|
Bicameral Mentality
Bicameral mentality is a hypothesis introduced by Julian Jaynes who argued human ancestors as late as the ancient Greeks did not consider emotions and desires as stemming from their own minds but as the consequences of actions of gods external to themselves. The theory posits that the human mind once operated in a state in which cognitive functions were divided between one part of the brain that appears to be "speaking" and a second part that listens and obeys—a ''bicameral mind''—and that the breakdown of this division gave rise to consciousness in humans. The term was coined by Jaynes, who presented the idea in his 1976 book '' The Origin of Consciousness in the Breakdown of the Bicameral Mind'', wherein he makes the case that a bicameral mentality was the normal and ubiquitous state of the human mind as recently as 3,000 years ago, at the end of the Mediterranean Bronze Age. ''The Origin of Consciousness in the Breakdown of the Bicameral Mind'' Jaynes uses "bicameral" (t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Julian Jaynes
Julian Jaynes (February 27, 1920 – November 21, 1997) was an American psychologist who worked at the universities of Yale and Princeton for nearly 25 years and became best known for his 1976 book '' The Origin of Consciousness in the Breakdown of the Bicameral Mind''. His work focused on the problem of consciousness: "the difference between what others see of us and our sense of our inner selves and the deep feelings that sustain it. ... Men have been conscious of the problem of consciousness almost since consciousness began." Jaynes's solution touches on many disciplines, including neuroscience, linguistics, psychology, archeology, history, religion and analysis of ancient texts. Early life Jaynes was born and lived in West Newton, Massachusetts, son of Julian Clifford Jaynes (1854–1922), a Unitarian minister, and Clara Bullard Jaynes (1884–1980). He had an older sister, Helen, and a younger brother, Robert. The family had a summer home in Keppoch, Prince Edward Is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Voice Hearing
An auditory hallucination, or paracusia, is a form of hallucination that involves perceiving sounds without auditory stimulus. While experiencing an auditory hallucination, the affected person hears a sound or sounds that did not come from the natural environment. A common form of auditory hallucination involves hearing one or more voices without a speaker present, known as an ''auditory verbal hallucination''. This may be associated with psychotic disorders, most notably schizophrenia, and this phenomenon is often used to diagnose these conditions. However, individuals without any psychiatric disease whatsoever may hear voices, including those under the influence of mind-altering substances, such as cannabis, cocaine, amphetamines, and PCP. There are three main categories into which the hearing of talking voices often fall: a person hearing a voice speak one's thoughts, a person hearing one or more voices arguing, or a person hearing a voice narrating their own actions. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deity
A deity or god is a supernatural being considered to be sacred and worthy of worship due to having authority over some aspect of the universe and/or life. The ''Oxford Dictionary of English'' defines ''deity'' as a God (male deity), god or goddess, or anything revered as divine. C. Scott Littleton defines a deity as "a being with powers greater than those of ordinary humans, but who interacts with humans, positively or negatively, in ways that carry humans to new Higher consciousness, levels of consciousness, beyond the grounded preoccupations of ordinary life". Religions can be categorized by how many deities they worship. Monotheism, Monotheistic religions accept only one deity (predominantly referred to as "God"), whereas Polytheism, polytheistic religions accept multiple deities. Henotheism, Henotheistic religions accept one God, supreme deity without denying other deities, considering them as aspects of the same divine principle. Nontheistic religions deny any supreme eter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iliad
The ''Iliad'' (; , ; ) is one of two major Ancient Greek epic poems attributed to Homer. It is one of the oldest extant works of literature still widely read by modern audiences. As with the ''Odyssey'', the poem is divided into 24 books and was written in dactylic hexameter. It contains 15,693 lines in its most widely accepted version. The ''Iliad'' is often regarded as the first substantial piece of Western literature, European literature and is a central part of the Epic Cycle. Set towards the end of the Trojan War, a ten-year siege of the city of Troy by a coalition of Mycenaean Greece, Mycenaean Greek states, the poem depicts significant events in the war's final weeks. In particular, it traces the anger () of Achilles, a celebrated warrior, from a fierce quarrel between him and King Agamemnon, to the death of the Trojan prince Hector.Homer, ''Iliad, Volume I, Books 1–12'', translated by A. T. Murray, revised by William F. Wyatt, Loeb Classical Library 170, Cambridge, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Homer
Homer (; , ; possibly born ) was an Ancient Greece, Ancient Greek poet who is credited as the author of the ''Iliad'' and the ''Odyssey'', two epic poems that are foundational works of ancient Greek literature. Despite doubts about his authorship, Homer is considered one of the most revered and influential authors in history. The ''Iliad'' centers on a quarrel between King Agamemnon and the warrior Achilles during the last year of the Trojan War. The ''Odyssey'' chronicles the ten-year journey of Odysseus, king of Homer's Ithaca, Ithaca, back to his home after the fall of Troy. The epics depict man's struggle, the ''Odyssey'' especially so, as Odysseus perseveres through the punishment of the gods. The poems are in Homeric Greek, also known as Epic Greek, a literary language that shows a mixture of features of the Ionic Greek, Ionic and Aeolic Greek, Aeolic dialects from different centuries; the predominant influence is Eastern Ionic. Most researchers believe that the poems w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interdisciplinary
Interdisciplinarity or interdisciplinary studies involves the combination of multiple academic disciplines into one activity (e.g., a research project). It draws knowledge from several fields such as sociology, anthropology, psychology, economics, etc. It is related to an ''interdiscipline'' or an ''interdisciplinary field,'' which is an organizational unit that crosses traditional boundaries between Outline of academic disciplines, academic disciplines or School of thought, schools of thought, as new needs and professions emerge. Large engineering teams are usually interdisciplinary, as a power station or mobile phone or other project requires the melding of several specialties. However, the term "interdisciplinary" is sometimes confined to academic settings. The term ''interdisciplinary'' is applied within education and training pedagogies to describe studies that use methods and insights of several established disciplines or traditional fields of study. Interdisciplinarity in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
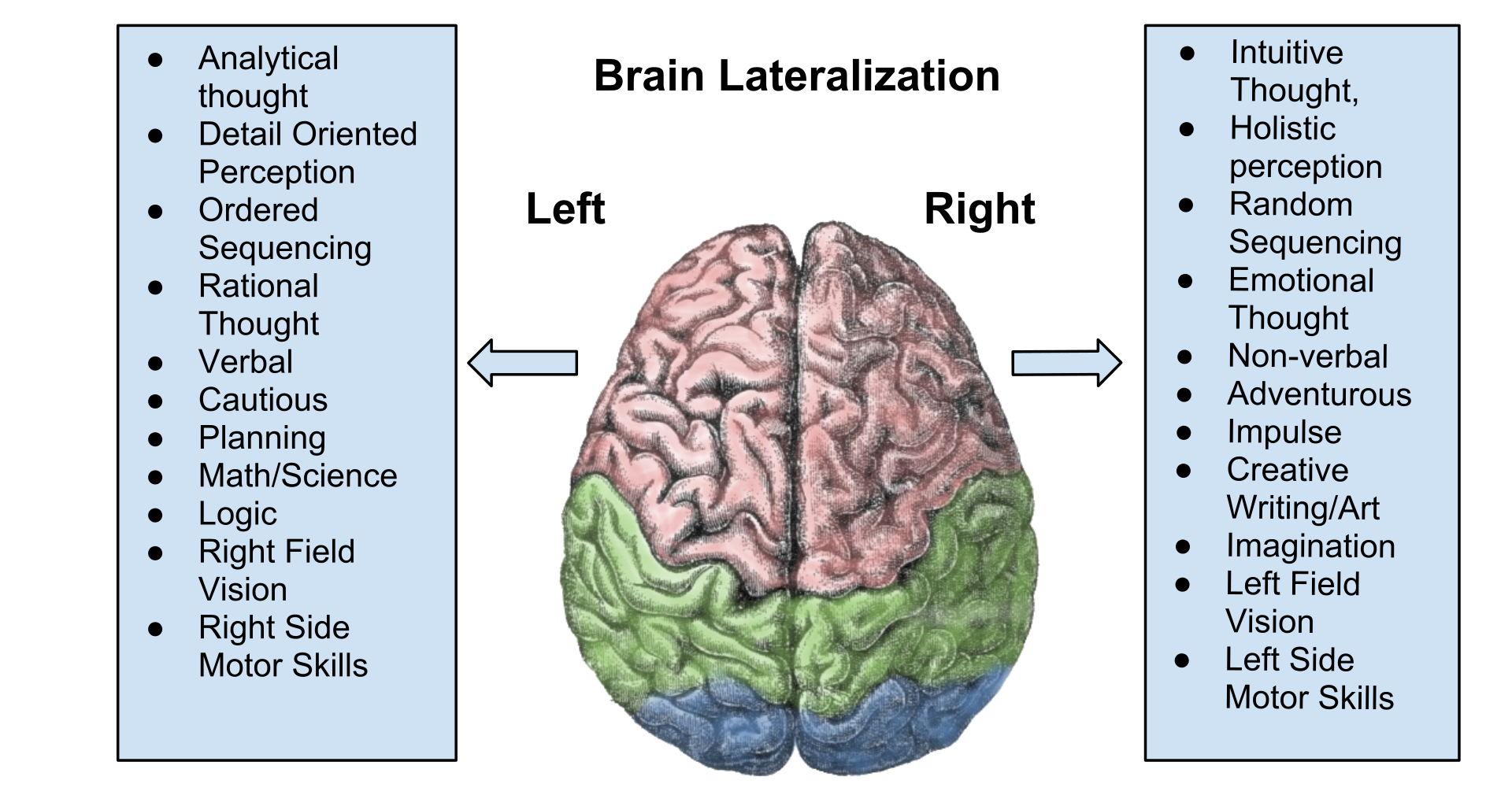
Left-brain Interpreter
The left-brain interpreter is a neuropsychological concept developed by the psychologist Michael S. Gazzaniga and the neuroscientist Joseph E. LeDoux. It refers to the construction of explanations by the left brain hemisphere in order to make sense of the world by reconciling new information with what was known before. The left-brain interpreter attempts to rationalize, reason and generalize new information it receives in order to relate the past to the present.''The Seven Sins of Memory: How the Mind Forgets and Remembers'' by Daniel L. Schacter 2002 page 15/ref> Left-brain interpretation is a case of the lateralization of brain function that applies to "explanation generation" rather than other lateralized activities.''The cognitive neuroscience of mind: a tribute to Michael S. Gazzaniga'' edited by Patricia A. Reuter-Lorenz, Kathleen Baynes, George R. Mangun, and Elizabeth A. Phelps; The MIT Press; 2010; ; pages 34-35 Although the concept of the left-brain interpreter was i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Split-brain
Split-brain or callosal syndrome is a type of disconnection syndrome when the corpus callosum connecting the two hemispheres of the brain is severed to some degree. It is an association of symptoms produced by disruption of, or interference with, the connection between the hemispheres of the brain. The surgical operation to produce this condition ( corpus callosotomy) involves transection of the corpus callosum, and is usually a last resort to treat refractory epilepsy. Initially, partial callosotomies are performed; if this operation does not succeed, a complete callosotomy is performed to mitigate the risk of accidental physical injury by reducing the severity and violence of epileptic seizures. Before using callosotomies, epilepsy is instead treated through pharmaceutical means. After surgery, neuropsychological assessments are often performed. After the right and left brain are separated, each hemisphere will have its own separate perception, concepts, and impulses to act ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Michael Gazzaniga
Michael S. Gazzaniga (born December 12, 1939) is an American Cognitive neuroscience, cognitive neuroscientist who is an emeritus professor of psychology at the University of California, Santa Barbara. He is the founder and retired director of the SAGE Center for the Study of the Mind at UCSB (2006–2023). Biography In 1961, Gazzaniga graduated from Dartmouth College with a B.A in Zoology. In 1964, he received a Ph.D. in psychobiology from the California Institute of Technology, where he carried out research on human split-brain patients for his doctoral thesis under Roger Sperry. In his subsequent work he has made important advances in our understanding of Lateralization of brain function, which functions are lateralized in the brain and how the left and right cerebral hemispheres communicate with one another. Career He has had a distinguished career in the field of cognitive neuroscience. Gazzaniga's academic career began as an assistant professor of psychology at University ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neuroscience
Neuroscience is the scientific study of the nervous system (the brain, spinal cord, and peripheral nervous system), its functions, and its disorders. It is a multidisciplinary science that combines physiology, anatomy, molecular biology, developmental biology, cytology, psychology, physics, computer science, chemistry, medicine, statistics, and mathematical modeling to understand the fundamental and emergent properties of neurons, glia and neural circuits. The understanding of the biological basis of learning, memory, behavior, perception, and consciousness has been described by Eric Kandel as the "epic challenge" of the biological sciences. The scope of neuroscience has broadened over time to include different approaches used to study the nervous system at different scales. The techniques used by neuroscientists have expanded enormously, from molecular and cellular studies of individual neurons to imaging of sensory, motor and cognitive tasks in the brain. Hist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oikos
''Oikos'' ( ; : ) was, in Ancient Greece, two related but distinct concepts: the family and the family's house. Its meaning shifted even within texts. The ''oikos'' was the basic unit of society in most Greek city-states. For regular Attic_Greek, Attic usage within the context of families, the ''oikos'' referred to a line of descent from father to son from generation to generation. Alternatively, as Aristotle used it in his ''Politics (Aristotle), Politics'', the term was sometimes used to refer to everybody living in a given house. Thus, the head of the ''oikos'', along with his immediate family and his slaves, would all be encompassed. Large ''oikoi'' also had farms that were usually tended by the slaves, which were also the basic agricultural unit of the Economy of ancient Greece, ancient Greek economy. House Traditional interpretations of the layout of the ''oikos'' in Classical Athens have divided into men's and women's spaces, with an area known as the ''gynaeceum, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Homeric Psychology
Homeric psychology is a field of study with regards to the psychology of ancient Greek culture no later than Mycenaean Greece, around 1700–1200 BCE, during the Homeric epic poems (specifically the '' Illiad'' and the ''Odyssey''). The first scholar to present a theory was Bruno Snell in his 1953 German book. He argued that an ancient Greek person did not have a sense of self, and the Greek culture later "self-realized" or "discovered" what he considered the "modern intellect". Eric Robertson Dodds in 1951 wrote how ancient Greek thought may have been irrational, relative to his. He posited that the Greeks may have known that a person did things, but the reason was attributed to divine externalities, such as gods and demons. Julian Jaynes Julian Jaynes (February 27, 1920 – November 21, 1997) was an American psychologist who worked at the universities of Yale and Princeton for nearly 25 years and became best known for his 1976 book '' The Origin of Consciousness in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |