|
Butt Plug
A butt plug is a sex toy that is designed to be inserted into the rectum for sexual pleasure. They often have a flanged end to prevent the device from being lost inside the rectum. History Rectal dilators were originally designed for therapeutic uses and later marketed with terms such as Dr. Young's Ideal Rectal Dilators, which were marketed as a cure for insanity and constipation. In the late 20th century, similar devices started to be marketed as sex toys. Basics Unlike the vagina, which is closed off by the cervix, the rectum leads to the sigmoid colon. Objects that are inserted into the rectum can therefore potentially travel up into the bowel; the flared end on a butt plug exists to prevent this. Some dildos lack a flared end, and thus it is not advised to use such dildos anally since they may get stuck; rectal foreign bodies may require medical extraction. In addition, the lower bowel above the rectum is easily perforated. For this reason, butt plugs tend to be shorte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Three Buttplugs
3 (three) is a number, numeral and digit. It is the natural number following 2 and preceding 4, and is the smallest odd prime number and the only prime preceding a square number. It has religious and cultural significance in many societies. Evolution of the Arabic digit The use of three lines to denote the number 3 occurred in many writing systems, including some (like Roman and Chinese numerals) that are still in use. That was also the original representation of 3 in the Brahmic (Indian) numerical notation, its earliest forms aligned vertically. However, during the Gupta Empire the sign was modified by the addition of a curve on each line. The Nāgarī script rotated the lines clockwise, so they appeared horizontally, and ended each line with a short downward stroke on the right. In cursive script, the three strokes were eventually connected to form a glyph resembling a with an additional stroke at the bottom: ३. The Indian digits spread to the Caliphate in the 9th c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
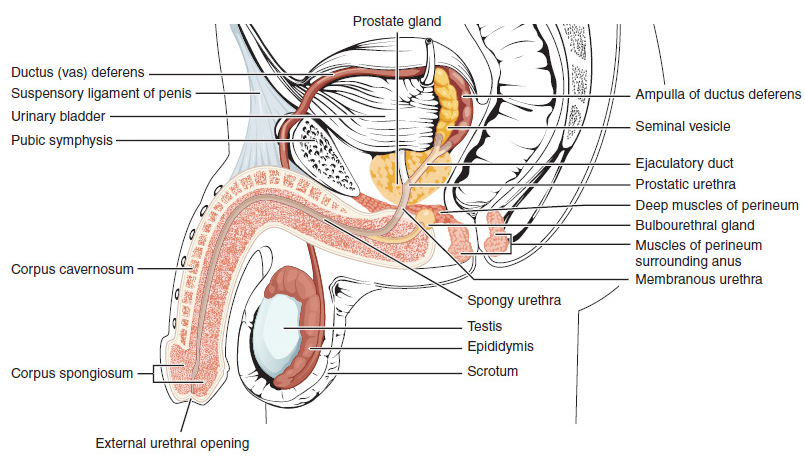
Prostate Massage
Prostate massage is the massage or stimulation of the male prostate gland for medicine, medical purposes or sexual stimulation. The prostate takes part in the Human sexual response cycle, sexual response cycle and is essential for the production of semen. Due to its proximity to the anterior rectal wall, it can be stimulated from the anterior wall of the rectum or externally via the perineum. Medical uses Digital rectal examination Prostate massage is part of the digital rectal examination (DRE) routinely given to men by urologists to look for nodules of prostate cancer and to obtain an expressed prostatic secretion (EPS) specimen for microscopy and microbiological culture to screen for prostatitis. Therapy for prostatitis In the late 1990s, a small number of doctors tried prostate massage in conjunction with antibiotics for the treatment of Prostatitis#Category II: Chronic bacterial prostatitis, chronic bacterial prostatitis with uncertain results. In recent trials, however, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glass
Glass is an amorphous (non-crystalline solid, non-crystalline) solid. Because it is often transparency and translucency, transparent and chemically inert, glass has found widespread practical, technological, and decorative use in window panes, tableware, and optics. Some common objects made of glass are named after the material, e.g., a Tumbler (glass), "glass" for drinking, "glasses" for vision correction, and a "magnifying glass". Glass is most often formed by rapid cooling (quenching) of the Melting, molten form. Some glasses such as volcanic glass are naturally occurring, and obsidian has been used to make arrowheads and knives since the Stone Age. Archaeological evidence suggests glassmaking dates back to at least 3600 BC in Mesopotamia, Ancient Egypt, Egypt, or Syria. The earliest known glass objects were beads, perhaps created accidentally during metalworking or the production of faience, which is a form of pottery using lead glazes. Due to its ease of formability int ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metal
A metal () is a material that, when polished or fractured, shows a lustrous appearance, and conducts electrical resistivity and conductivity, electricity and thermal conductivity, heat relatively well. These properties are all associated with having electrons available at the Fermi level, as against nonmetallic materials which do not. Metals are typically ductile (can be drawn into a wire) and malleable (can be shaped via hammering or pressing). A metal may be a chemical element such as iron; an alloy such as stainless steel; or a molecular compound such as polythiazyl, polymeric sulfur nitride. The general science of metals is called metallurgy, a subtopic of materials science; aspects of the electronic and thermal properties are also within the scope of condensed matter physics and solid-state chemistry, it is a multidisciplinary topic. In colloquial use materials such as steel alloys are referred to as metals, while others such as polymers, wood or ceramics are nonmetallic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wood
Wood is a structural tissue/material found as xylem in the stems and roots of trees and other woody plants. It is an organic materiala natural composite of cellulosic fibers that are strong in tension and embedded in a matrix of lignin that resists compression. Wood is sometimes defined as only the secondary xylem in the stems of trees, or more broadly to include the same type of tissue elsewhere, such as in the roots of trees or shrubs. In a living tree, it performs a mechanical-support function, enabling woody plants to grow large or to stand up by themselves. It also conveys water and nutrients among the leaves, other growing tissues, and the roots. Wood may also refer to other plant materials with comparable properties, and to material engineered from wood, woodchips, or fibers. Wood has been used for thousands of years for fuel, as a construction material, for making tools and weapons, furniture and paper. More recently it emerged as a feedstock for the production ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neoprene
Neoprene (also polychloroprene) is a family of synthetic rubbers that are produced by polymerization of chloroprene.Werner Obrecht, Jean-Pierre Lambert, Michael Happ, Christiane Oppenheimer-Stix, John Dunn and Ralf Krüger "Rubber, 4. Emulsion Rubbers" in Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry, 2012, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim. Neoprene exhibits good chemical stability and maintains flexibility over a wide temperature range. Neoprene is sold either as solid rubber or in latex form and is used in a wide variety of commercial applications, such as laptop sleeves, orthopaedic braces (wrist, knee, etc.), electrical insulation, medical gloves, liquid and sheet-applied elastomeric membranes or flashings, and Motor vehicle, automotive fan belt (mechanical), belts. Production Neoprene is produced by free-radical polymerization of chloroprene. In commercial production, this polymer is prepared by Emulsion_polymerization, free radical emulsion polymerization. Polymerization is initiated us ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Silicone
In Organosilicon chemistry, organosilicon and polymer chemistry, a silicone or polysiloxane is a polymer composed of repeating units of siloxane (, where R = Organyl group, organic group). They are typically colorless oils or elastomer, rubber-like substances. Silicones are used in sealants, adhesives, lubricants, medicine, cooking utensils, thermal insulation, and electrical insulation. Some common forms include silicone oil, silicone grease, grease, silicone rubber, rubber, silicone resin, resin, and Caulking, caulk. Silicone is often confused with one of its constituent elements, silicon, but they are distinct substances. Silicon is a chemical element, a hard dark-grey semiconductor, semiconducting metalloid, which in its crystalline form is used to make integrated circuits ("electronic chips") and solar cells. Silicones are compounds that contain silicon, carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, and perhaps other kinds of atoms as well, and have many very different physical and chemical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Latex
Latex is an emulsion (stable dispersion) of polymer microparticles in water. Latices are found in nature, but synthetic latices are common as well. In nature, latex is found as a wikt:milky, milky fluid, which is present in 10% of all flowering plants (angiosperms) and in some Mushroom, mushrooms (especially species of ''Lactarius''). It is a complex emulsion that coagulation, coagulates on exposure to air, consisting of proteins, alkaloids, starches, sugars, Vegetable oil, oils, tannins, resins, and Natural gum, gums. It is usually exuded after tissue injury. In most plants, latex is white, but some have yellow, orange, or scarlet latex. Since the 17th century, latex has been used as a term for the fluid substance in plants, deriving from the Latin word for "liquid". It serves mainly as Antipredator adaptation, defense against Herbivore, herbivores and Fungivore, fungivores.Taskirawati, I. and Tuno, N., 2016Fungal defense against mycophagy in milk caps ''Science Report Kanazaw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Human Penis
In Human body, human anatomy, the penis (; : penises or penes; from the Latin ''pēnis'', initially 'tail') is an external sex organ (intromittent organ) through which males urination, urinate and ejaculation, ejaculate, as Penis, on other animals. Together with the testes and surrounding structures, the penis functions as part of the male reproductive system. The main parts of the penis are the Root of penis, root, Body of penis, body, the epithelium of the penis, including the shaft skin, and the foreskin covering the glans penis, glans. The body of the penis is made up of three columns of tissue (biology), tissue: two Corpus cavernosum penis, corpora cavernosa on the dorsal side and corpus spongiosum penis, corpus spongiosum between them on the ventral side. The Urethra#Male, urethra passes through the prostate gland, where it is joined by the ejaculatory ducts, and then through the penis. The urethra goes across the corpus spongiosum and ends at the tip of the glans as the o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sexually Transmitted Infection
A sexually transmitted infection (STI), also referred to as a sexually transmitted disease (STD) and the older term venereal disease (VD), is an infection that is Transmission (medicine), spread by Human sexual activity, sexual activity, especially Sexual intercourse, vaginal intercourse, anal sex, oral sex, or sometimes Non-penetrative sex#Manual sex, manual sex. STIs often do not initially cause symptoms, which results in a risk of transmitting them to others. The term ''sexually transmitted infection'' is generally preferred over ''sexually transmitted disease'' or ''venereal disease'', as it includes cases with no Signs and symptoms#Symptomatic, symptomatic disease. Symptoms and signs of STIs may include vaginal discharge, penile discharge, genital ulcers, ulcers on or around the genitals, and pelvic pain. Some STIs can cause infertility. Bacterial STIs include Chlamydia infection, chlamydia, gonorrhea, and syphilis. Viral STIs include genital warts, genital herpes, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hachette Books
Hachette Books, formerly Hyperion Books, is a general-interest book imprint of the Perseus Books Group, which is a division of Hachette (publisher), Hachette Book Group and ultimately a part of Lagardère Group. Established in 1990, Hachette publishes general-interest fiction and non-fiction books for adults. A former subsidiary of The Walt Disney Company, it was originally named after Hyperion Avenue, the location of Walt Disney Studios (Burbank), Walt Disney Studios prior to 1939. Hachette took over a 1,000 book backlist when Hyperion was purchased from Disney in 2013 with 250 bestseller, bestselling novels, including Mitch Albom’s ''The Five People You Meet in Heaven''. History Hyperion Books Hyperion Books was founded in 1990 from scratch with no backlist under Disney's then-C.E.O. Michael Eisner and Robert S. Miller.Getlin, JoshHyperion founder exits April 04, 2008. Los Angeles Times. Accessed July 3, 2013. Hyperion's strategy was to not purchase backlists, but to go aft ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Human Feces
Human feces (American English) or faeces (British English), commonly and in medical literature more often called stool, are the solid or semisolid remains of food that could not be digested or absorbed in the small intestine of humans, but has been further broken down by bacteria in the large intestine. It also contains bacteria and a relatively small amount of metabolic waste products such as bacterially altered bilirubin, and the dead epithelial cells from the lining of the gut. It is discharged through the anus during a process called defecation. Human feces has similarities to the feces of other animals and varies significantly in appearance (i.e. size, color, texture), according to the state of the diet, digestive system, and general health. Normally, human feces are semisolid, with a mucus coating. Small pieces of harder, less moist feces can sometimes be seen impacted in the distal (final or lower) end. This is a normal occurrence when a prior bowel movement is incomp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |