|
Buddleja Davidii
''Buddleja davidii'' (spelling variant ''Buddleia davidii''), also called summer lilac, butterfly-bush, or orange eye, is a species of flowering plant in the family (biology), family Scrophulariaceae, native plant, native to Sichuan and Hubei provinces in central China, and also Japan. It is widely used as an ornamental plant, and many named varieties are in cultivation. The genus was named ''Buddleja'' after Reverend Adam Buddle, an English botanist. The species name ''davidii'' honors the French missionary and explorer in China, Father Armand David, who was the first European to report the shrub. It was found near Yichang by Dr Augustine Henry about 1887 and sent to St Petersburg. Another botanist-missionary in China, Jean-André Soulié, sent seed to the French nursery Vilmorin, and ''B. davidii'' entered commerce in the 1890s. ''B. davidii'' was accorded the Royal Horticultural Society, RHS Award of Merit (AM) in 1898, and the Award of Garden Merit (AGM) in 1941.Hillier & So ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Franch
Franch is a surname. Notable persons with that surname include: * Adrianna Franch (born 1990), American football (soccer) player * Josep Franch (born 1991), Spanish basketball player * Pau Franch (born 1988), Spanish football (soccer) player See also * French (other) *France France, officially the French Republic, is a country located primarily in Western Europe. Overseas France, Its overseas regions and territories include French Guiana in South America, Saint Pierre and Miquelon in the Atlantic Ocean#North Atlan ... {{surname Catalan-language surnames ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tomentose
Trichomes (; ) are fine outgrowths or appendages on plants, algae, lichens, and certain protists. They are of diverse structure and function. Examples are hairs, glandular hairs, scales, and papillae. A covering of any kind of hair on a plant is an indumentum, and the surface bearing them is said to be pubescent. Algal trichomes Certain, usually filamentous, algae have the terminal cell produced into an elongate hair-like structure called a trichome. The same term is applied to such structures in some cyanobacteria, such as '' Spirulina'' and ''Oscillatoria''. The trichomes of cyanobacteria may be unsheathed, as in ''Oscillatoria'', or sheathed, as in '' Calothrix''. These structures play an important role in preventing soil erosion, particularly in cold desert climates. The filamentous sheaths form a persistent sticky network that helps maintain soil structure. Plant trichomes Plant trichomes have many different features that vary between both species of plants and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
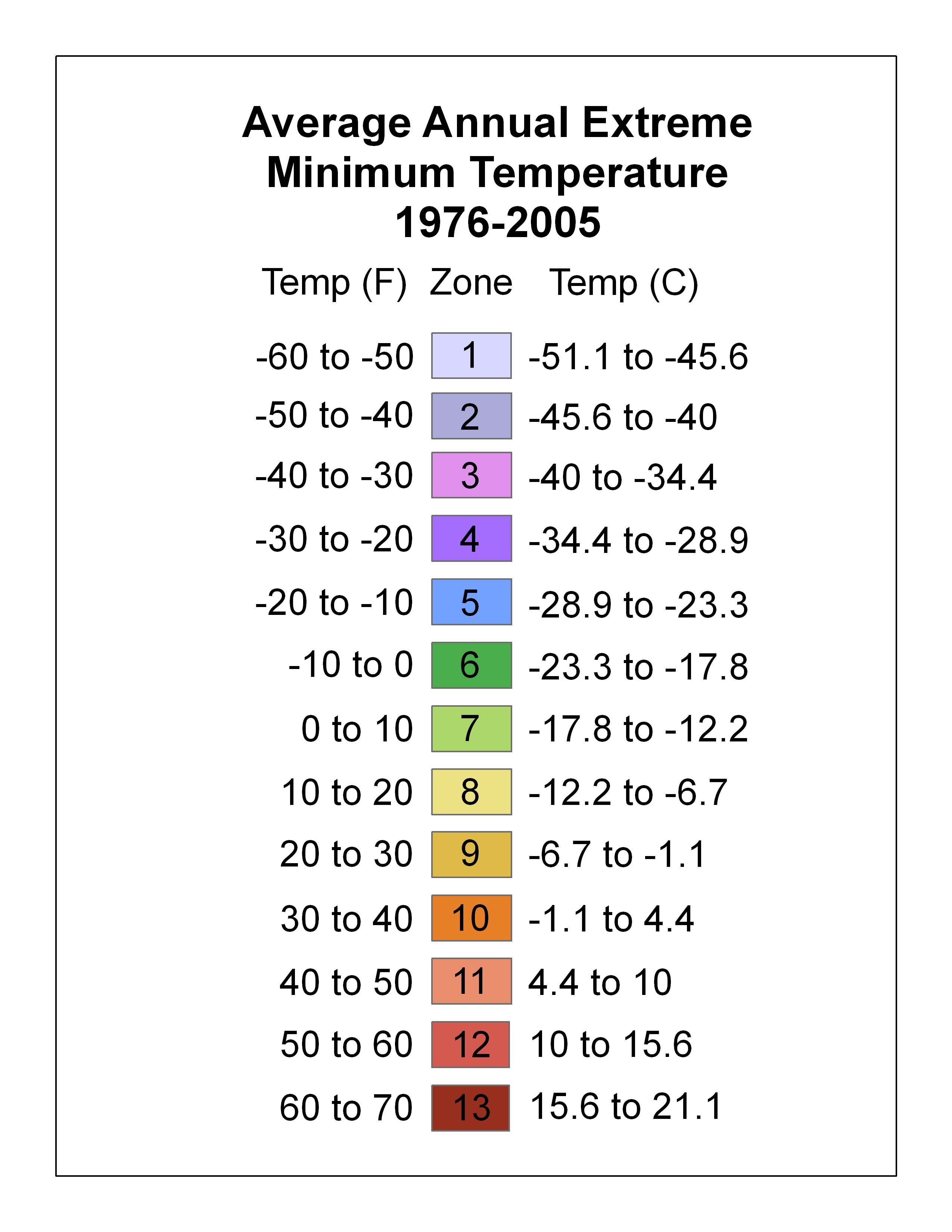
Hardiness Zone
A hardiness zone is a geographic area defined as having a certain average annual minimum temperature, a factor relevant to the survival of many plants. In some systems other statistics are included in the calculations. The original and most widely used system, developed by the United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) as a rough guide for landscaping and gardening, defines 13 zones by long-term average annual extreme minimum temperatures. It has been adapted by and to other countries (such as Canada) in various forms. A plant may be described as "hardy to zone 10": this means that the plant can withstand a minimum temperature of . Unless otherwise specified, in American contexts "hardiness zone" or simply "zone" usually refers to the USDA scale. However, some confusion can exist in discussing buildings and HVAC, where "climate zone" can refer to the International Energy Conservation Code zones, where Zone 1 is warm and Zone 8 is cold. Other hardiness rating schemes have been ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Floriferous
{{Short pages monitor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Montane Ecosystems
Montane ecosystems are found on the slopes of mountains. The alpine climate in these regions strongly affects the ecosystem because temperatures lapse rate, fall as elevation increases, causing the ecosystem to stratify. This stratification is a crucial factor in shaping plant community, biodiversity, metabolic processes and ecosystem dynamics for montane ecosystems. Dense montane forests are common at moderate elevations, due to moderate temperatures and high rainfall. At higher elevations, the climate is harsher, with lower temperatures and higher winds, preventing the growth of trees and causing the plant community to transition to montane grasslands and shrublands or alpine tundra. Due to the unique climate conditions of montane ecosystems, they contain increased numbers of endemic species. Montane ecosystems also exhibit variation in ecosystem services, which include carbon storage and water supply. Life zones As elevation increases, the alpine climate, climate becomes co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Butterfly
Butterflies are winged insects from the lepidopteran superfamily Papilionoidea, characterized by large, often brightly coloured wings that often fold together when at rest, and a conspicuous, fluttering flight. The oldest butterfly fossils have been dated to the Paleocene, about 56 million years ago, though molecular evidence suggests that they likely originated in the Cretaceous. Butterflies have a four-stage life cycle, and like other holometabolous insects they undergo complete metamorphosis. Winged adults lay eggs on the food plant on which their larvae, known as caterpillars, will feed. The caterpillars grow, sometimes very rapidly, and when fully developed, pupate in a chrysalis. When metamorphosis is complete, the pupal skin splits, the adult insect climbs out, expands its wings to dry, and flies off. Some butterflies, especially in the tropics, have several generations in a year, while others have a single generation, and a few in cold locations may take s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nectar
Nectar is a viscous, sugar-rich liquid produced by Plant, plants in glands called nectaries, either within the flowers with which it attracts pollination, pollinating animals, or by extrafloral nectaries, which provide a nutrient source to animal Mutualism (biology), mutualists, which in turn provide plant defense against herbivory#Indirect defenses, herbivore protection. Common nectar-consuming pollinators include mosquitoes, hoverfly, hoverflies, wasps, bees, butterfly, butterflies and moths, hummingbirds, honeyeaters and Bat#Fruit and nectar, bats. Nectar is an economically important substance as it is the sugar source for honey. It is also useful in agriculture and horticulture because the adult stages of some predatory insects feed on nectar. For example, a number of predacious or Parasitoid wasp, parasitoid wasps (e.g., the social wasp species ''Apoica flavissima'') rely on nectar as a primary food source. In turn, these wasps then hunt agricultural pest insects as food ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buddleja Davidii Var
''Buddleja'' (; ''Buddleia''; also historically given as ''Buddlea'') is a genus comprising over 140 species of flowering plants endemic to Asia, Africa, and the Americas. The generic name bestowed by Linnaeus posthumously honoured the Reverend Adam Buddle (1662–1715), an English botanist and rector, at the suggestion of William Houstoun. Houstoun sent the first plants to become known to science as buddleja ( ''B. americana'') to England from the Caribbean about 15 years after Buddle's death. ''Buddleja'' species, especially ''Buddleja davidii'' and interspecific hybrids, are commonly known as butterfly bushes and are frequently cultivated as garden shrubs. ''Buddleja davidii'' has become an invasive species in both Europe and North America. Nomenclature The botanic name has been the source of some confusion. By modern practice of botanical Latin, the spelling of a generic name made from ''Buddle'' would be ''Buddleia'', but Linnaeus in his ''Species Plantarum'' of 1753 a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anthonius Josephus Maria Leeuwenberg
Anthonius Josephus Maria "Toon" Leeuwenberg (11 August 1930, in Amsterdam – 2010) was a Dutch botanist and taxonomist best known for his research into the genus ''Buddleja'' at the Laboratory of Plant Taxonomy and Plant Geography, Wageningen. He was responsible for sinking many Asiatic species as varieties, notably within '' Buddleja crispa''. In 1962, he worked with Jan de Wilde on the flora of the Ivory Coast Ivory Coast, also known as Côte d'Ivoire and officially the Republic of Côte d'Ivoire, is a country on the southern coast of West Africa. Its capital city of Yamoussoukro is located in the centre of the country, while its largest List of ci .... Selected publications *Leeuwenberg, A. J. M. (1979). ''The Loganiaceae of Africa XVIII Buddleja L. II, Revision of the African & Asiatic species.'' H. Veenman & Zonen B. V., Wageningen, Nederland. *Leeuwenberg, A. J. M. (1991). ''A Revision of Tabernaemontana: the old world species''. *Leeuwenberg, A. J. M. (1994). ''A R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ploidy
Ploidy () is the number of complete sets of chromosomes in a cell, and hence the number of possible alleles for autosomal and pseudoautosomal genes. Here ''sets of chromosomes'' refers to the number of maternal and paternal chromosome copies, respectively, in each homologous chromosome pair—the form in which chromosomes naturally exist. Somatic cells, tissues, and individual organisms can be described according to the number of sets of chromosomes present (the "ploidy level"): monoploid (1 set), diploid (2 sets), triploid (3 sets), tetraploid (4 sets), pentaploid (5 sets), hexaploid (6 sets), heptaploid or septaploid (7 sets), etc. The generic term polyploid is often used to describe cells with three or more sets of chromosomes. Virtually all sexually reproducing organisms are made up of somatic cells that are diploid or greater, but ploidy level may vary widely between different organisms, between different tissues within the same organism, and at different stages in an o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monoecious
Monoecy (; adj. monoecious ) is a sexual system in seed plants where separate male and female cones or flowers are present on the same plant. It is a monomorphic sexual system comparable with gynomonoecy, andromonoecy and trimonoecy, and contrasted with dioecy where individual plants produce cones or flowers of only one sex and with bisexual or hermaphroditic plants in which male and female gametes are produced in the same flower. Monoecy often co-occurs with anemophily, because it prevents self-pollination of individual flowers and reduces the probability of self-pollination between male and female flowers on the same plant. Monoecy in Flowering plant, angiosperms has been of interest for evolutionary biologists since Charles Darwin. Terminology Monoecious comes from the Greek words for one house. History The term monoecy was first introduced in 1735 by Carl Linnaeus. Darwin noted that the flowers of monoecious species sometimes showed traces of the opposite sex function, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
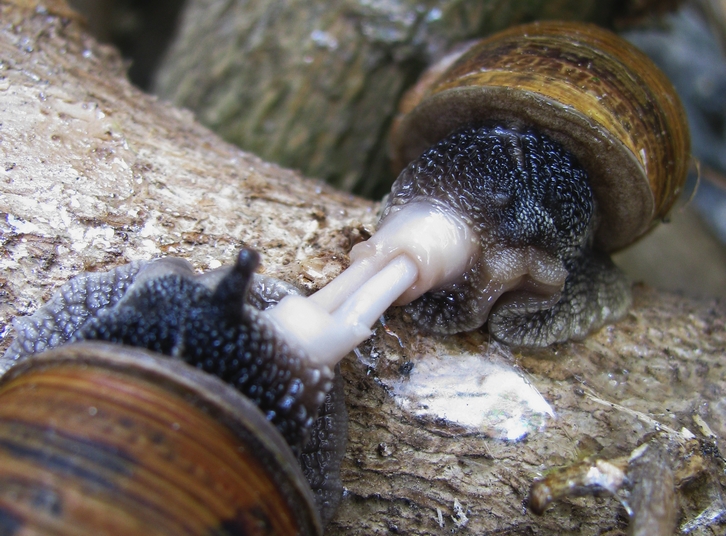
Hermaphrodite
A hermaphrodite () is a sexually reproducing organism that produces both male and female gametes. Animal species in which individuals are either male or female are gonochoric, which is the opposite of hermaphroditic. The individuals of many taxonomic groups of animals, primarily invertebrates, are hermaphrodites, capable of producing viable gametes of both sexes. In the great majority of tunicates, mollusks, and earthworms, hermaphroditism is a normal condition, enabling a form of sexual reproduction in which either partner can act as the female or male. Hermaphroditism is also found in some fish species, but is rare in other vertebrate groups. Most hermaphroditic species exhibit some degree of self-fertilization. The distribution of self-fertilization rates among animals is similar to that of plants, suggesting that similar pressures are operating to direct the evolution of selfing in animals and plants. A rough estimate of the number of hermaphroditic animal species ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |