|
Bishop Of Wrocław
Bishops of the (Breslau )Wrocław Bishopric, Prince-Bishopric (1290–1918), and Archdiocese (since 1930; see Roman Catholic Archdiocese of Wrocław for details). Bishops * 1000–? – John (Johannes) * 1051–1062 – Hieronymus * 1063–1072 – John I * 1074–1111 – Piotr I * 1112–1120 – Żyrosław I * 1120–1126 – Haymo * 1127–1140 – Robert I IJurek T., ''Zagadka biskupa wrocławskiego Roberta'', "Śląski Kwartalnik Historyczny Sobótka" 1990, pp. 1–11 * 1140–1142 – Robert II * 1145–1146 – Konrad * 1146–1149 – Jan * 1149–1169 – Walter * 1170–1198 – Siroslaus II * 1198–1201 – Jarosław, Duke of Opole (Jaroslaw of Opole) * 1201–1207 – Cyprian, (1196–1201 Bishop of Lebus) * 1207–1232 – Wawrzyniec * 1232–1268 – Tomasz I **1268–1270 – Ladislaus of Salzburg, administrator * 1270–1290 – Thomas II. Prince-Bishops *1290–1292 – Thomas II, granted princely regalia by Henry IV Probus for the episcopal Duchy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diocese
In Ecclesiastical polity, church governance, a diocese or bishopric is the ecclesiastical district under the jurisdiction of a bishop. History In the later organization of the Roman Empire, the increasingly subdivided Roman province, provinces were administratively associated in a larger unit, the Roman diocese, diocese (Latin ''dioecesis'', from the Greek language, Greek term διοίκησις, meaning "administration"). Christianity was given legal status in 313 with the Edict of Milan. Churches began to organize themselves into Roman diocese, dioceses based on the Roman diocese, civil dioceses, not on the larger regional imperial districts. These dioceses were often smaller than the Roman province, provinces. Christianity was declared the Empire's State church of the Roman Empire, official religion by Theodosius I in 380. Constantine the Great, Constantine I in 318 gave litigants the right to have court cases transferred from the civil courts to the bishops. This situa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyprian(Bishop Of Wrocław)
Cyprian (; ; to 14 September 258 AD''The Liturgy of the Hours according to the Roman Rite: Vol. IV.'' New York: Catholic Book Publishing Company, 1975. p. 1406.) was a bishop of Carthage and an early Christian writer of Berber descent, many of whose Latin works are extant. He is recognized as a saint in the Western and Eastern churches. He was born around the beginning of the 3rd century in North Africa, perhaps at Carthage, where he received a classical education. Soon after converting to Christianity, he became a bishop in 249. A controversial figure during his lifetime, his strong pastoral skills, firm conduct during the Novatianist controversy and outbreak of the Plague of Cyprian (named for his description of it), and eventual martyrdom at Carthage established his reputation and proved his sanctity in the eyes of the Church. His skilful Latin rhetoric led to his being considered the pre-eminent Latin writer of Western Christianity until Jerome and Augustine. Early life ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nikolaus Of Banz
Nicholas of Banz, also known as Nikolaus von Banz, was a Roman Catholic canon and an important mediator in the dynastic struggles of 13th century Poland and for a time was administrator of the diocese of Wroclaw. at GCatholic.org. Nicholas came from a patrician family and by 1305 AD was a canon in the . From 1308 to 1315 he was |
Sede Vacante
In the Catholic Church, ''sede vacante'' is the state during which a diocese or archdiocese is without a prelate installed in office, with the prelate's office being the cathedral. The term is used frequently in reference to a papal interregnum occurring upon the pope's death or resignation. History Early in church history, the archpriest, archdeacon, and " of the notaries" in the papal court made up a regency council which governed the period. It was the obligation of the Camerarius (papal chamberlain), the head of the Camera Apostolica, to formally establish the death of the pope. Gradually, this led to the theory that the Camerarius, as the chief of the Roman Curia, should conduct normal business even after the death of the pope, and also conduct the burial and the preparation for the new election. This process was evident with Camerarius Boso Breakspeare. During the long of 1268 to 1271, the importance of the Camerarius was so clear that the Cardinals prepa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henryk Z Wierzbnej
Henry of Wierzbna (, ; probably before 1270 – 23 September 1319) was a Bishop of Wrocław in Poland in 1302–1319. Life He was born into the Wierzbna noble family of Würben toward the end of the 1260s and was the third and youngest son of John, the Castellan of Ryczyna in Silesia. He was made a Canon of Wrocław on 31 August 1290 and supported King Wenceslaus II of Bohemia and his relative Jan Muskata, Bishop of Kraków in the dynastic struggles of the day. He was made bishop in 1302 by Pope Boniface VIII and he was the first of the Bishops of Wrocław to take the princely title. His time in office was notable for his organization of a Court of the Inquisition in 1315, the result of which included burning at the stake more than 50 people convicted of heresy in the towns of Wrocław, Swidnica and Nysa. His inquisition was particularly against Beguines and Beghards. He died on 23 September 1319. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Johann III Romka
Jan Romka was a thirteenth century Bishop of Wrocław. He was Bishop from 1292 to his death on 19 November 1301. at GCatholic.org. Early life The first mention of him is in 1267 as of the , Thomas Zaremba and in 1268 records state he was a of |
Otmuchów
Otmuchów (pronounced: ; ) is a town in Nysa County, Opole Voivodeship, in southern Poland, with 6,581 inhabitants (2019). Etymology The city was mentioned for the first time as ''Otemochow'' in 1155. It was named in its Old Polish form ''Othmuchow'' in the 13th-century ''Book of Henryków''. The name ''Othmuchow'' was also listed in the Chronicles of the Kingdom of Poland written in the years 1455-1480 by Jan Długosz and the Latinized name ''Othmuchouie'' appeared in the '':pl:Statuta synodalia episcoporum Wratislaviensium, Statuta synodalia episcoporum Wratislaviensium'' from 1475. In 1613 the Silesian regionalist and historian Nicholas Henkel stated in his own work entitled ''Fri Silesiographia'' two names in Latin, Otmuchovia and Othmuchaw. The Germanized form was ''Ottmachau'', and the Polish name in the modern Polish spelling was restored in 1945. History The first known mentioning of Otmuchów comes from 1155, however, it certainly existed, along with the Otmuchów Cast ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Duchy Of Nysa
The Duchy of Nysa (, ) or Duchy of Neisse () was one of the duchies of Silesia with its capital at Nysa in Lower Silesia. Alongside the Duchy of Siewierz, it was the only ecclesiastical duchy in the Silesian region, as it was ruled by a bishop of the Catholic Church. Nowadays its territory is divided between Poland and the Czech Republic. History Upon his appointment as Bishop of Wrocław in 1198, Jarosław of Opole, elder son of the Silesian duke Bolesław I the Tall, received the territories around the town of Nysa from his father. After Jarosław's death in 1201, his half-brother Duke Henry I the Bearded of Silesia decided to leave Nysa, as well as the castellany of Otmuchów, under the control of the Diocese of Wrocław, while the rest of the late Jarosław's Upper Silesian lands were annexed by his uncle Mieszko IV Tanglefoot in the following year. In 1290 Henry IV Probus, duke of Lower Silesia at Wrocław, gave the bishops privileges of autonomy on their land ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
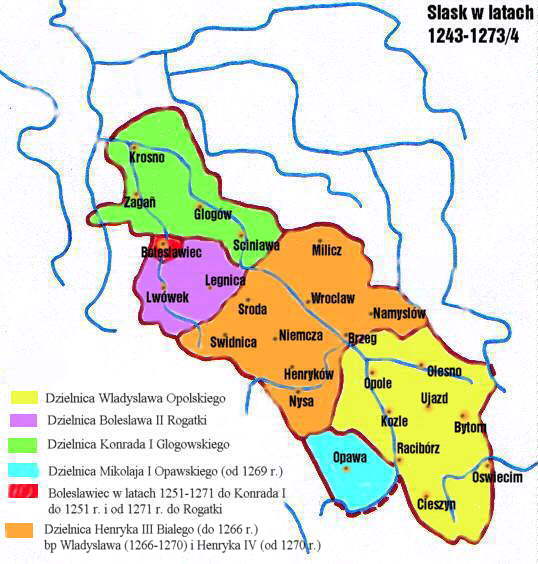
Henry IV Probus
Henry Probus (Latin for the Righteous; or ''Prawy''; ; – 23 June 1290) was a member of the Silesian branch of the royal Polish Piast dynasty. He was Duke of Silesia at Wrocław from 1266 as well as the ruler of the Seniorate Province of Kraków and High Duke of Poland from 1288 until his death in 1290. Life Henry IV was the only son of Duke Henry III the White of Silesia-Wrocław by his first wife Judith, daughter of Duke Konrad I of Masovia. Early life and tutelage A minor upon the early death of his father in 1266, Henry IV was placed under the guardianship of his paternal uncle, Archbishop Władysław of Salzburg. The Archbishop decided that the constant travels between Wrocław and Salzburg were inappropriate for a child, and, in 1267, sent Henry to Prague to be raised at the court of King Ottokar II of Bohemia. Ottokar after Władysław's death in 1270 also took over Wrocław. Shortly after the death of his uncle (who left him as his universal heir), Henry IV ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thomas II, Bishop Of Wrocław
Thomas may refer to: People * List of people with given name Thomas * Thomas (name) * Thomas (surname) * Saint Thomas (other) * Thomas Aquinas (1225–1274) Italian Dominican friar, philosopher, and Doctor of the Church * Thomas the Apostle * Thomas (bishop of the East Angles) (fl. 640s–650s), medieval Bishop of the East Angles * Thomas (Archdeacon of Barnstaple) (fl. 1203), Archdeacon of Barnstaple * Thomas, Count of Perche (1195–1217), Count of Perche * Thomas (bishop of Finland) (1248), first known Bishop of Finland * Thomas, Earl of Mar (1330–1377), 14th-century Earl, Aberdeen, Scotland Geography Places in the United States * Thomas, Idaho * Thomas, Illinois * Thomas, Oklahoma * Thomas, Oregon * Thomas, South Dakota * Thomas, Virginia * Thomas, Washington * Thomas, West Virginia * Thomas County (other) * Thomas Township (other) Elsewhere * Thomas Glacier (Greenland) Arts and entertainment * ''Thomas'' (Burton novel), a 1969 novel by Hes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diocesan Administrator
A diocesan administrator (also known as archdiocesan administrator, archiepiscopal administrator and eparchial administrator for the case, respectively, of an archdiocese, archeparchy, and eparchy) is a provisional ordinary of a Catholic particular church. Diocesan or archdiocesan administrators in canon law The college of consultors elects an administrator within eight days after the see is known to be vacant. The college must elect as administrator a priest, bishop, or archbishop at least 35 years old. If the college of consultors fails to elect a priest of the required minimum age within the time allotted, the choice of an administrator passes to the metropolitan archbishop or, if the metropolitan see is vacant, to the senior by appointment of the suffragan bishops of the ecclesiastical province. If a diocese has a coadjutor bishop, the coadjutor succeeds immediately to the episcopal see upon the previous bishop's death or resignation, and there is no vacancy of the se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ladislaus Of Salzburg
Władysław of Salzburg, also known as Władysław of Wrocław () or Władysław of Silesia (, ; – 27 April 1270), a member of the Silesian Piasts, was co-ruler in the Duchy of Wrocław since 1248. He served as chancellor of King Ottokar II of Bohemia from 1255 and was elected Bishop of Bamberg in 1257 and Bishop of Passau in 1265. Władysław became Prince-Archbishop of Salzburg in the same year, and from 1268 also served as administrator of the Wrocław diocese. Family Władysław was the fifth and youngest son of the Polish Duke Henry II the Pious, by his wife Anna, daughter of the Přemyslid king Ottokar I of Bohemia. He was a member of the Silesian Piasts, elder line of the Polish ruling Piast dynasty. Władysław's grandfather, Duke Henry the Bearded, also regained the Seniorate Province and the Polish throne as High Duke in 1232. Duke Henry II became co-ruler of his father in 1226 and was able to succeed him as Silesian duke and High Duke of Poland in 1238. Whe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |