|
Builders' Rites
Builders' rites are ceremony, ceremonies attendant on the laying of foundation stones, including wikt:ecclesiastical, ecclesiastical, masonic or other traditions connected with foundation (architecture), foundations or other aspects of construction. One such custom is that of placing a few coins, newspapers, etc. within a cavity beneath the stone. Should the stone later be removed, the relics may be found. Though this tradition is still practiced, such memorials are likely deposited in the hope that they will never be disturbed. Another such rite is topping out, when the last beam (or its equivalent) is placed atop a structure during its construction. According to the above, the best succinct account of these rites was to be obtained in George Speth, G. W. Speth's ''Builders' Rites and Ceremonies'' (1893). History Historians and folklorists in the 19th and early 20th centuries were fascinated by possible "foundation sacrifices". Jacob Grimm remarked, "It was often thought necessa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Washington Laying Cornerstone
Washington most commonly refers to: * George Washington (1732–1799), the first president of the United States * Washington (state), a state in the Pacific Northwest of the United States * Washington, D.C., the capital of the United States ** A metonym for the federal government of the United States ** Washington metropolitan area, the metropolitan area centered on Washington, D.C. Washington may also refer to: Places England * Washington Old Hall, ancestral home of the family of George Washington * Washington, Tyne and Wear, a town in the City of Sunderland metropolitan borough * Washington, West Sussex, a village and civil parish Greenland * Cape Washington, Greenland * Washington Land Philippines *New Washington, Aklan, a municipality *Washington, a barangay in Catarman, Northern Samar *Washington, a barangay in Escalante, Negros Occidental *Washington, a barangay in San Jacinto, Masbate *Washington, a barangay in Surigao City United States * Fort Washington (disambiguati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
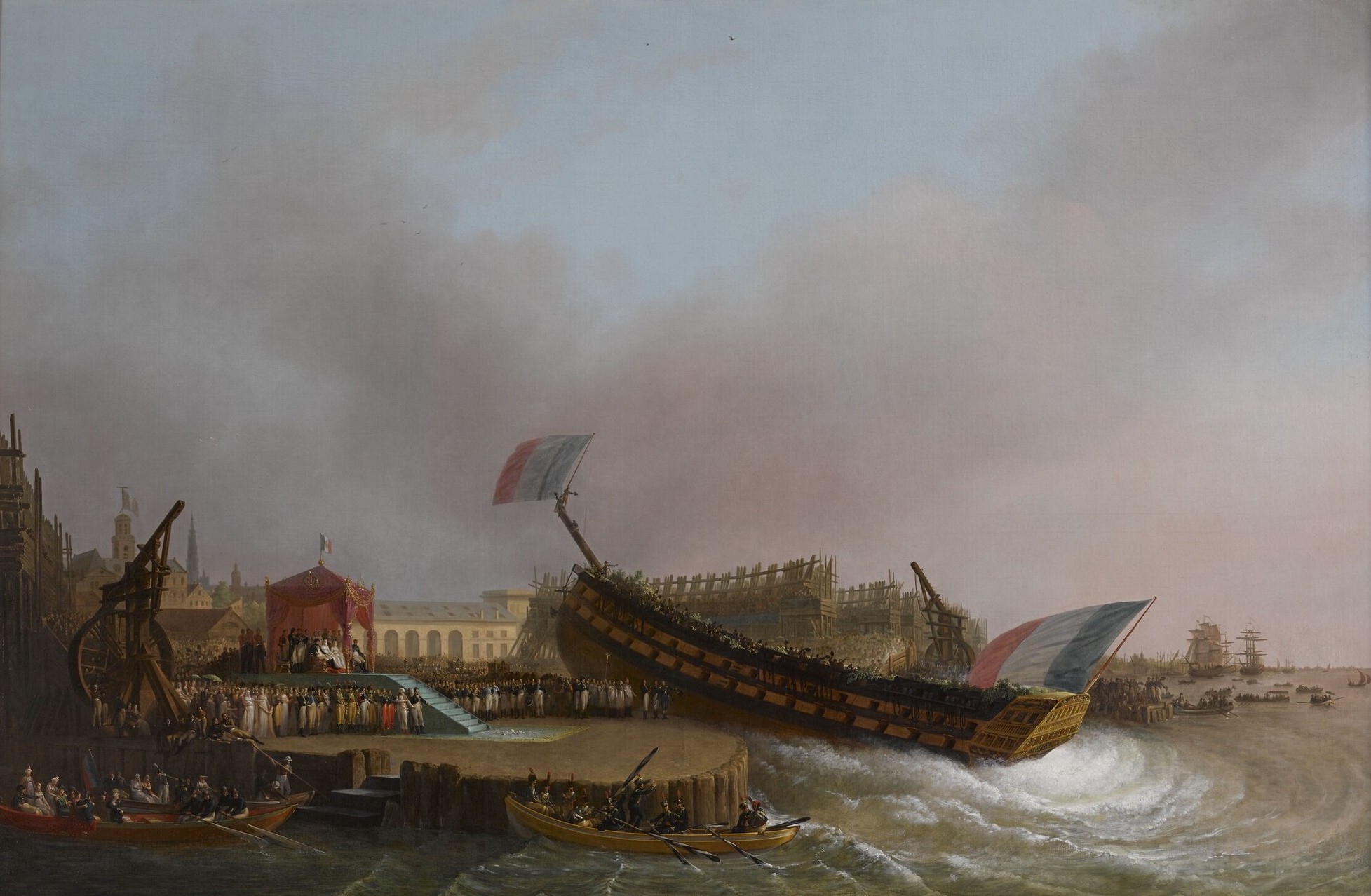
Ceremonial Ship Launching
Ceremonial ship launching involves the performing of ceremonies associated with the process of transferring a vessel to the water. It is a nautical tradition in many cultures, dating back millennia, to accompany the physical process with ceremonies which have been observed as public celebration and a solemn blessing, usually but not always, in association with the launch itself. Ship launching imposes stresses on the ship not met during normal operation and in addition to the size and weight of the vessel represents a considerable engineering challenge as well as a public spectacle. The process also involves Sailors' superstitions, many traditions intended to invite good luck, such as baptism#Boats and ships, christening by breaking a sacrificial bottle of champagne over the bow (ship), bow as the ship is named aloud and launched. Methods There are three principal methods of conveying a new ship from building site to water, only two of which are called "launching". The ol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Building Engineering
Architectural engineering or architecture engineering, also known as building engineering, is a Academic discipline, discipline that deals with the engineering and construction of buildings, such as environmental, structural, mechanical, electrical, computational, embeddable, and other research domains. It is related to Architecture, Mechatronics Engineering, Computer engineering, Computer Engineering, Aerospace engineering, Aerospace Engineering, and civil engineering, Civil Engineering, but distinguished from Interior design, Interior Design and architectural design, Architectural Design as an art and science of designing infrastructure through these various engineering disciplines, from which properly align with many related surrounding engineering advancements. From reduction of greenhouse gas emissions to the construction of resilient buildings, architectural engineers are at the forefront of addressing several major challenges of the 21st century. They apply the latest scie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ceremonies
A ceremony (, ) is a unified ritualistic event with a purpose, usually consisting of a number of artistic components, performed on a special occasion. The word may be of Etruscan origin, via the Latin . Religious and civil (secular) ceremonies According to Dally Messenger and Alain de Botton, in most Western countries the values and ideals articulated in both church and civil ceremonies are generally similar. The difference is in what Messenger calls the "supernatural infrastructure" or de Botton the "implausible supernatural element".Messenger, Dally; ''Murphy's Law and the Pursuit of Happiness: a History of the Civil Celebrant Movement'', Spectrum Publications, Melbourne (Australia), 2012 Most religions claim some extra advantage conferred by the deity, e.g., Roman Catholics believe that through the words of consecration in the mass ceremony, God himself becomes actually present on the altar. Both religious and civil ceremonies share the powerful psychological, social ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Building
A building or edifice is an enclosed Structure#Load-bearing, structure with a roof, walls and window, windows, usually standing permanently in one place, such as a house or factory. Buildings come in a variety of sizes, shapes, and functions, and have been adapted throughout history for numerous factors, from building materials available, to weather conditions, land prices, ground conditions, specific uses, monument, prestige, and aesthetic reasons. To better understand the concept, see ''Nonbuilding structure'' for contrast. Buildings serve several societal needs – occupancy, primarily as shelter from weather, security, living space, privacy, to store belongings, and to comfortably live and work. A building as a shelter represents a physical separation of the :Human habitats, human habitat (a place of comfort and safety) from the ''outside'' (a place that may be harsh and harmful at times). buildings have been objects or canvasses of much architecture, artistic expression. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
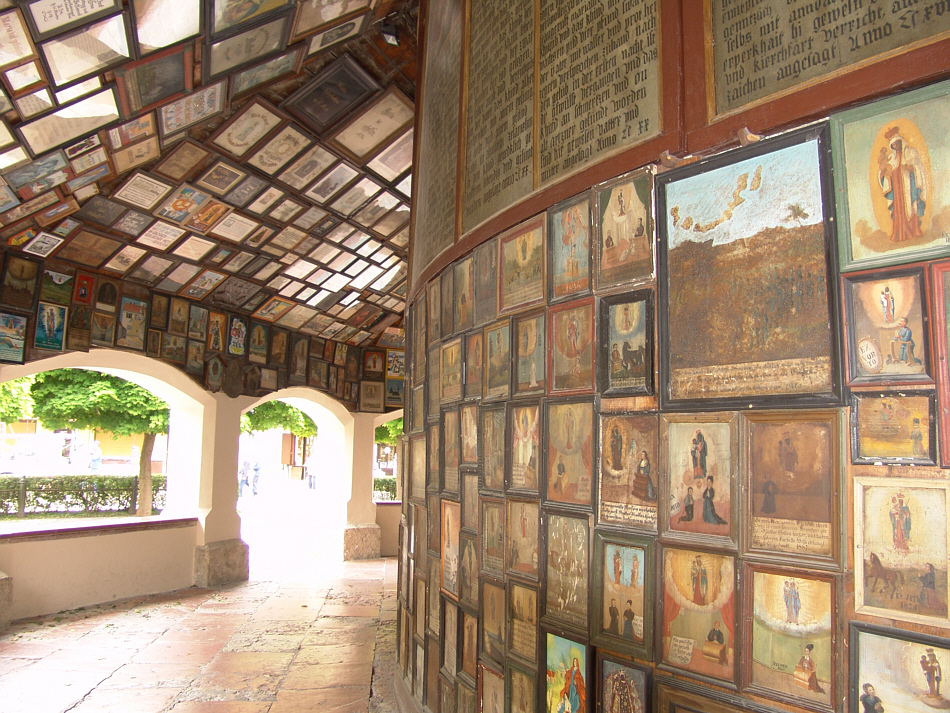
Votive Offering
A votive offering or votive deposit is one or more objects displayed or deposited, without the intention of recovery or use, in a sacred place for religious purposes. Such items are a feature of modern and ancient societies and are generally made to gain favor with supernatural forces. While some offerings were apparently made in anticipation of the achievement of a particular wish, in Western cultures from which documentary evidence survives it was more typical to wait until the wish had been fulfilled before making the offering, for which the more specific term ex-voto may be used. Other offerings were very likely regarded just as gifts to the deity, not linked to any particular need. In Buddhism, votive offering such as construction of stupas was a prevalent practice in Ancient India, an example of which can be observed in the ruins of the ancient Vikramshila University and other contemporary structures. Votive offerings have been described in historical Roman era and Gree ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Topping Out
In building construction, topping out (sometimes referred to as topping off) is a builders' rite traditionally held when the last beam (or its equivalent) is placed at the top of a structure during its construction. Nowadays, the ceremony is often parlayed into a media event for public relations purposes. It has since come to mean more generally finishing the structure of the building, whether there is a ceremony or not. It is also commonly used to determine the amount of wind on the top of the structure. A Scandinavian tradition of hoisting a pine tree to the top of framed out buildings had a more functional purpose: when the pine needles fell off, the builders knew the wood frame below had cured/dried out so they could enclose the building. History The practice of "topping out" a new building can be traced to the ancient Scandinavian religious rite of placing a tree atop a new building to appease the tree-dwelling spirits displaced in its construction. The tradition also ser ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Time Capsule
A time capsule is a historic treasure trove, cache of goods or information, usually intended as a deliberate method of communication with future people, and to help future archaeologists, anthropologists, or historians. The preservation of holy relics dates back for millennia, but the practice of preparing and preserving a collection of everyday artifacts and messages to the future appears to be a more recent practice. Time capsules are sometimes created and buried during celebrations such as world's fairs or cornerstone layings for building or at other ceremonies. History Early examples It is widely debated when time capsules were first used, but the concept is fairly simple, and the idea and first use of time capsules could be much older than is currently documented. The term "time capsule" appears to be a relatively recent coinage dating from 1938. In Poland a time capsule dating to 1726 has been found. Around 1761, some dated artifacts were placed inside the hollow copp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Masonic Manuscripts
There are a number of masonic manuscripts that are important in the study of the emergence of Freemasonry. Most numerous are the ''Old Charges'' or ''Constitutions''. These documents outlined a "history" of masonry, tracing its origins to a biblical or classical root, followed by the regulations of the organisation, and the responsibilities of its different grades. More rare are old hand-written copies of ritual, affording a limited understanding of early masonic rites. All of those that pre-date the formation of Grand Lodges are found in Scotland and Ireland, and show such similarity that the Irish rituals are usually assumed to be of Scottish origin. The earliest Minutes of lodges formed before the first Grand Lodge are also located in Scotland. Early records of the first Grand Lodge in 1717 allow an elementary understanding of the immediate pre-Grand Lodge era and some insight into the personalities and events that shaped early-18th-century Freemasonry in Britain. Other early d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
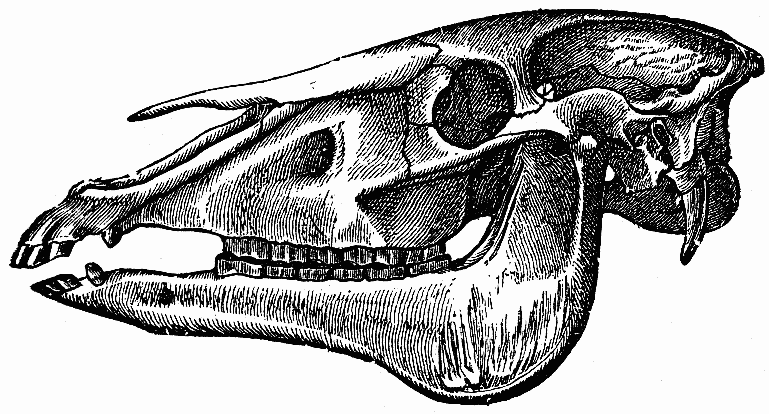
Horse Skulls
In Ireland, England, Wales, and the Scandinavian Peninsula, horse skulls have been found concealed in the structures of buildings, usually under the Foundation (engineering), foundation or floor. Horse skulls have also been found in buildings in the United States, although in far fewer numbers. As part of the larger folk religion, folk tradition of concealing objects in structures, horse skulls are related to concealed shoes, dried cats, and witch bottles. There are two main theories as to the reason for depositing the horse skulls in buildings: as a method for enhancing the acoustics of a room, such as in a church or in a threshing barn; or as a method for repelling evil spirits such as witchcraft, witches and ghosts. See also * Hobby horse * Mari Lwyd References * * * Master's thesis, Anthropology Program, Ball State University, Muncie, IN. * {{refend External links Horse Skulls at Bay Farm Cottage, Carnlough Jim Mallory and Finbar McCormick. Scandinavian cultu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hitobashira
, also known in Chinese as ''da sheng zhuang'' ( zh, t=打生樁, s=打生桩, p=dǎshēngzhuāng, c=, j=daa2saang1zong1), is a cultural practice of human sacrifice of premature burial before the construction of buildings. ''Hitobashira'' was practiced formerly in Japan as a form of human sacrifice. A person was buried alive under or near large-scale buildings like dams, bridges and castles, as a prayer to Shinto Kami, gods. It was believed this would Builders' rites, protect the building from being destroyed by natural disasters such as floods or by enemy attacks. ''Hitobashira'' can also refer to workers who were buried alive under inhumane conditions. ''Hitobashira'' Some of the earliest written records of ''hitobashira'' can be found in the ''Nihon Shoki (The Chronicles of Japan)''. One story centered on Emperor Nintoku (323 A.D.) discusses the overflowing of the Kitakawa and Mamuta Rivers. Protection against the torrent was beyond the ability of the stricken populace. The Emp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
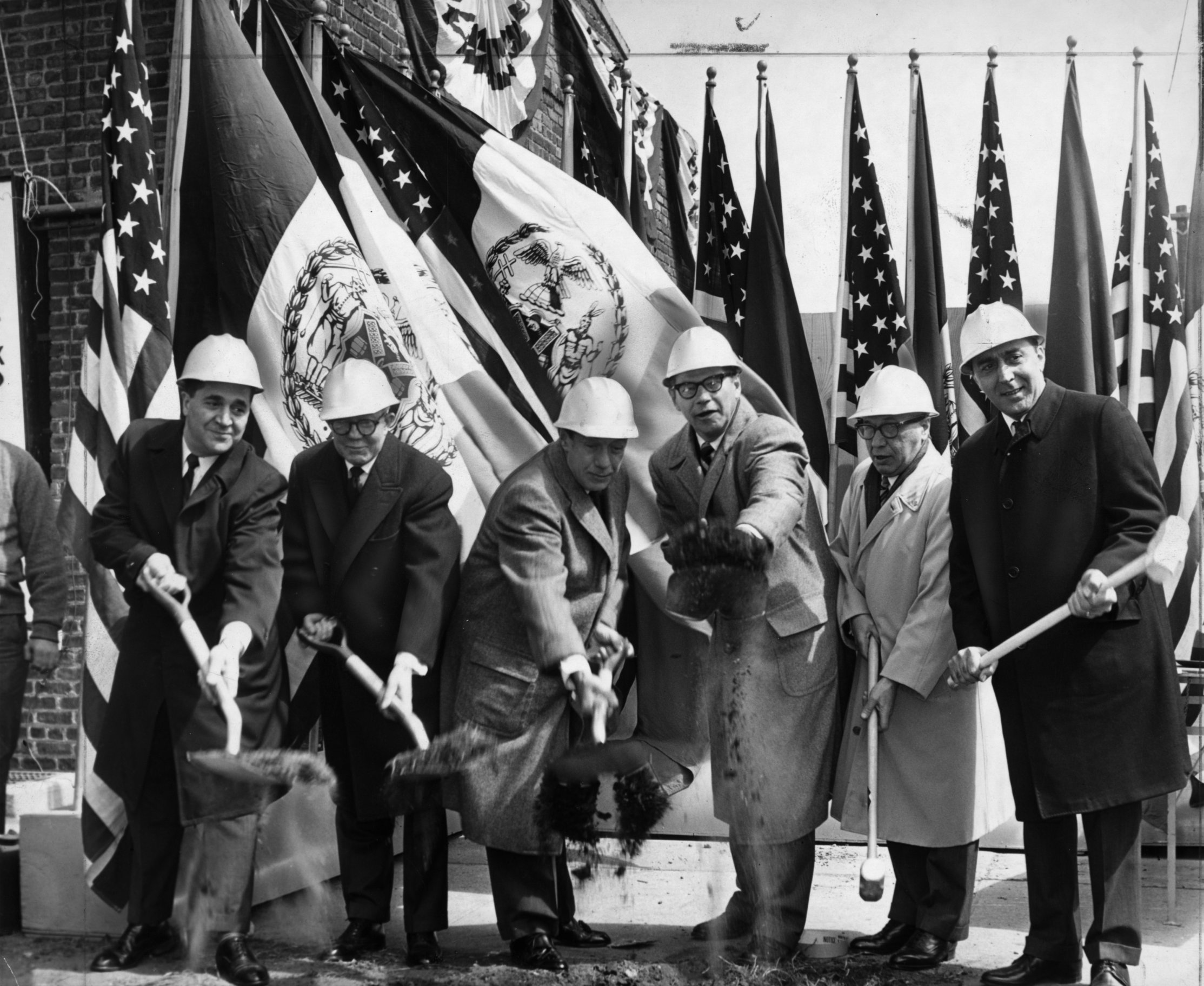
Groundbreaking
Groundbreaking, also known as cutting, sod-cutting, turning the first sod, turf-cutting, or a sod-turning ceremony, is a traditional ceremony in many cultures that celebrates the first day of construction for a building or other project. Such ceremonies are often attended by dignitaries such as politicians and businesspeople. The shovel used during the groundbreaking is often a special ceremonial shovel, sometimes colored gold, meant to be saved for subsequent display and may be engraved. In other groundbreaking ceremonies, a bulldozer is used instead of a shovel to mark the first day of construction. In some groundbreaking ceremonies, the shovel and the bulldozer mark the first day of construction. In other places, this ceremony can be replaced by a "laying of the first stone" event. Meaning When used as an adjective, the term ''groundbreaking'' may mean being or making something that has never been done, seen, or made before, "stylistically innovative works". History Groun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |