|
Baptism With The Holy Spirit
In Christian theology, baptism with the Holy Spirit, also called baptism in the Holy Spirit or baptism in the Holy Ghost, has been interpreted by different Christian denominations and traditions in a variety of ways due to differences in the doctrines of salvation and ecclesiology. It is frequently associated with incorporation into the Christian Church, the bestowal of spiritual gifts, and empowerment for Christian ministry. Spirit baptism has been variously defined as part of the sacraments of initiation into the church, as being synonymous with regeneration, or as being synonymous with Christian perfection. The term ''baptism with the Holy Spirit'' originates in the New Testament, and all Christian traditions accept it as a theological concept. Prior to the 18th century, most denominations believed that Christians received the baptism with the Holy Spirit either upon conversion and regeneration or through rites of Christian initiation, such as water baptism and confirmation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Confirmation
In Christian denominations that practice infant baptism, confirmation is seen as the sealing of the covenant (religion), covenant created in baptism. Those being confirmed are known as confirmands. The ceremony typically involves laying on of hands. Catholicism views Baptism as a sacrament. The sacrament is called chrismation in Eastern Christianity. In the East it takes place immediately after baptism; in the Western Christianity, West, when a child reaches the Age of reason (canon law), age of reason or early adolescence, or in the case of adult baptism immediately afterwards in the same ceremony. Among those Christians who practise confirmation during their teenage years, the practice may be perceived, secondarily, as a coming of age Rite of passage, rite. In many Protestantism, Protestant denominations, such as the Lutheran, Reformed tradition, Reformed, Anglican and Methodist traditions, confirmation is a Rite (Christianity), rite that often includes a profession of fai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Christian Theology
Christian theology is the theology – the systematic study of the divine and religion – of Christianity, Christian belief and practice. It concentrates primarily upon the texts of the Old Testament and of the New Testament, as well as on Christian tradition. Christian theologians use biblical exegesis, rationality, rational analysis and argument. Theologians may undertake the study of Christian theology for a variety of reasons, such as in order to: * help them better understand Christian tenets * make comparative religion, comparisons between Christianity and other traditions * Christian apologetics, defend Christianity against objections and criticism * facilitate reforms in the Christian church * assist in the evangelism, propagation of Christianity * draw on the resources of the Christian tradition to address some present situation or perceived need * education in Christian philosophy, especially in Neoplatonism, Neoplatonic philosophyLouth, Andrew. The Origins of the Ch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Second Work Of Grace
According to certain Christian traditions, a second work of grace (also second blessing) is a transforming interaction with God that may occur in the life of an individual Christian. The defining characteristics of the second work of grace are that it is separate from and subsequent to the New Birth (the first work of grace), and that it brings about significant changes in the life of the believer. In the Methodist, the Quaker and the Holiness Pentecostal traditions of Christianity, the second work of grace is traditionally taught to be Christian perfection (entire sanctification). Methodism (inclusive of the holiness movement) John Wesley, the founder of the Methodist movement, taught that there were two distinct phases in the Christian experience. In the first work of grace, the new birth, the believer receives forgiveness and becomes a Christian. During the second work of grace, entire sanctification, the believer is purified and made holy. Wesley taught that entire sa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of Ancient Israel And Judah
The history of ancient Israel and Judah spans from the early appearance of the Israelites in Canaan's hill country during the late second millennium BCE, to the establishment and subsequent downfall of the two Israelite kingdoms in the mid-first millennium BCE. This history unfolds within the Southern Levant during the Iron Age. The earliest documented mention of "Israel" as a people appears on the Merneptah Stele, an ancient Egyptian inscription dating back to around 1208 BCE. Archaeological evidence suggests that ancient Israelite culture evolved from the pre-existing Canaanite civilization. During the Iron Age II period, two Israelite kingdoms emerged, covering much of Canaan: the Kingdom of Israel in the north and the Kingdom of Judah in the south. According to the Hebrew Bible, a " United Monarchy" consisting of Israel and Judah existed as early as the 11th century BCE, under the reigns of Saul, David, and Solomon; the great kingdom later was separated into tw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Messianic Age
In Abrahamic religions, the Messianic Age () is the future eternal period of time on Earth in which the messiah will reign and bring universal peace and brotherhood, without any evil (through mankind's own terms). Many believe that there will be such an age; some refer to it as the consummate "kingdom of God" or the "world to come". Judaism, Jews believe that such a figure is yet to come, while Christianity, Christians believe that this figure is Second Coming, Jesus Christ. Judaism According to Jewish tradition, the Messianic Era will be one of global peace and harmony; an era free of strife and hardship, conducive to the furtherment of the knowledge of the Creator. The theme of the Messiah in Judaism, Messiah ushering in an era of global peace is encapsulated in two of the most famous scriptural passages from the Book of Isaiah: In his Mishneh Torah, Maimonides describes the Messianic Era: According to the Talmud, the Midrash,Pirke De Rabbi Eliezer, Gerald Friedlander, Sep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rabbinic Literature
Rabbinic literature, in its broadest sense, is the entire corpus of works authored by rabbis throughout Jewish history. The term typically refers to literature from the Talmudic era (70–640 CE), as opposed to medieval and modern rabbinic writings. It aligns with the Hebrew term ''Sifrut Chazal'' (), which translates to “literature f oursages” and generally pertains only to the sages (''Chazal'') from the Talmudic period. This more specific sense of "Rabbinic literature"—referring to the Talmud, Midrashim (), and related writings, but hardly ever to later texts—is how the term is generally intended when used in contemporary academic writing. The terms ''mefareshim'' and ''parshanim'' (commentaries and commentators) almost always refer to later, post-Talmudic writers of rabbinic glosses on Biblical and Talmudic texts. Mishnaic literature The Midr'she halakha, Mishnah, and Tosefta (compiled from materials pre-dating the year 200 CE) are the earliest extan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prophets In Judaism
According to the Talmud, there were 48 prophets and 7 prophetesses of Judaism ( ''Nəvīʾīm'', Tiberian: ''Năḇīʾīm,'' "Prophets", literally "spokespersons"). The last Jewish prophet is believed to have been Malachi. In Jewish tradition it is believed that the period of prophecy, called '' Nevuah'', ended with Haggai, Zechariah and Malachi (mid-5th century BCE) at which time the " Shechinah departed from Israel". Rabbinic tradition According to the Talmud, there were 48 prophets and 7 prophetesses who prophesied to Israel. The 46 prophets to Israel (46 according to Rashi, commentary on Tractate Megillah 14a) * Abraham * Isaac * Jacob * Moses * Aaron * Joshua * Phinehas * Eli * Elkanah * Samuel * Gad * Natan * David * Ahijah the Shilonite * Solomon * Iddo * Obadiah * Jehu * Azariah * Jahaziel * Eliezer * Elijah * Elisha * Micaiah * Jonah * Amos * Hosea * Amoz * Isaiah * Micah * Joel * Zephaniah * Nahum * Habakkuk * Urijah * Jeremiah * E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
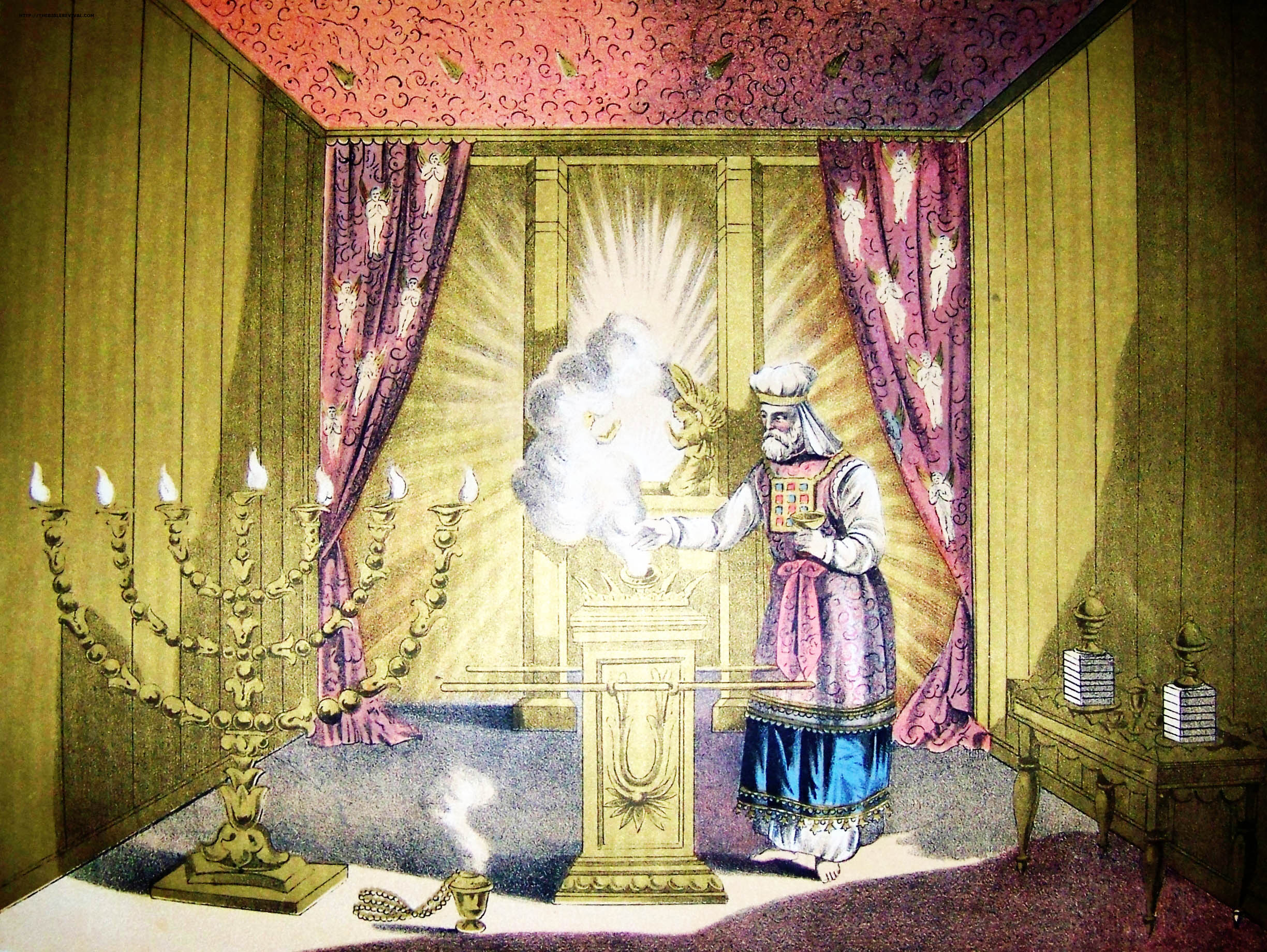
High Priest (Judaism)
In Judaism, the High Priest of Israel (, lit. ‘great priest’; Aramaic: ''Kahana Rabba'') was the head of the Israelite priesthood. He played a unique role in the worship conducted in the Tabernacle and later in the Temple in Jerusalem, as well as in some non-ritual matters. Like all priests, he was required to be descended from Aaron (the first biblical priest). But unlike other priests, the high priest followed more restrictive laws, wore unique priestly garments, and was the only priest allowed to perform certain ceremonies. Titles The high priest is referred to by a number of titles in the Hebrew Bible; the title ''kohen gadol'' did not become dominant until well into the Second Temple period. In addition to the title of "great priest" (''kohen gadol'') which later became the standard Hebrew title, the term "head priest" (''kohen harosh''; ) was used, as was "anointed priest" (''kohen mashiach''; )., , The Torah sometimes uses longer descriptions: "the great priest ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pentecost
Pentecost (also called Whit Sunday, Whitsunday or Whitsun) is a Christianity, Christian holiday which takes place on the 49th day (50th day when inclusive counting is used) after Easter Day, Easter. It commemorates the descent of the Holy Spirit in Christianity, Holy Spirit upon the Apostles in the New Testament, Apostles of Jesus, Mary, mother of Jesus, Mary, and other followers of the Christ, while they were in Jerusalem during the Second Temple Period, Jerusalem celebrating the Feast of Weeks, as described in the Acts of the Apostles (Acts 2:1–31). Pentecost marks the "Birthday of the Church". Pentecost is one of the Great feasts in the Eastern Orthodox Church, a Solemnity in the Roman Rite of the Catholic Church, a Liturgical calendar (Lutheran)#Festivals, Festival in the Lutheranism, Lutheran Churches, and a Principal Feast in the Anglican Communion. Many Christian denominations provide a special liturgy for this holy celebration. Since its date depends on the date of Eas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Covenant
The New Covenant () is a biblical interpretation which was originally derived from a Book of Jeremiah#Sections of the Book, phrase which is contained in the Book of Jeremiah (Jeremiah 31:31–34), in the Hebrew Bible (or the Old Testament of the Christian Bible). Generally, Christian theology, Christians believe that the promised New Covenant—new relationship with God in Christianity, God—was instituted at the Last Supper as part of the Eucharist, which, in the Gospel of John, includes the New Commandment. Based on the biblical passage which reads that, "For where a testament is, there must also of necessity be the death of the testator. For a testament is of force after men are dead: otherwise it is of no strength at all while the testator liveth", Protestants tend to believe that the New Covenant only came into force with the death of Jesus Christ (title), Christ. The commentary to the Roman Catholic New American Bible also affirms that Christ is the "testator whose death ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Old Covenant
Abrahamic religions believe in the Mosaic covenant (named after Moses), also known as the Sinaitic covenant (after the biblical Mount Sinai), which refers to a covenant between the Israelite tribes and God, including their proselytes, not limited to the ten commandments, nor the event when they were given, but including the entirety of laws that their patriarch Moses delivered from God in the five books of Torah. According to the biblical narrative, the Book of the Covenant, recording all the commands of the , was written by Moses in the desert and read to the people, and to seal the covenant, the blood of sacrificial oxen was then sprinkled, half on an altar and half on the people. Historical-critical scholarship The concept of a covenant began long before the biblical era, specifically the beginnings of Israel. According to George E. Mendenhall, covenants were originally established as legal customs and then later were replicated in the field of religion. These covenan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Third Work Of Grace
The third work of grace, also called the third blessing, is a doctrine, chiefly associated with Holiness Pentecostalism, that refers to baptism with the Holy Spirit with speaking in tongues as evidence for the same. The baptism of the Holy Ghost is taught by Holiness Pentecostals to empower the Christian believer for service to God. History Methodism, in accordance with the teachings of John Wesley, teaches two works of grace, the New Birth (first work of grace) and entire sanctification (second work of grace). The systematic theologian of Methodism, John William Fletcher, termed the reception of entire sanctification as Baptism with the Holy Spirit, which is reflected in the doctrine of various Methodist denominations, including those of the holiness movement. The fathers of Holiness Pentecostalism, Charles Parham (who established Bethel Bible College) and William Seymour (who organized the Azusa Street Revival) taught that in addition to the first work of the New ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |