|
Bogosort
In computer science, bogosort (also known as permutation sort and stupid sort) is a sorting algorithm based on the generate and test paradigm. The function successively generates permutations of its input until it finds one that is sorted. It is not considered useful for sorting, but may be used for educational purposes, to contrast it with more efficient algorithms. The algorithm's name is a portmanteau of the words ''bogus'' and ''sort''. Two versions of this algorithm exist: a deterministic version that enumerates all permutations until it hits a sorted one,. and a randomized version that randomly permutes its input and checks whether it is sorted. An analogy for the working of the latter version is to sort a deck of cards by throwing the deck into the air, picking the cards up at random, and repeating the process until the deck is sorted. In a worst-case scenario with this version, the random source is of low quality and happens to make the sorted permutation unlikely to o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sorting Algorithm
In computer science, a sorting algorithm is an algorithm that puts elements of a List (computing), list into an Total order, order. The most frequently used orders are numerical order and lexicographical order, and either ascending or descending. Efficient sorting is important for optimizing the Algorithmic efficiency, efficiency of other algorithms (such as search algorithm, search and merge algorithm, merge algorithms) that require input data to be in sorted lists. Sorting is also often useful for Canonicalization, canonicalizing data and for producing human-readable output. Formally, the output of any sorting algorithm must satisfy two conditions: # The output is in monotonic order (each element is no smaller/larger than the previous element, according to the required order). # The output is a permutation (a reordering, yet retaining all of the original elements) of the input. Although some algorithms are designed for sequential access, the highest-performing algorithms assum ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bubble Sort
Bubble sort, sometimes referred to as sinking sort, is a simple sorting algorithm that repeatedly steps through the input list element by element, comparing the current element with the one after it, Swap (computer science), swapping their values if needed. These passes through the list are repeated until no swaps have to be performed during a pass, meaning that the list has become fully sorted. The algorithm, which is a comparison sort, is named for the way the larger elements "bubble" up to the top of the list. It performs poorly in real-world use and is used primarily as an educational tool. More efficient algorithms such as quicksort, timsort, or merge sort are used by the sorting libraries built into popular programming languages such as Python and Java. History The earliest description of the bubble sort algorithm was in a 1956 paper by mathematician and actuary Edward Harry Friend, ''Sorting on electronic computer systems'', published in the third issue of the third volume ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sorting
Sorting refers to ordering data in an increasing or decreasing manner according to some linear relationship among the data items. # ordering: arranging items in a sequence ordered by some criterion; # categorizing: grouping items with similar properties. Ordering items is the combination of categorizing them based on equivalent order, and ordering the categories themselves. By type Information or data In , arranging in an ordered sequence is called "sorting". Sorting is a common operation in many applications, and efficient algorithms have been developed to perform it. The most common uses of sorted sequences are: * making lookup or search efficient; * making merging of sequences efficient; * enabling processing of data in a defined order. The opposite of sorting, rearranging a sequence of items in a random or meaningless order, is called shuffling. For sorting, either a weak order, "should not come after", can be specified, or a strict weak order, "should come before" ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Google Code Jam
Google Code Jam was an international programming competition hosted and administered by Google. The competition began in 2003. The competition consists of a set of algorithmic problems which must be solved in a fixed amount of time. Competitors may use any programming language and development environment to obtain their solutions. From 2003 to 2007, Google Code Jam was deployed on Topcoder's platform. Since 2008 Google has developed their own dedicated infrastructure for the contest. Between 2015 and 2018, Google also ran Distributed Code Jam, with the focus on distributed algorithms. This was run in parallel with the regular Code Jam, with its own qualification and final round, for a top prize of $10,000, but was only open for people who qualified to Round 2 of Code Jam (up to 3000 people). Several Google Code Jam problems have led to academic research. On February 22, 2023, Google announced that Code Jam was to be discontinued alongside their other programming competitions, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Las Vegas Algorithm
In computing, a Las Vegas algorithm is a randomized algorithm that always gives Correctness (computer science), correct results; that is, it always produces the correct result or it informs about the failure. However, the runtime of a Las Vegas algorithm differs depending on the input. The usual definition of a Las Vegas algorithm includes the restriction that the ''expected'' runtime be finite, where the expectation is carried out over the space of random information, or entropy, used in the algorithm. An alternative definition requires that a Las Vegas algorithm always terminates (is Effective method, effective), but may output a Partial function#Bottom element, symbol not part of the solution space to indicate failure in finding a solution. The nature of Las Vegas algorithms makes them suitable in situations where the number of possible solutions is limited, and where verifying the correctness of a candidate solution is relatively easy while finding a solution is complex. Systema ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
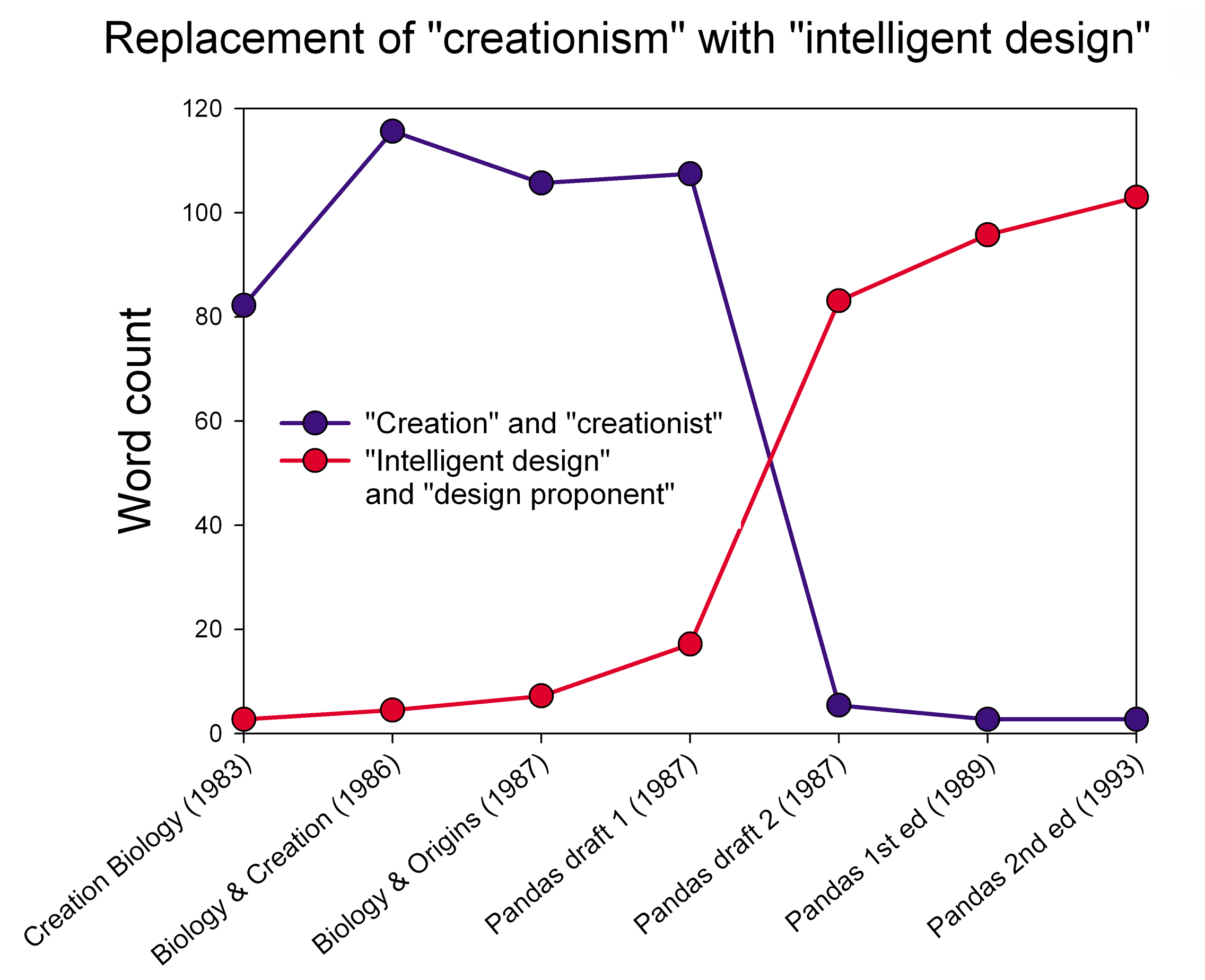
Intelligent Design
Intelligent design (ID) is a pseudoscientific argument for the existence of God, presented by its proponents as "an evidence-based scientific theory about life's origins".#Numbers 2006, Numbers 2006, p. 373; "[ID] captured headlines for its bold attempt to rewrite the basic rules of science and its claim to have found indisputable evidence of a God-like being. Proponents, however, insisted it was 'not a religious-based idea, but instead an evidence-based scientific theory about life's origins – one that challenges strictly materialistic views of evolution.' Although the intellectual roots of the design argument go back centuries, its contemporary incarnation dates from the 1980s" Article available froUniversiteit Gent/ref> Proponents claim that "certain features of the universe and of living things are best explained by an intelligent cause, not an undirected process such as natural selection." * * ID is a form of creationism that lacks empirical support and offers no te ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
While(true)
In computer programming, an infinite loop (or endless loop) is a sequence of instructions that, as written, will continue endlessly, unless an external intervention occurs, such as turning off power via a switch or pulling a plug. It may be intentional. There is no general algorithm to determine whether a computer program contains an infinite loop or not; this is the halting problem. Overview This differs from "a type of computer program that runs the same instructions continuously until it is either stopped or interrupted". Consider the following pseudocode: how_many = 0 while is_there_more_data() do how_many = how_many + 1 end display "the number of items counted = " how_many ''The same instructions'' were run ''continuously until it was stopped or interrupted'' . . . by the ''FALSE'' returned at some point by the function ''is_there_more_data''. By contrast, the following loop will not end by itself: birds = 1 fish = 2 while birds + fish > 1 do birds = 3 - birds ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Optimizing Compiler
An optimizing compiler is a compiler designed to generate code that is optimized in aspects such as minimizing program execution time, memory usage, storage size, and power consumption. Optimization is generally implemented as a sequence of optimizing transformations, a.k.a. compiler optimizations algorithms that transform code to produce semantically equivalent code optimized for some aspect. Optimization is limited by a number of factors. Theoretical analysis indicates that some optimization problems are NP-complete, or even undecidable. Also, producing perfectly ''optimal'' code is not possible since optimizing for one aspect often degrades performance for another. Optimization is a collection of heuristic methods for improving resource usage in typical programs. Categorization Local vs. global scope Scope describes how much of the input code is considered to apply optimizations. Local scope optimizations use information local to a basic block. Since basic blocks cont ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Single-event Upset
A single-event upset (SEU), also known as a single-event error (SEE), is a change of state caused by one single ionizing particle (e.g. ions, electrons, photons) striking a sensitive node in a live micro-electronic device, such as in a microprocessor, semiconductor memory, or power transistors. The state change is a result of the free charge created by ionization in or close to an important node of a logic element (e.g. memory "bit"). The error in device output or operation caused as a result of the strike is called an SEU or a soft error. The SEU itself is not considered permanently damaging to the transistors' or circuits' functionality, unlike the case of single-event latch-up (SEL), single-event gate rupture (SEGR), or single-event burnout (SEB). These are all examples of a general class of radiation effects in electronic devices called ''single-event effects'' (SEEs). History Single-event upsets were first described during above-ground nuclear testing, from 1954 to 19 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Miracle
A miracle is an event that is inexplicable by natural or scientific lawsOne dictionary define"Miracle"as: "A surprising and welcome event that is not explicable by natural or scientific laws and is therefore considered to be the work of a divine agency." and accordingly gets attributed to some supernatural or praeternatural cause. Various religions often attribute a phenomenon characterized as miraculous to the actions of a supernatural being, (especially) a deity, a miracle worker, a saint, or a religious leader. Informally, English-speakers often use the word ''miracle'' to characterise any beneficial event that is statistically unlikely but not contrary to the laws of nature, such as surviving a natural disaster, or simply a "wonderful" occurrence, regardless of likelihood (e.g. "the miracle of childbirth"). Some coincidences may be seen as miracles. A true miracle would, by definition, be a non-natural phenomenon, leading many writers to dismiss miracles as physically i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Many-worlds Interpretation
The many-worlds interpretation (MWI) is an interpretation of quantum mechanics that asserts that the universal wavefunction is Philosophical realism, objectively real, and that there is no wave function collapse. This implies that all Possible world, possible outcomes of quantum measurements are physically realized in different "worlds". The evolution of reality as a whole in MWI is rigidly Determinism, deterministic and principle of locality, local. Many-worlds is also called the relative state formulation or the Everett interpretation, after physicist Hugh Everett III, Hugh Everett, who first proposed it in 1957.Hugh Everett]Theory of the Universal Wavefunction Thesis, Princeton University, (1956, 1973), pp. 1–140. Bryce DeWitt popularized the formulation and named it ''many-worlds'' in the 1970s. See also Cécile DeWitt-Morette, Cecile M. DeWitt, John A. Wheeler (eds,) The Everett–Wheeler Interpretation of Quantum Mechanics, ''Battelle Rencontres: 1967 Lectures in Mathema ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
In-joke
An in-joke, also known as an inside joke or a private joke, is a joke with humour that is understandable only to members of an ingroup; that is, people who are ''in'' a particular social group, occupation, or other community of shared interest. It is, therefore, an esoteric joke, only humorous to those who are aware of the circumstances behind it. Typically, inside jokes use a reference in the punchline to imply that which is associated with the reference. Often, this reference refers to the punchline of another joke which was already heard by the ingroup. In-jokes may exist within a small social clique, such as a group of friends, or extend to an entire profession or other relatively large group. When the ingroup only includes people which heard the previous portion of a comedic set, the type of inside joke is known as a callback. An example is: ::Q: What's yellow and equivalent to the axiom of choice? ::A: Zorn's lemon. Individuals not familiar with the mathematical res ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |