|
Bulverket
The Bulverket is the remnants of a large wooden fortification or Glossary of architecture#B, bulwark at Lake Tingstäde on the island of Gotland, Sweden. When built, it consisted of a platform with houses surrounded by a double palisade with the entire construction around in diameter. According to a 1989 archeological survey, the structure was built in the 1130s and may have been used for less than a century. Although its original purpose is unknown, theories suggest it was either used as a shelter during the turbulent times on Gotland at the end of the Viking Age or that it was the site of a last stand. Among the archeological finds at the Bulverket are the remains of three boats. One of these served as a model for the reconstruction of a Viking boat, the ''Krampmacken'', in 1980. ''Krampmacken'' has subsequently made several journeys following old Viking waterways through Eastern Europe. Etymology The name Bulverket originates from the old Swedish words ''bul'', meaning "l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bulverket Pålar Från Palissaden 1923
The Bulverket is the remnants of a large wooden fortification or bulwark at Lake Tingstäde on the island of Gotland, Sweden. When built, it consisted of a platform with houses surrounded by a double palisade with the entire construction around in diameter. According to a 1989 archeological survey, the structure was built in the 1130s and may have been used for less than a century. Although its original purpose is unknown, theories suggest it was either used as a shelter during the turbulent times on Gotland at the end of the Viking Age or that it was the site of a last stand. Among the archeological finds at the Bulverket are the remains of three boats. One of these served as a model for the reconstruction of a Viking boat, the ''Krampmacken'', in 1980. ''Krampmacken'' has subsequently made several journeys following old Viking waterways through Eastern Europe. Etymology The name Bulverket originates from the old Swedish words ''bul'', meaning "log", and ''verk'' which refe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tingstäde
Tingstäde is a populated area, a socken (not to be confused with parish), on the Swedish island of Gotland. It comprises the same area as the administrative Tingstäde District, established on 1January 2016. Tingstäde is most noted for its nearby lake Lake Tingstäde, which contains the sunken Bulverket fortification, built, used and abandoned during the 12th century. Geography Tingstäde is the name of the socken as well as the district. It is also the name of the larger locality within the district and the small village surrounding the medieval Tingstäde Church, sometimes referred to as ''Tingstäde kyrkby''. Tingstäde is located in the central north part of Gotland. , Tingstäde Church belongs to Stenkyrka parish in Norra Gotlands pastorat, along with the churches in Stenkyrka, Martebo, and Lummelunda. One of the asteroids in the asteroid belt, 8679 Tingstäde, is named after this place. References External links *Objects from Tingstäde at the Digital Museumb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lake Tingstäde
Lake Tingstäde is a lake next to Tingstäde in the central northern part of Gotland, Sweden. It is the second biggest lake on Gotland, after Lake Bästeträsk. The surface of the lake is above sea level. The lake was used as a landing site for seaplanes during the interwar period, such as the first regular passenger planes between Gotland and mainland Sweden 1933–39, and a stopover on the Stockholm/Lindarängen - Danzig line, serviced by the AB Aerotransport in 1925–26. History During the 1120s, a square timber platform was built in the middle of the lake. On the platform was a number of closely built wooden houses. The remnants of this construction, known as the Bulverket, are still present on the bottom of the lake. It is still not known why the bulwark was built. The name ''Tingstäde'' is probably related to the thing that was located north of the Tingstäde Church close by the lake. The word ''träsk'' is an old Gutnish word for 'lake'. Biology Lake Ting ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Slavs
Slavs are the largest European ethnolinguistic group. They speak the various Slavic languages, belonging to the larger Balto-Slavic language, Balto-Slavic branch of the Indo-European languages. Slavs are geographically distributed throughout northern Eurasia, mainly inhabiting Central Europe, Central and Eastern Europe, and the Balkans to the west; and Siberia to the east. A large Slavic minority is also scattered across the Baltic states and Central Asia, while a substantial Slavic diaspora is found throughout the Americas, as a result of immigration. Present-day Slavs are classified into East Slavs (chiefly Belarusians, Russians, Rusyns, and Ukrainians), West Slavs (chiefly Czechs, Kashubians, Poles, Slovaks and Sorbs) and South Slavs (chiefly Bosniaks, Bulgarians, Croats, Macedonians (ethnic group), Macedonians, Montenegrins, Serbs and Slovenes). The vast majority of Slavs are traditionally Christians. However, modern Slavic nations and ethnic groups are considerably dive ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deep Foundation
A deep foundation is a type of foundation that transfers building loads to the earth farther down from the surface than a shallow foundation does to a subsurface layer or a range of depths. A pile or piling is a vertical structural element of a deep foundation, driven or drilled deep into the ground at the building site. There are many reasons that a geotechnical engineer would recommend a deep foundation over a shallow foundation, such as for a skyscraper. Some of the common reasons are very large design loads, a poor soil at shallow depth, or site constraints like property lines. There are different terms used to describe different types of deep foundations including the pile (which is analogous to a pole), the pier (which is analogous to a column), drilled shafts, and caissons. Piles are generally driven into the ground in situ; other deep foundations are typically put in place using excavation and drilling. The naming conventions may vary between engineering dis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Post-and-plank
The method of building wooden buildings with a traditional timber frame with horizontal plank or log infill has many names, the most common of which are piece sur piece (French. Also used to describe log building), corner post construction, post-and-plank, Ständerbohlenbau (German) and skiftesverk (Swedish). This traditional building method is believed to be the predecessor to half-timber construction widely known by its German name ''fachwerkbau'' which has wall infill of wattle and daub, brick, or stone. This carpentry was used from parts of Scandinavia to Switzerland to western Russia. Though relatively rare now, two types are found in a number of regions in North America, more common are the walls with planks or timbers which slide in a groove in the posts and less common is a type where horizontal logs are tenoned into individual mortises in the posts. This method is not the same as the plank-frame buildings in North America with vertical plank walls. Other names * Fren ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Log House
A log house, or log building, is a structure built with horizontal logs interlocked at the corners by notching. Logs may be round, squared or hewn to other shapes, either handcrafted or milled. The term "log cabin" generally refers to a smaller, more rustic log house, such as a hunting cabin in the woods, that may or may not have electricity or plumbing. Log construction was the most common building technique in large regions of Sweden, Finland, Norway, the Baltic states and Russia, where straight and tall coniferous trees, such as pine and spruce, are readily available. It was also widely used for vernacular buildings in Eastern Central Europe, the Alps, the Balkans and parts of Asia, where similar climatic conditions prevail. In warmer and more westerly regions of Europe, where deciduous trees predominate, timber framing was favoured instead. *''Sawn logs'', logs sawn to a standard width, but with their original heights *''Milled'' (also called ''machine-profiled''), ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palisade Church
A palisade church is a church building that is constructed with palisade walls, standing split logs of timber, rammed into the ground, set in gravel or resting on a sill. The palisade walls form an integral part of the load-bearing system. Construction This type of construction is often believed to predate a construction method with posts set directly into the earth, sometimes called a post church, and the later stave construction method, or stave church. A palisade church often had its walls set fully or partly in gravel and therefore they can be detected in archaeological surveys. Sometimes a new church was built around an existing one, and remnants of the old church can be found under the floor. The palisade church construction itself consisted, in its simplest form, of posts set closely together into a trench in the earth, with the roof resting directly on top of the logs. Later the logs were split in two halves, with the flat side facing into the enclosed room. The edges coul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lennart Von Post
Ernst Jakob Lennart von Post (16June 188411January 1951) was a Swedish naturalist and geologist. He was the first to publish quantitative analysis of pollen and is counted as one of the founders of palynology. He was a professor at Stockholm University 1929–1950. Early life Lennart von Post was born in Johannesberg, near Västerås in Västmanland County, Sweden. He was the son of Carl-Fabian Axel von Post (1849-1927) and Beata Jacqueline Charlotta Christina (1852-1885). Von Post was an only child. His father served in the Swedish Army as a judge-advocate but also worked as a civilian lawyer, farmer and assistant cantonal judge. Education Von Post studied geology at Uppsala University from 1902 to 1907, eventually obtaining his ''licentiat'' degree. At Uppsala he learned from lecturers such as A.G. Högbom, who developed the concept of the geochemical carbon cycle and Rutger Sernander, of the Blytt-Sernander Pleistocene sequence. Von Post began working on a history of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
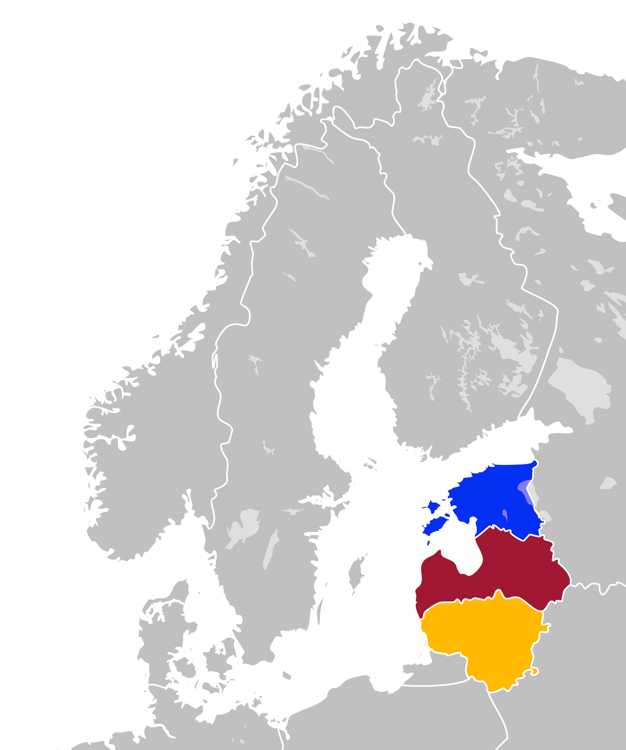
Baltic States
The Baltic states, et, Balti riigid or the Baltic countries is a geopolitical term, which currently is used to group three countries: Estonia, Latvia, and Lithuania. All three countries are members of NATO, the European Union, the Eurozone, and the OECD. The three sovereign states on the eastern coast of the Baltic Sea are sometimes referred to as the "Baltic nations", less often and in historical circumstances also as the "Baltic republics", the "Baltic lands", or simply the Baltics. All three Baltic countries are classified as high-income economies by the World Bank and maintain a very high Human Development Index. The three governments engage in intergovernmental and parliamentary cooperation. There is also frequent cooperation in foreign and security policy, defence, energy, and transportation. The term "Baltic states" ("countries", "nations", or similar) cannot be used unambiguously in the context of cultural areas, national identity, or language. While the majori ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Christianity
Christianity is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus of Nazareth Jesus, likely from he, יֵשׁוּעַ, translit=Yēšūaʿ, label=Hebrew/Aramaic ( AD 30 or 33), also referred to as Jesus Christ or Jesus of Nazareth (among other names and titles), was a first-century Jewish preacher and religious .... It is the Major religious groups, world's largest and most widespread religion with roughly 2.38 billion followers representing one-third of the global population. Its adherents, known as Christians, are estimated to make up a majority of the population in Christianity by country, 157 countries and territories, and believe that Jesus in Christianity, Jesus is the Son of God (Christianity), Son of God, whose coming as the Messiah#Christianity, messiah was Old Testament messianic prophecies quoted in the New Testament, prophesied in the Hebrew Bible (called the Old Testament in Christianity) and chronicled in the New Testamen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |