|
Binomial Distribution
In probability theory and statistics, the binomial distribution with parameters and is the discrete probability distribution of the number of successes in a sequence of statistical independence, independent experiment (probability theory), experiments, each asking a yes–no question, and each with its own Boolean-valued function, Boolean-valued outcome (probability), outcome: ''success'' (with probability ) or ''failure'' (with probability ). A single success/failure experiment is also called a Bernoulli trial or Bernoulli experiment, and a sequence of outcomes is called a Bernoulli process; for a single trial, i.e., , the binomial distribution is a Bernoulli distribution. The binomial distribution is the basis for the binomial test of statistical significance. The binomial distribution is frequently used to model the number of successes in a sample of size drawn with replacement from a population of size . If the sampling is carried out without replacement, the draws ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
WikiProject Probability
A WikiProject, or Wikiproject, is an affinity group for contributors with shared goals within the Wikimedia movement. WikiProjects are prevalent within the largest wiki, Wikipedia, and exist to varying degrees within sibling projects such as Wiktionary, Wikiquote, Wikidata, and Wikisource. They also exist in different languages, and translation of articles is a form of their collaboration. During the COVID-19 pandemic, CBS News noted the role of Wikipedia's WikiProject Medicine in maintaining the accuracy of articles related to the disease. Another WikiProject that has drawn attention is WikiProject Women Scientists, which was profiled by '' Smithsonian'' for its efforts to improve coverage of women scientists which the profile noted had "helped increase the number of female scientists on Wikipedia from around 1,600 to over 5,000". On Wikipedia Some Wikipedia WikiProjects are substantial enough to engage in cooperative activities with outside organizations relevant to the fie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bernoulli Distribution
In probability theory and statistics, the Bernoulli distribution, named after Swiss mathematician Jacob Bernoulli, is the discrete probability distribution of a random variable which takes the value 1 with probability p and the value 0 with probability q = 1-p. Less formally, it can be thought of as a model for the set of possible outcomes of any single experiment that asks a yes–no question. Such questions lead to outcome (probability), outcomes that are Boolean-valued function, Boolean-valued: a single bit whose value is success/yes and no, yes/Truth value, true/Binary code, one with probability ''p'' and failure/no/false (logic), false/Binary code, zero with probability ''q''. It can be used to represent a (possibly biased) coin toss where 1 and 0 would represent "heads" and "tails", respectively, and ''p'' would be the probability of the coin landing on heads (or vice versa where 1 would represent tails and ''p'' would be the probability of tails). In particular, unfair co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Floor And Ceiling Functions
In mathematics, the floor function is the function that takes as input a real number , and gives as output the greatest integer less than or equal to , denoted or . Similarly, the ceiling function maps to the least integer greater than or equal to , denoted or . For example, for floor: , , and for ceiling: , and . The floor of is also called the integral part, integer part, greatest integer, or entier of , and was historically denoted (among other notations). However, the same term, ''integer part'', is also used for truncation towards zero, which differs from the floor function for negative numbers. For an integer , . Although and produce graphs that appear exactly alike, they are not the same when the value of is an exact integer. For example, when , . However, if , then , while . Notation The ''integral part'' or ''integer part'' of a number ( in the original) was first defined in 1798 by Adrien-Marie Legendre in his proof of the Legendre's formula. Carl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cumulative Distribution Function
In probability theory and statistics, the cumulative distribution function (CDF) of a real-valued random variable X, or just distribution function of X, evaluated at x, is the probability that X will take a value less than or equal to x. Every probability distribution Support (measure theory), supported on the real numbers, discrete or "mixed" as well as Continuous variable, continuous, is uniquely identified by a right-continuous Monotonic function, monotone increasing function (a càdlàg function) F \colon \mathbb R \rightarrow [0,1] satisfying \lim_F(x)=0 and \lim_F(x)=1. In the case of a scalar continuous distribution, it gives the area under the probability density function from negative infinity to x. Cumulative distribution functions are also used to specify the distribution of multivariate random variables. Definition The cumulative distribution function of a real-valued random variable X is the function given by where the right-hand side represents the probability ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fair Coin
In probability theory and statistics, a sequence of Independence (probability theory), independent Bernoulli trials with probability 1/2 of success on each trial is metaphorically called a fair coin. One for which the probability is not 1/2 is called a biased or unfair coin. In theoretical studies, the assumption that a coin is fair is often made by referring to an ideal coin. John Edmund Kerrich performed experiments in coin flipping and found that a coin made from a wooden disk about the size of a Crown (British coin), crown and coated on one side with lead landed heads (wooden side up) 679 times out of 1000. In this experiment the coin was tossed by balancing it on the forefinger, flipping it using the thumb so that it spun through the air for about a foot before landing on a flat cloth spread over a table. Edwin Thompson Jaynes claimed that when a coin is caught in the hand, instead of being allowed to bounce, the physical bias in the coin is insignificant compared to the met ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Floor And Ceiling Functions
In mathematics, the floor function is the function that takes as input a real number , and gives as output the greatest integer less than or equal to , denoted or . Similarly, the ceiling function maps to the least integer greater than or equal to , denoted or . For example, for floor: , , and for ceiling: , and . The floor of is also called the integral part, integer part, greatest integer, or entier of , and was historically denoted (among other notations). However, the same term, ''integer part'', is also used for truncation towards zero, which differs from the floor function for negative numbers. For an integer , . Although and produce graphs that appear exactly alike, they are not the same when the value of is an exact integer. For example, when , . However, if , then , while . Notation The ''integral part'' or ''integer part'' of a number ( in the original) was first defined in 1798 by Adrien-Marie Legendre in his proof of the Legendre's formula. Carl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mode (statistics)
In statistics, the mode is the value that appears most often in a set of data values. If is a discrete random variable, the mode is the value at which the probability mass function takes its maximum value (i.e., ). In other words, it is the value that is most likely to be sampled. Like the statistical mean and median, the mode is a way of expressing, in a (usually) single number, important information about a random variable or a population (statistics), population. The numerical value of the mode is the same as that of the mean and median in a normal distribution, and it may be very different in highly skewed distributions. The mode is not necessarily unique in a given discrete distribution since the probability mass function may take the same maximum value at several points , , etc. The most extreme case occurs in Uniform distribution (discrete), uniform distributions, where all values occur equally frequently. A mode of a continuous probability distribution is often conside ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Binomial Coefficient
In mathematics, the binomial coefficients are the positive integers that occur as coefficients in the binomial theorem. Commonly, a binomial coefficient is indexed by a pair of integers and is written \tbinom. It is the coefficient of the term in the polynomial expansion of the binomial power ; this coefficient can be computed by the multiplicative formula : \binom nk = \frac, which using factorial notation can be compactly expressed as : \binom = \frac. For example, the fourth power of is : \begin (1 + x)^4 &= \tbinom x^0 + \tbinom x^1 + \tbinom x^2 + \tbinom x^3 + \tbinom x^4 \\ &= 1 + 4x + 6 x^2 + 4x^3 + x^4, \end and the binomial coefficient \tbinom =\tfrac = \tfrac = 6 is the coefficient of the term. Arranging the numbers \tbinom, \tbinom, \ldots, \tbinom in successive rows for gives a triangular array called Pascal's triangle, satisfying the recurrence relation : \binom = \binom + \binom . The binomial coefficients occur in many areas of mathematics, and espe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Probability Mass Function
In probability and statistics, a probability mass function (sometimes called ''probability function'' or ''frequency function'') is a function that gives the probability that a discrete random variable is exactly equal to some value. Sometimes it is also known as the discrete probability density function. The probability mass function is often the primary means of defining a discrete probability distribution, and such functions exist for either scalar or multivariate random variables whose domain is discrete. A probability mass function differs from a continuous probability density function (PDF) in that the latter is associated with continuous rather than discrete random variables. A continuous PDF must be integrated over an interval to yield a probability. The value of the random variable having the largest probability mass is called the mode. Formal definition Probability mass function is the probability distribution of a discrete random variable, and provides the p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Natural Number
In mathematics, the natural numbers are the numbers 0, 1, 2, 3, and so on, possibly excluding 0. Some start counting with 0, defining the natural numbers as the non-negative integers , while others start with 1, defining them as the positive integers Some authors acknowledge both definitions whenever convenient. Sometimes, the whole numbers are the natural numbers as well as zero. In other cases, the ''whole numbers'' refer to all of the integers, including negative integers. The counting numbers are another term for the natural numbers, particularly in primary education, and are ambiguous as well although typically start at 1. The natural numbers are used for counting things, like "there are ''six'' coins on the table", in which case they are called ''cardinal numbers''. They are also used to put things in order, like "this is the ''third'' largest city in the country", which are called ''ordinal numbers''. Natural numbers are also used as labels, like Number (sports), jersey ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Random Variable
A random variable (also called random quantity, aleatory variable, or stochastic variable) is a Mathematics, mathematical formalization of a quantity or object which depends on randomness, random events. The term 'random variable' in its mathematical definition refers to neither randomness nor variability but instead is a mathematical function (mathematics), function in which * the Domain of a function, domain is the set of possible Outcome (probability), outcomes in a sample space (e.g. the set \ which are the possible upper sides of a flipped coin heads H or tails T as the result from tossing a coin); and * the Range of a function, range is a measurable space (e.g. corresponding to the domain above, the range might be the set \ if say heads H mapped to -1 and T mapped to 1). Typically, the range of a random variable is a subset of the Real number, real numbers. Informally, randomness typically represents some fundamental element of chance, such as in the roll of a dice, d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
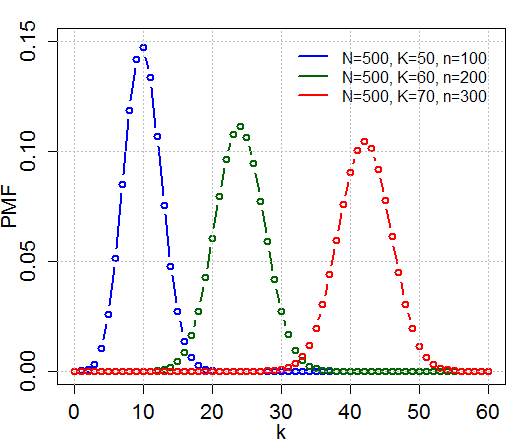
Hypergeometric Distribution
In probability theory and statistics, the hypergeometric distribution is a Probability distribution#Discrete probability distribution, discrete probability distribution that describes the probability of k successes (random draws for which the object drawn has a specified feature) in n draws, ''without'' replacement, from a finite Statistical population, population of size N that contains exactly K objects with that feature, wherein each draw is either a success or a failure. In contrast, the binomial distribution describes the probability of k successes in n draws ''with'' replacement. Definitions Probability mass function The following conditions characterize the hypergeometric distribution: * The result of each draw (the elements of the population being sampled) can be classified into one of Binary variable, two mutually exclusive categories (e.g. Pass/Fail or Employed/Unemployed). * The probability of a success changes on each draw, as each draw decreases the population ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |