|
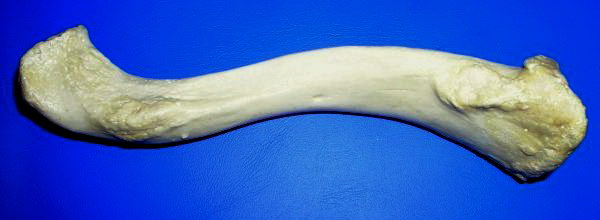
Breastbone
The sternum (: sternums or sterna) or breastbone is a long flat bone located in the central part of the chest. It connects to the ribs via cartilage and forms the front of the rib cage, thus helping to protect the heart, lungs, and major blood vessels from injury. Shaped roughly like a necktie, it is one of the largest and longest flat bones of the body. Its three regions are the manubrium, the body, and the xiphoid process. The word ''sternum'' originates from Ancient Greek στέρνον (''stérnon'') 'chest'. Structure The sternum is a narrow, flat bone, forming the middle portion of the front of the chest. The top of the sternum supports the clavicles (collarbones) and its edges join with the costal cartilages of the first two pairs of ribs. The inner surface of the sternum is also the attachment of the sternopericardial ligaments. Its top is also connected to the sternocleidomastoid muscle. The sternum consists of three main parts, listed from the top: * Manubrium * Body ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clavicle
The clavicle, collarbone, or keybone is a slender, S-shaped long bone approximately long that serves as a strut between the scapula, shoulder blade and the sternum (breastbone). There are two clavicles, one on each side of the body. The clavicle is the only long bone in the body that lies horizontally. Together with the shoulder blade, it makes up the shoulder girdle. It is a palpable bone and, in people who have less fat in this region, the location of the bone is clearly visible. It receives its name from Latin ''clavicula'' 'little key' because the bone rotates along its axis like a key when the shoulder is Abduction (kinesiology), abducted. The clavicle is the most commonly fractured bone. It can easily be fractured by impacts to the shoulder from the force of falling on outstretched arms or by a direct hit. Structure The collarbone is a thin doubly curved long bone that connects the human arm, arm to the torso, trunk of the body. Located directly above the first rib, it ac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clavicles
The clavicle, collarbone, or keybone is a slender, S-shaped long bone approximately long that serves as a strut between the shoulder blade and the sternum (breastbone). There are two clavicles, one on each side of the body. The clavicle is the only long bone in the body that lies horizontally. Together with the shoulder blade, it makes up the shoulder girdle. It is a palpable bone and, in people who have less fat in this region, the location of the bone is clearly visible. It receives its name from Latin ''clavicula'' 'little key' because the bone rotates along its axis like a key when the shoulder is abducted. The clavicle is the most commonly fractured bone. It can easily be fractured by impacts to the shoulder from the force of falling on outstretched arms or by a direct hit. Structure The collarbone is a thin doubly curved long bone that connects the arm to the trunk of the body. Located directly above the first rib, it acts as a strut to keep the scapula in place so th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xiphoid Process
The xiphoid process (), also referred to as the ensiform process, xiphisternum, or metasternum, constitutes a small cartilaginous process (extension) located in the inferior segment of the sternum, typically ossified in adult humans. Both the Greek-derived term ''xiphoid'' and its Latin equivalent, ''ensiform'', connote a "swordlike" or "sword-shaped" morphology. Structure The xiphoid process is anatomically situated at the level of the 9th thoracic vertebra (T9) and corresponds to the T7 dermatome. Development In neonates and young infants, particularly smaller infants, the tip of the xiphoid process may be seen as a palpable lump situated just below the sternal notch. Between the ages of 15 and 29, the xiphoid process typically undergoes fusion with the body of the sternum through a fibrous joint. Unlike the synovial articulation of major joints, this joint does not permit movement. Ossification of the xiphoid process typically occurs around the age of 40. Variation The xip ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sternopericardial Ligaments
The fibrous pericardium is attached to the posterior surface of the sternum by the superior and inferior sternopericardiac ligaments (sternopericardial ligaments); the upper passing to the manubrium, and the lower to the xiphoid process The xiphoid process (), also referred to as the ensiform process, xiphisternum, or metasternum, constitutes a small cartilaginous process (extension) located in the inferior segment of the sternum, typically ossified in adult humans. Both the Gr .... References External links Cardiac anatomy {{Ligament-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Articular Facets
A joint or articulation (or articular surface) is the connection made between bones, ossicles, or other hard structures in the body which link an animal's skeletal system into a functional whole.Saladin, Ken. Anatomy & Physiology. 7th ed. McGraw-Hill Connect. Webp.274/ref> They are constructed to allow for different degrees and types of movement. Some joints, such as the knee, elbow, and shoulder, are self-lubricating, almost frictionless, and are able to withstand compression and maintain heavy loads while still executing smooth and precise movements. Other joints such as sutures between the bones of the skull permit very little movement (only during birth) in order to protect the brain and the sense organs. The connection between a tooth and the jawbone is also called a joint, and is described as a fibrous joint known as a gomphosis. Joints are classified both structurally and functionally. Joints play a vital role in the human body, contributing to movement, stability, and ov ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blood Vessel
Blood vessels are the tubular structures of a circulatory system that transport blood throughout many Animal, animals’ bodies. Blood vessels transport blood cells, nutrients, and oxygen to most of the Tissue (biology), tissues of a Body (biology), body. They also take waste and carbon dioxide away from the tissues. Some tissues such as cartilage, epithelium, and the lens (anatomy), lens and cornea of the eye are not supplied with blood vessels and are termed ''avascular''. There are five types of blood vessels: the arteries, which carry the blood away from the heart; the arterioles; the capillaries, where the exchange of water and chemicals between the blood and the tissues occurs; the venules; and the veins, which carry blood from the capillaries back towards the heart. The word ''vascular'', is derived from the Latin ''vas'', meaning ''vessel'', and is mostly used in relation to blood vessels. Etymology * artery – late Middle English; from Latin ''arteria'', from Gree ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation
Cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) is an emergency procedure used during Cardiac arrest, cardiac or Respiratory arrest, respiratory arrest that involves chest compressions, often combined with artificial ventilation, to preserve brain function and maintain circulation until spontaneous breathing and heartbeat can be restored. It is indication (medicine), recommended for those who are unresponsive with no breathing or abnormal breathing, for example, agonal respirations. CPR involves chest compressions for adults between and deep and at a rate of at least 100 to 120 per minute. The rescuer may also provide artificial ventilation by either exhaling air into the subject's mouth or nose (mouth-to-mouth resuscitation) or using a device that pushes air into the subject's lungs (mechanical ventilation). Current recommendations emphasize early and high-quality chest compressions over artificial ventilation; a simplified CPR method involving only chest compressions is recommended for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xiphoid Process - Close-up - Animation
The xiphoid process (), also referred to as the ensiform process, xiphisternum, or metasternum, constitutes a small cartilaginous process (extension) located in the inferior segment of the sternum, typically ossified in adult humans. Both the Greek-derived term ''xiphoid'' and its Latin equivalent, ''ensiform'', connote a "swordlike" or "sword-shaped" morphology. Structure The xiphoid process is anatomically situated at the level of the 9th thoracic vertebra (T9) and corresponds to the T7 dermatome. Development In neonates and young infants, particularly smaller infants, the tip of the xiphoid process may be seen as a palpable lump situated just below the sternal notch. Between the ages of 15 and 29, the xiphoid process typically undergoes fusion with the body of the sternum through a fibrous joint. Unlike the synovial articulation of major joints, this joint does not permit movement. Ossification of the xiphoid process typically occurs around the age of 40. Variation The xipho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
True Rib
True most commonly refers to truth, the state of being in congruence with fact or reality. True may also refer to: Places * True, West Virginia, an unincorporated community in the United States * True, Wisconsin, a town in the United States * True, a townland in County Tyrone, Northern Ireland People * True (singer) (stylized as TRUE), the stage name of Japanese singer Miho Karasawa * True (surname) * True O'Brien (born 1994), an American model and actress Arts, entertainment, and media Music Albums * ''True'' (Avicii album), 2013 * ''True'' (Jon Anderson album), 2024 * ''True'' (L'Arc-en-Ciel album), 1996 * ''True'' (Mika Nakashima album), 2002 * ''True'' (Roy Montgomery and Chris Heaphy album), 1999 * ''True'' (Spandau Ballet album) or the title song (see below), 1983 * ''True'' (TrinityRoots album) or the title song, 2001 * ''True'' (TRU album), 1995 * ''True'' (EP), by Solange Knowles, 2012 Songs * "True" (Brandy song), 2008 * "True" (Concrete Blonde song), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Costal Cartilage
Costal cartilage, also known as rib cartilage, are bars of hyaline cartilage that serve to prolong the ribs forward and contribute to the elasticity of the walls of the thorax. Costal cartilage is only found at the anterior ends of the ribs, providing medial extension. Differences from ribs 1-12 The first seven pairs are connected with the sternum; the next three are each articulated with the lower border of the cartilage of the preceding rib; the last two have pointed extremities, which end in the wall of the abdomen. Like the ribs, the costal cartilages vary in their length, breadth, and direction. They increase in length from the first to the seventh, then gradually decrease to the twelfth. Their breadth, as well as that of the intervals between them, diminishes from the first to the last. They are broad at their attachments to the ribs, and taper toward their sternal extremities, excepting the first two, which are of the same breadth throughout, and the sixth, seventh, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sternal Angle
The sternal angle (also known as the angle of Lewis, angle of Louis, angle of Ludovic, or manubriosternal junction) is the projecting angle formed between the manubrium and body of a sternum at their junction at the manubriosternal joint. The sternal angle is a palpable and visible landmark in surface anatomy, presenting as either a slight body ridge or depression upon the upper chest wall which corresponds to the underlying manubriosternal joint. The sternal angle is palpable and often visible in young people. The sternal angle corresponds to the level of the 2nd costal cartilage on either side, and the level between the fourth and fifth thoracic vertebra. The sternal angle is used to define the Thoracic plane, transverse thoracic plane which represents the imaginary boundary between the superior mediastinum, superior and inferior mediastinum. It is also used to identify the second rib during physical examination and then the rest of the ribs by counting. Anatomy The sternal angl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |