|
Bond Duration
In finance, the duration of a financial asset that consists of fixed cash flows, such as a Bond (finance), bond, is the weighted average of the times until those fixed cash flows are received. When the price of an asset is considered as a function of Yield (finance), yield, duration also measures the price sensitivity to yield, the rate of change of price with respect to yield, or the percentage change in price for a parallel shift in yields. The dual use of the word "duration", as both the weighted average time until repayment and as the percentage change in price, often causes confusion. Strictly speaking, Macaulay duration is the name given to the weighted average time until cash flows are received and is measured in years. Modified duration is the name given to the price sensitivity. It is (-1) times the rate of change in the price of a bond as a function of the change in its yield. Both measures are termed "duration" and have the same (or close to the same) numerical value, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Finance
Finance refers to monetary resources and to the study and Academic discipline, discipline of money, currency, assets and Liability (financial accounting), liabilities. As a subject of study, is a field of Business administration, Business Administration wich study the planning, organizing, leading, and controlling of an organization's resources to achieve its goals. Based on the scope of financial activities in financial systems, the discipline can be divided into Personal finance, personal, Corporate finance, corporate, and public finance. In these financial systems, assets are bought, sold, or traded as financial instruments, such as Currency, currencies, loans, Bond (finance), bonds, Share (finance), shares, stocks, Option (finance), options, Futures contract, futures, etc. Assets can also be banked, Investment, invested, and Insurance, insured to maximize value and minimize loss. In practice, Financial risk, risks are always present in any financial action and entities. Due ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Weighted-average Life
In finance, the weighted-average life (WAL) of an amortizing loan or amortizing bond, also called average life, is the weighted average of the times of the ''principal repayments'': it's the average time until a dollar of principal is repaid. In a formula, :\text = \sum_^n \frac t_i, where: * P is the (total) principal, * P_i is the principal repayment that is included in payment i, hence * \frac is the fraction of the total principal that is included in payment i, and * t_i is the time (in years) from the calculation date to payment i. If desired, t_i can be expanded as \frac(i+\alpha-1) for a monthly bond, where \alpha is the fraction of a month between settlement date and first cash flow date. WAL of classes of loans In loans that allow prepayment, the WAL cannot be computed from the amortization schedule alone; one must also make assumptions about the prepayment and default behavior, and the quoted WAL will be an estimate. The WAL is usually computed from a single cash-flow ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
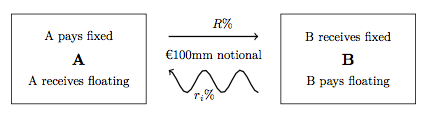
Interest Rate Swap
In finance, an interest rate swap (IRS) is an interest rate derivative (IRD). It involves exchange of interest rates between two parties. In particular it is a "linear" IRD and one of the most liquid, benchmark products. It has associations with forward rate agreements (FRAs), and with zero coupon swaps (ZCSs). In its December 2014 statistics release, the Bank for International Settlements reported that interest rate swaps were the largest component of the global OTC derivative market, representing 60%, with the notional amount outstanding in OTC interest rate swaps of $381 trillion, and the gross market value of $14 trillion. Interest rate swaps can be traded as an index through the FTSE MTIRS Index. Interest rate swaps General description An interest rate swap's (IRS's) effective description is a derivative contract, agreed between two counterparties, which specifies the nature of an exchange of payments benchmarked against an interest rate index. The most common IRS ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yield Curve
In finance, the yield curve is a graph which depicts how the Yield to maturity, yields on debt instruments – such as bonds – vary as a function of their years remaining to Maturity (finance), maturity. Typically, the graph's horizontal or x-axis is a time line of months or years remaining to maturity, with the shortest maturity on the left and progressively longer time periods on the right. The vertical or y-axis depicts the annualized yield to maturity. Those who issue and trade in forms of debt, such as loans and bonds, use yield curves to determine their value. Shifts in the shape and slope of the yield curve are thought to be related to investor expectations for the economy and interest rates. Ronald Melicher and Merle Welshans have identified several characteristics of a properly constructed yield curve. It should be based on a set of securities which have differing lengths of time to maturity, and all yields should be calculated as of the same point in time. Al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Basis Point Value
In finance, basis point value (BPV) denotes the change in the price of a bond given a basis point change in the yield of the bond.Martellini, Priaulet, Priaulet, Fixed-income securities. Wiley Finance, page 169 Basis point value tells us how much money the positions will gain or lose for a 0.01% per annum parallel (i.e. uniform at all durations) movement in the yield curve In finance, the yield curve is a graph which depicts how the Yield to maturity, yields on debt instruments – such as bonds – vary as a function of their years remaining to Maturity (finance), maturity. Typically, the graph's horizontal .... It is specified for interest rate risk and quantifies the interest rate risk for small changes in interest rates. The basis point value of a bond is roughly proportional to its duration. Notes {{reflist Fixed income analysis Bond valuation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
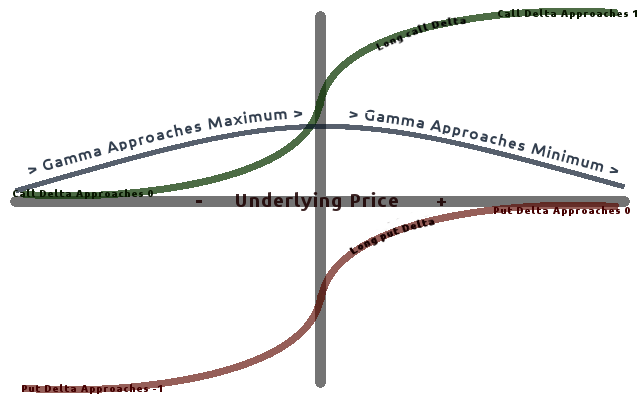
Greeks (finance)
In mathematical finance, the Greeks are the quantities (known in calculus as partial derivatives; first-order or higher) representing the sensitivity of the price of a derivative instrument such as an option to changes in one or more underlying parameters on which the value of an instrument or portfolio of financial instruments is dependent. The name is used because the most common of these sensitivities are denoted by Greek letters (as are some other finance measures). Collectively these have also been called the risk sensitivities, risk measures or hedge parameters. Use of the Greeks The Greeks are vital tools in risk management. Each Greek measures the sensitivity of the value of a portfolio to a small change in a given underlying parameter, so that component risks may be treated in isolation, and the portfolio rebalanced accordingly to achieve a desired exposure; see for example delta hedging. The Greeks in the Black–Scholes model (a relatively simple idealised mode ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kindle Direct Publishing
Kindle Direct Publishing is Amazon.com's e-book publishing platform launched in November 2007, concurrently with the first Amazon Kindle device. Originally called Digital Text Platform, the platform allows authors and publishers to publish their books to the Amazon Kindle Store. Authors can upload documents in several formats for delivery via the KDP website and charge between $0.99 and $200.00 for their works. KDP accepts books in 44 languages. In 2016, Amazon also added a paperback option, and in 2021, a hardback (case laminated) option, both of which use print-on-demand technology. History Kindle Direct Publishing (KDP) was in open beta testing in late 2007. In a December 5, 2009 interview with ''The New York Times'', Amazon CEO Jeff Bezos revealed that Amazon keeps 65% of the revenue from all e-book sales for the Kindle. The remaining 35% is split between the author and publisher. In 2010, they improved the rate from 35% to 70% to compete with Apple, provided the publi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bond Duration Closed-form Formula
In finance, the duration of a financial asset that consists of fixed cash flows, such as a bond, is the weighted average of the times until those fixed cash flows are received. When the price of an asset is considered as a function of yield, duration also measures the price sensitivity to yield, the rate of change of price with respect to yield, or the percentage change in price for a parallel shift in yields. The dual use of the word "duration", as both the weighted average time until repayment and as the percentage change in price, often causes confusion. Strictly speaking, Macaulay duration is the name given to the weighted average time until cash flows are received and is measured in years. Modified duration is the name given to the price sensitivity. It is (-1) times the rate of change in the price of a bond as a function of the change in its yield. Both measures are termed "duration" and have the same (or close to the same) numerical value, but it is important to keep in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thomas Ho (finance)
Thomas Ho may refer to: * Thomas Ho (actor), British actor of Chinese descent * Thomas Ho (finance), pioneering financial modeller * Tommy Ho, American former tennis player * Thomas Heffernan Ho, Hong Kong equestrian See also * Ho (surname) {{hndis, Ho, Thomas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Wolfram Demonstrations Project
The Wolfram Demonstrations Project is an open-source collection of interactive programmes called Demonstrations. It is hosted by Wolfram Research. At its launch, it contained 1300 demonstrations but has grown to over 10,000. The site won a Parents' Choice Award in 2008. Wolfram Research's staff organizes and edits the Demonstrations, which may be created by any user of Mathematica, then freely published and freely downloaded. Technology The Demonstrations run in Mathematica 6 or above and in Wolfram CDF Player, which is a free modified version of Wolfram Mathematica and available for Windows, Linux, and macOS and can operate as a web browser plugin. Demonstrations can also be embedded into a website. Each Demonstration page includes a snippet of JavaScript JavaScript (), often abbreviated as JS, is a programming language and core technology of the World Wide Web, alongside HTML and CSS. Ninety-nine percent of websites use JavaScript on the client side for webp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interest Rate
An interest rate is the amount of interest due per period, as a proportion of the amount lent, deposited, or borrowed (called the principal sum). The total interest on an amount lent or borrowed depends on the principal sum, the interest rate, the compounding frequency, and the length of time over which it is lent, deposited, or borrowed. The annual interest rate is the rate over a period of one year. Other interest rates apply over different periods, such as a month or a day, but they are usually annualized. The interest rate has been characterized as "an index of the preference . . . for a dollar of present ncomeover a dollar of future income". The borrower wants, or needs, to have money sooner, and is willing to pay a fee—the interest rate—for that privilege. Influencing factors Interest rates vary according to: * the government's directives to the central bank to accomplish the government's goals * the currency of the principal sum lent or borrowed * the term to m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
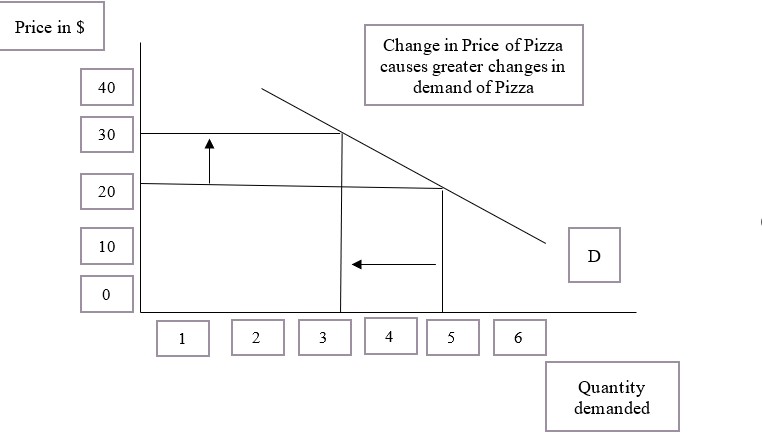
Elasticity (economics)
In economics, elasticity measures the responsiveness of one economic variable to a change in another. For example, if the price elasticity of the demand of a good is −2, then a 10% increase in price will cause the quantity demanded to fall by 20%. Elasticity in economics provides an understanding of changes in the behavior of the buyers and sellers with price changes. There are two types of elasticity for demand and supply, one is inelastic demand and supply and the other one is elastic demand and supply. Introduction The concept of price elasticity was first cited in an informal form in the book ''Principles of Economics (Marshall book), Principles of Economics'' published by the author Alfred Marshall in 1890. Subsequently, a major study of the price elasticity of supply and the price elasticity of demand for US products was undertaken by Joshua Levy and Trevor Pollock in the late 1960s. Elasticity is an important concept in neoclassical economic theory, and enables in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |