|
Bosnian Cyrillic
Bosnian Cyrillic, widely known as Bosančica, is a variant of the Cyrillic alphabet that originated in medieval Bosnia. The term was coined at the end of the 19th century by Ćiro Truhelka. It was widely used in modern-day Bosnia and Herzegovina and the bordering areas of modern-day Croatia (southern and middle Dalmatia and Dubrovnik regions). Its name in Serbo-Croatian is ''Bosančica'' and ''Bosanica'' the latter of which might be translated as ''Bosnian script''. Serb scholars call it ''Serbian script'', ''Serbian–Bosnian script'', ''Bosnian–Serb Cyrillic'', as part of variant of Serbian Cyrillic and deem the term "bosančica" Austro-Hungarian propaganda. Croat scholars also call it ''Croatian script'', ''Croatian–Bosnian script'', ''Bosnian–Croat Cyrillic'', ''harvacko pismo'', ''arvatica'' or ''Western Cyrillic''. For other names of Bosnian Cyrillic, see below. The use of Bosančica amongst Bosnian Muslims was replaced by Arebica upon the introduction of Islam in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Cyrillic Script
The Cyrillic script ( ) is a writing system used for various languages across Eurasia. It is the designated national script in various Slavic languages, Slavic, Turkic languages, Turkic, Mongolic languages, Mongolic, Uralic languages, Uralic, Caucasian languages, Caucasian and Iranian languages, Iranic-speaking countries in Southeastern Europe, Eastern Europe, the Caucasus, Central Asia, North Asia, and East Asia, and used by many other minority languages. , around 250 million people in Eurasia use Cyrillic as the official script for their national languages, with Russia accounting for about half of them. With the accession of Bulgaria to the European Union on 1 January 2007, Cyrillic became the third official script of the Languages of the European Union#Writing systems, European Union, following the Latin script, Latin and Greek alphabet, Greek alphabets. The Early Cyrillic alphabet was developed during the 9th century AD at the Preslav Literary School in the First Bulga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Srećko M
Srećko () or Srečko is a South Slavic masculine given name. It is a Slavic form of Felix. The name may refer to: *Srećko Bogdan, Croatian footballer * Srečko Brodar, Slovenian archaeologist *Srećko Horvat, Croatian philosopher, author and political activist * Srećko Ilić, Yugoslav footballer *Srećko Juričić, Croatian professional footballer *Srečko Katanec, Slovenian professional football manager and former player *Srečko Kosovel, Slovenian poet *Srećko Lisinac, Serbian volleyball player *Srećko Mitrović, Bosnian soccer player *Srećko Pejović, Serbian sport shooter *Srećko Puntarić, Croatian cartoonist *Srećko Štiglić, Croatian Olympic athlete See also * *Srećković Srećković () is a Serbian surname derived form a masculine given name Srećko. It may refer to: * Aleksandar Srećković (born 1981), footballer * Nenad Srećković (born 1988), footballer * Nikola Srećković (born 1996), footballer * Panta Sre ... {{DEFAULTSORT:Srecko Slavic masculine g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Seminary
A seminary, school of theology, theological college, or divinity school is an educational institution for educating students (sometimes called seminarians) in scripture and theology, generally to prepare them for ordination to serve as clergy, in academics, or mostly in Christian ministry. The English word is taken from , translated as 'seed-bed', an image taken from the Council of Trent document which called for the first modern seminaries. In the United States, the term is currently used for graduate-level theological institutions, but historically it was used for high schools. History The establishment of seminaries in modern times resulted from Roman Catholic reforms of the Counter-Reformation after the Council of Trent. These Tridentine seminaries placed great emphasis on spiritual formation and personal discipline as well as the study, first of philosophy as a base, and, then, as the final crown, theology. The oldest Catholic seminary in the United States is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Omiš
Omiš () is a town and port in the Dalmatia region of Croatia, and a municipality in the Split-Dalmatia County. The town is approximately south-east of Croatia's second largest city, Split (city), Split, where the Cetina River meets the Adriatic Sea. In 2021, the municipality had a population of 14,139. Name It is supposed that the name of this city, ''Omiš'', developed from the Slavic ''Holm'', ''Hum'' as a translation from the Illyrian language, Illyrian - Greek language, Greek word ''Onaion'', ''Oneon'', meaning "hill" or "place on the hill", or from Greek onos (όνος) meaning donkey, perhaps from the shape of the rocky promontory by the city (naming a city after a natural form was common practice then, as it is now); there is also the possibility that the name of the settlement ''Onaeum'' was derived from the name of the river which was called ''Nestos'' by the Greek colonists in its lower flow, during Antiquity. According to Petar Šimunović, Omiš is derived from Proto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Kvarner Gulf
The Kvarner Gulf (, or ; ; or ) sometimes also Kvarner Bay, is a bay in the northern Adriatic Sea, located between the Istrian peninsula and the northern Croatian Littoral mainland. The bay is a part of Croatia's internal waters. The largest islands within the Kvarner are Cres, Krk, Pag, Rab and Lošinj. A portion of the Kvarner Bay, located between Cres, Krk, Rab and Pag is also called (literally "little Kvarner"; or ), and the portion east of Krk and Rab is called Senj Channel (after the mainland town of Senj). The bay is notable for its depth (more than 100 meters), which allows for the city of Rijeka at its northernmost point to have a sea port that can accommodate Capesize ships. Environment The bay is home to many beaches and tourist locations because of its beautiful waters and warm climate. Important Bird Area Collectively, the islands of the Kvarner Gulf form the Kvarner Islands Important Bird Area (IBA), designated as such by BirdLife International because it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Istria
Istria ( ; Croatian language, Croatian and Slovene language, Slovene: ; Italian language, Italian and Venetian language, Venetian: ; ; Istro-Romanian language, Istro-Romanian: ; ; ) is the largest peninsula within the Adriatic Sea. Located at the top of the Adriatic between the Gulf of Trieste and the Kvarner Gulf, the peninsula is shared by three countries: Croatia, Slovenia, and Italy,Marcel Cornis-Pope, John Neubauer''History of the literary cultures of East-Central Europe: junctures and disjunctures in the 19th And 20th Centuries'' John Benjamins Publishing Co. (2006), Alan John Day, Roger East, Richard Thomas''A political and economic dictionary of Eastern Europe'' Routledge, 1sr ed. (2002), 90% of its area being part of Croatia. Most of Croatian Istria is part of Istria County. Geography The geographical features of Istria include the Učka/Monte Maggiore mountain range, which is the highest portion of the Ćićarija/Cicceria mountain range; the rivers Dragonja/Dragogna, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Monastery Of Saint Peter In The Forest
A monastery is a building or complex of buildings comprising the domestic quarters and workplaces of monastics, monks or nuns, whether living in communities or alone (hermits). A monastery generally includes a place reserved for prayer which may be a chapel, church, or temple, and may also serve as an oratory, or in the case of communities anything from a single building housing only one senior and two or three junior monks or nuns, to vast complexes and estates housing tens or hundreds. A monastery complex typically comprises a number of buildings which include a church, dormitory, cloister, refectory, library, balneary and infirmary and outlying granges. Depending on the location, the monastic order and the occupation of its inhabitants, the complex may also include a wide range of buildings that facilitate self-sufficiency and service to the community. These may include a hospice, a school, and a range of agricultural and manufacturing buildings such as a barn, a forge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Poljica Statute
The Poljica Statute is the most important historical source for the Republic of Poljica. First mentioned in the late 14th century, and preserved in codified form since the 15th century, the statute determined the law of Poljica, which is, by its form, style, content and establishment of social-economic relations, totally different from the rest of Croatian statutes. It is written in short, picturesque sentences that include the norms of Poljica's society from those regarding the highest political authorities to those that include all Poljicians' interests. Besides the laws written in this statute, the Poljica Statute also contains various decisions and verdicts of authority that, in a few occasions, refer to individuals. The Poljica Statute was changed as the society of Poljica changed. Another important value of the Poljica Statute is its archaic form, which can be used to study the people from Poljica and those from Croatia in general at the time it was formulated. Typical feat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Bosnia And Herzegovina
Bosnia and Herzegovina, sometimes known as Bosnia-Herzegovina and informally as Bosnia, is a country in Southeast Europe. Situated on the Balkans, Balkan Peninsula, it borders Serbia to the east, Montenegro to the southeast, and Croatia to the north and southwest, with a coast on the Adriatic Sea in the south. Bosnia (region), Bosnia has a moderate continental climate with hot summers and cold, snowy winters. Its geography is largely mountainous, particularly in the central and eastern regions, which are dominated by the Dinaric Alps. Herzegovina, the smaller, southern region, has a Mediterranean climate and is mostly mountainous. Sarajevo is the capital and the largest city. The area has been inhabited since at least the Upper Paleolithic, with permanent human settlement traced to the Neolithic cultures of Butmir culture, Butmir, Kakanj culture, Kakanj, and Vučedol culture, Vučedol. After the arrival of the first Proto-Indo-Europeans, Indo-Europeans, the area was populated ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Stećak
Stećak (plural stećci; Cyrillic стећак, стећци) is the name for monumental medieval tombstones, that lie scattered across Bosnia and Herzegovina, and the border parts of Croatia, Montenegro and Serbia. An estimated 60,000 are found within the borders of modern Bosnia and Herzegovina and the rest of 10,000 are found in what are today Croatia (4,400), Montenegro (3,500), and Serbia (2,100), at more than 3,300 odd sites with over 90% in poor condition. They are cut in a variety of recognizable stećak forms, with certain percentage being richly decorated and some individual stećci also containing inscriptions in form of epitaphs. Appearing in the mid 12th century, with the first phase in the 13th century, the custom of cutting and using stećci tombstones reached its peak in the 14th and 15th century, before being discontinued in the very early 16th century during the Ottoman conquest of Bosnia and Herzegovina. They were a common tradition amongst Bosnian, Catholic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Charter Of Ban Kulin
The Charter of Ban Kulin ( bcs-Latn-Cyrl, Povelja Kulina bana, Повеља Кулина бана) was a trade agreement between the Banate of Bosnia and the Republic of Ragusa that effectively regulated Ragusan trade rights in Bosnia, written on 29 August 1189. It is one of the oldest written state documents in the region. According to the charter, Bosnian Ban Kulin promises to '' knez'' Krvaš and all the people of Dubrovnik full freedom of movement and trading across his country. The charter is written in two languages: Latin and an old form of Shtokavian dialect, with the Shtokavian part being a loose translation of the Latin original. The scribe was named Radoje, and the script is Bosnian Cyrillic (''Bosančica''). Language The Charter is the first diplomatic document written in the old Bosnian language and represents the oldest work written in the Bosnian Cyrillic script (''Bosančica''). As such, it is of particular interest to both linguists and historians. Apart ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
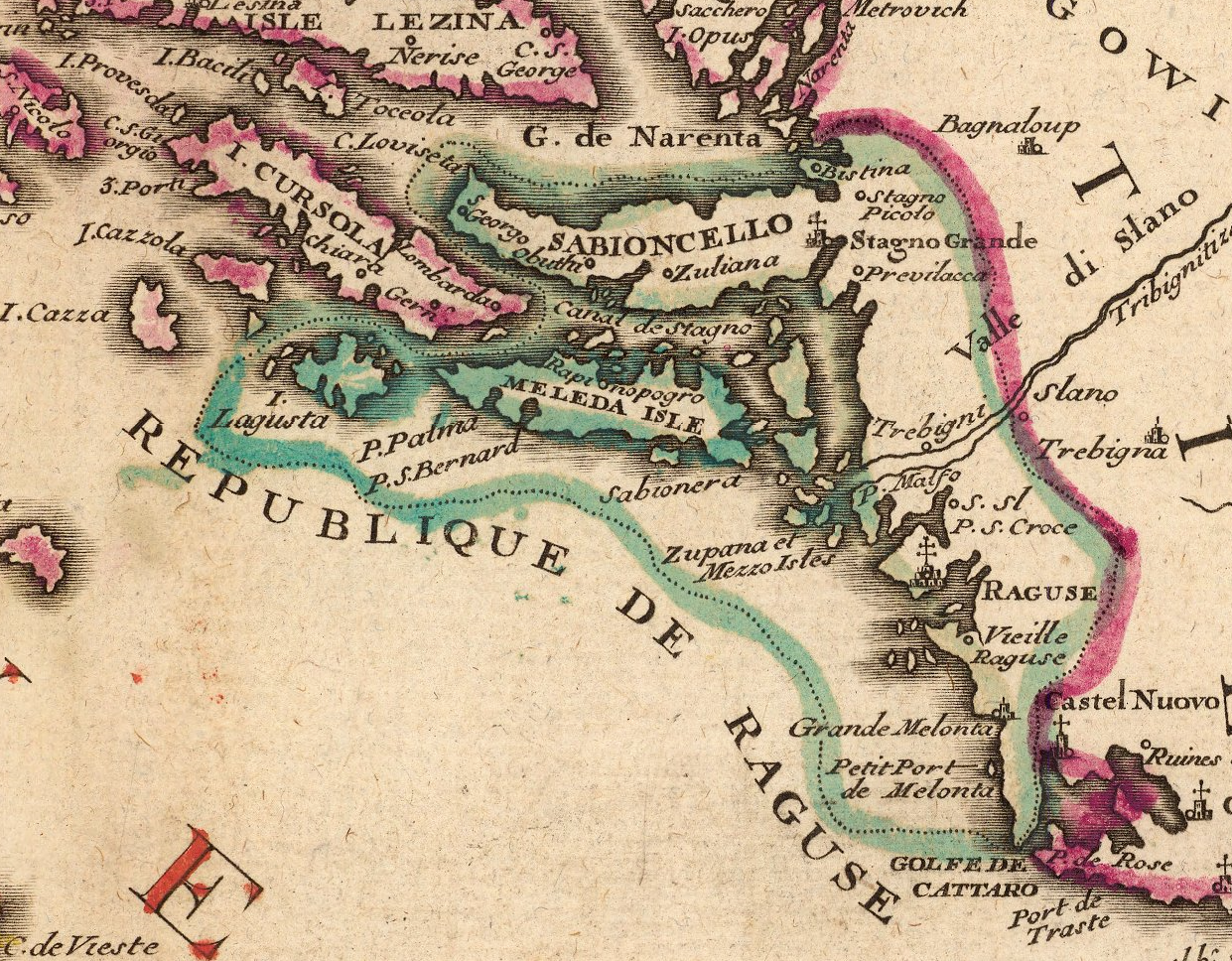
Republic Of Ragusa
The Republic of Ragusa, or the Republic of Dubrovnik, was an maritime republics, aristocratic maritime republic centered on the city of Dubrovnik (''Ragusa'' in Italian and Latin; ''Raguxa'' in Venetian) in South Dalmatia (today in southernmost Croatia) that carried that name from 1358 until 1808. It reached its commercial peak in the 15th and the 16th centuries, before being conquered by Napoleon's First French Empire, French Empire and formally annexed by the Kingdom of Italy (Napoleonic), Napoleonic Kingdom of Italy in 1808. It had a population of about 30,000 people, of whom 5,000 lived within the city walls. Its motto was "'", a Latin phrase which can be translated as "Liberty is not well sold for all the gold". Names Originally named ' (Latin for "Ragusan municipality" or "community"), in the 14th century it was renamed ' (Latin for ''Ragusan Republic''), first mentioned in 1385. It was nevertheless a Republic under its previous name, although its Rector was appointed b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |