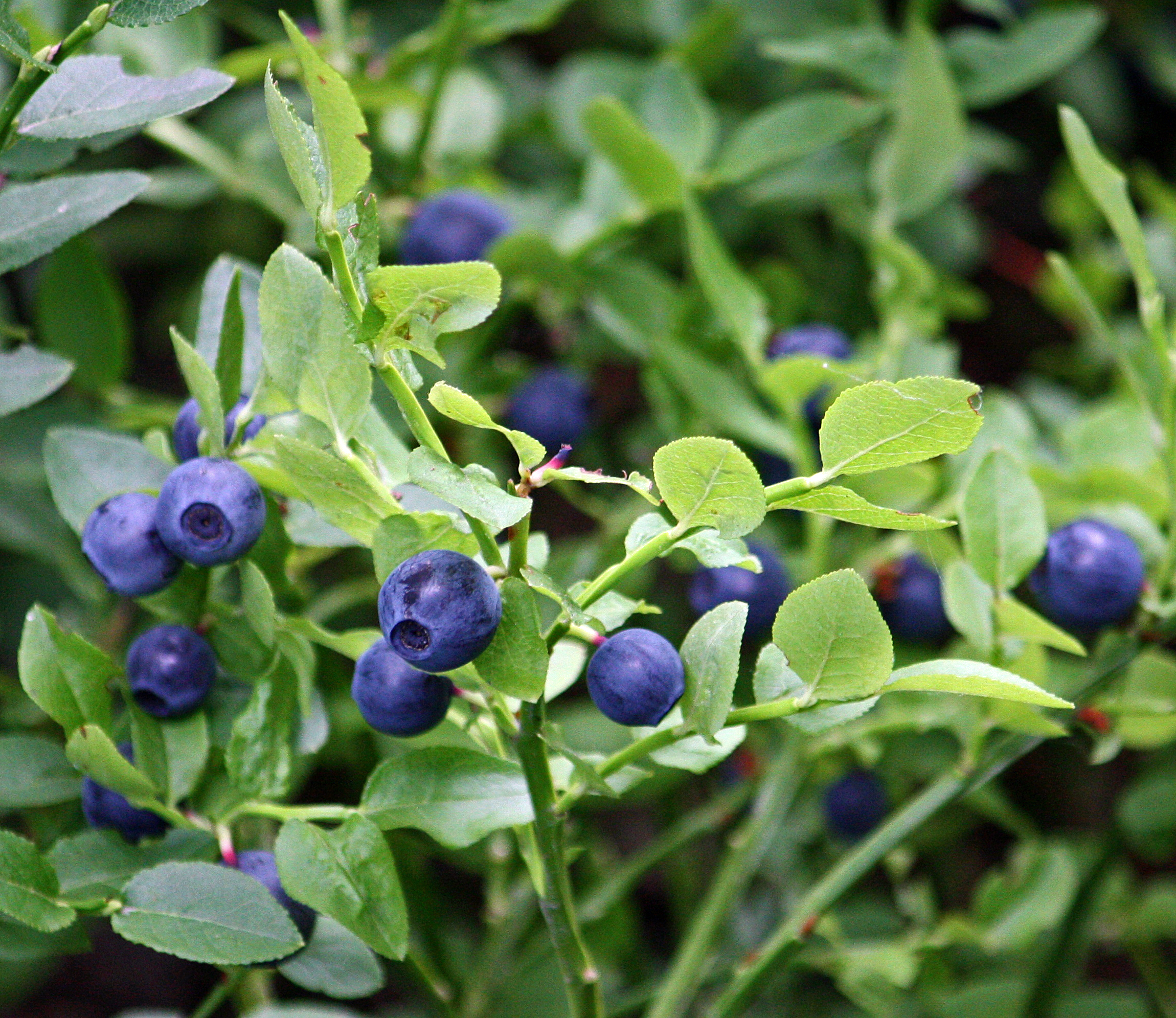
Bilberry
Bilberries (), or sometimes European blueberries, are a primarily Eurasian species of low-growing shrubs in the genus ''Vaccinium'' (family Ericaceae), bearing edible, dark blue berries. The species most often referred to is '' Vaccinium myrtillus'' L., but there are several other closely related species. Etymology and common names The name "bilberry" appears to have a Scandinavian origin, possibly from as early as 1577, being similar to the Danish word ''bølle'' for whortleberry with the addition of "berry". In Scandinavian languages bilberries have names that translate to "blueberry": ''blåbär'' in Swedish and ''blåbær'' in Danish and Norwegian. The bilberry (especially '' Vaccinium myrtillus'') is also known by a number of other names including blaeberry in Scottish and Northern English regional dialects and the Scots language, whortleberry in southern England, and w(h)imberry or w(h)inberry in Derbyshire, Lancashire, along the Anglo-Welsh border, and south Wal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Molinia
''Molinia'', or moor grass, is a genus of two species of flowering plants in the grass family, native to damp moorland in Eurasia and northern Africa. They are both herbaceous perennial grasses. The genus is named after Juan Ignacio Molina, a 19th-century Chilean naturalist. ; Species * '' Molinia caerulea'' (L.) Moench - (purple moor grass) - Eurasia + northern Africa from Ireland + Morocco to Ethiopia + Kazakhstan; naturalized in parts of United States + Canada * ''Molinia japonica'' Hack. (Japanese moor grass) - Japan, Korea, Anhui, Zhejiang, Sakhalin, Kuril ; formerly included see '' Arctophila Catabrosa Cleistogenes Diarrhena Disakisperma Festuca Glyceria ''Glyceria'' is a widespread genus of grass family common across Eurasia, Australia, North Africa, and the Americas. ''Glyceria'' is known commonly as mannagrass in the United States, or, in the UK, sweet-grass. These are perennial rhizomatous ... Poa Puccinellia'' References Molinieae Bunchgr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subtropical
The subtropical zones or subtropics are geographical and climate zones to the north and south of the tropics. Geographically part of the temperate zones of both hemispheres, they cover the middle latitudes from to approximately 35° north and south. The horse latitudes lie within this range. Subtropical climates are often characterized by hot summers and mild winters with infrequent frost. Most subtropical climates fall into two basic types: humid subtropical ( Koppen climate Cfa), where rainfall is often concentrated in the warmest months, for example Southeast China and the Southeastern United States, and dry summer or Mediterranean climate ( Koppen climate Csa/Csb), where seasonal rainfall is concentrated in the cooler months, such as the Mediterranean Basin or Southern California. Subtropical climates can also occur at high elevations within the tropics, such as in the southern end of the Mexican Plateau and in Da Lat of the Vietnamese Central Highlands. The six c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |