|
Bid–ask Matrix
The bid–ask matrix is a matrix with elements corresponding with exchange rates between the assets. These rates are in ''physical units'' (e.g. number of stocks) and not with respect to any '' numeraire''. The (i,j) element of the matrix is the number of units of asset i which can be exchanged for 1 unit of asset j. Mathematical definition A d \times d matrix \Pi = \left pi_\right is a ''bid-ask matrix'', if # \pi_ > 0 for 1 \leq i,j \leq d. Any trade has a positive exchange rate. # \pi_ = 1 for 1 \leq i \leq d. Can always trade 1 unit with itself. # \pi_ \leq \pi_\pi_ for 1 \leq i,j,k \leq d. A direct exchange is always at most as expensive as a chain of exchanges. Example Assume a market with 2 assets (A and B), such that x units of A can be exchanged for 1 unit of B, and y units of B can be exchanged for 1 unit of A. Then the ''bid–ask matrix'' \Pi is: : \Pi = \begin 1 & x \\ y & 1 \end Relation to solvency cone If given a bid–ask matrix \Pi for d assets such that \P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Matrix (mathematics)
In mathematics, a matrix (plural matrices) is a rectangular array or table of numbers, symbols, or expressions, arranged in rows and columns, which is used to represent a mathematical object or a property of such an object. For example, \begin1 & 9 & -13 \\20 & 5 & -6 \end is a matrix with two rows and three columns. This is often referred to as a "two by three matrix", a "-matrix", or a matrix of dimension . Without further specifications, matrices represent linear maps, and allow explicit computations in linear algebra. Therefore, the study of matrices is a large part of linear algebra, and most properties and operations of abstract linear algebra can be expressed in terms of matrices. For example, matrix multiplication represents composition of linear maps. Not all matrices are related to linear algebra. This is, in particular, the case in graph theory, of incidence matrices, and adjacency matrices. ''This article focuses on matrices related to linear algebra, and, un ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Assets
In financial accounting, an asset is any resource owned or controlled by a business or an economic entity. It is anything (tangible or intangible) that can be used to produce positive economic value. Assets represent value of ownership that can be converted into cash (although cash itself is also considered an asset). The balance sheet of a firm records the monetaryThere are different methods of assessing the monetary value of the assets recorded on the Balance Sheet. In some cases, the ''Historical Cost'' is used; such that the value of the asset when it was bought in the past is used as the monetary value. In other instances, the present fair market value of the asset is used to determine the value shown on the balance sheet. value of the assets owned by that firm. It covers money and other valuables belonging to an individual or to a business. Assets can be grouped into two major classes: tangible assets and intangible assets. Tangible assets contain various subclasses, inc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
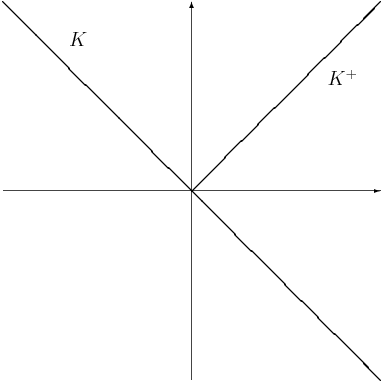
Solvency Cone
The solvency cone is a concept used in financial mathematics which models the possible trades in the Market (economics), financial market. This is of particular interest to markets with transaction costs. Specifically, it is the convex cone of portfolios that can be exchanged to portfolios of non-negative components (including paying of any transaction costs). Mathematical basis If given a bid-ask matrix \Pi for d assets such that \Pi = \left(\pi^\right)_ and m \leq d is the number of assets which with any non-negative quantity of them can be "discarded" (traditionally m = d), then the solvency cone K(\Pi) \subset \mathbb^d is the convex cone spanned by the unit vectors e^i, 1 \leq i \leq m and the vectors \pi^e^i-e^j, 1 \leq i,j \leq d. Definition A solvency cone K is any closed convex cone such that K \subseteq \mathbb^d and K \supseteq \mathbb^d_+. Uses A process of (random) solvency cones \left\_^T is a model of a financial market. This is sometimes called a market process. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bid–ask Spread
The bid–ask spread (also bid–offer or bid/ask and buy/sell in the case of a market maker) is the difference between the prices quoted (either by a single market maker or in a limit order book) for an immediate sale ( ask) and an immediate purchase ( bid) for stocks, futures contracts, options, or currency pairs in some auction scenario. The size of the bid–ask spread in a security is one measure of the liquidity of the market and of the size of the transaction cost. If the spread is 0 then it is a frictionless asset. Liquidity The trader initiating the transaction is said to demand liquidity, and the other party (counterparty) to the transaction supplies liquidity. Liquidity demanders place market orders and liquidity suppliers place limit orders. For a round trip (a purchase and sale together) the liquidity demander pays the spread and the liquidity supplier earns the spread. All limit orders outstanding at a given time (i.e. limit orders that have not been executed) are t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frictionless Market
Frictionless can refer to: * Frictionless market * Frictionless continuant * Frictionless sharing * Frictionless plane The frictionless plane is a concept from the writings of Galileo Galilei. In his 1638 '' The Two New Sciences'', Galileo presented a formula that predicted the motion of an object moving down an inclined plane. His formula was based upon his past e ... * Frictionless flow {{disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |