|
Battles Of The Seven Years' War
The Seven Years' War, 1754–1763, spanned four continents, affecting Europe, the Americas, West Africa, and India and the Philippines, in Asia. The conflict split Europe into two coalitions: Kingdom of Great Britain, Kingdom of Prussia, Prussia, Kingdom of Portugal, Portugal, Electorate of Brunswick-Lüneburg, Hanover, and other small German states on one side ''versus'' the Kingdom of France, Habsburg monarchy, Austria-led Holy Roman Empire, Russian Empire, Russia, Bourbon Spain, Spain, several small German states, and Sweden on the other. The coalitions represented a "revolution" in diplomatic alliances, reflected in the Diplomatic Revolution. Ultimately, the victory of the Anglo-Prussian coalition undercut the balance of power in Europe, a balance that was not reestablished until Congress of Vienna, 1815. Situation Although Anglo-French skirmishes over their American colonies had already begun in 1754, the seven year long large-scale war that drew in most of the European power ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seven Years' War
The Seven Years' War, 1756 to 1763, was a Great Power conflict fought primarily in Europe, with significant subsidiary campaigns in North America and South Asia. The protagonists were Kingdom of Great Britain, Great Britain and Kingdom of Prussia, Prussia versus Kingdom of France, France and Habsburg monarchy, Austria, the respective coalitions receiving by countries including Portuguese Empire, Portugal, Spanish Empire, Spain, Electorate of Saxony, Saxony, Age of Liberty, Sweden, and Russian Empire, Russia. Related conflicts include the Third Silesian War, French and Indian War, Carnatic wars, Third Carnatic War, Anglo-Spanish War (1762–1763), Anglo-Spanish War (1762–1763), and Spanish–Portuguese War (1762–1763), Spanish–Portuguese War. Although the War of the Austrian Succession ended with the Treaty of Aix-la-Chapelle (1748), none of the signatories were happy with the terms, and it was generally viewed as a temporary armistice. It led to a strategic realignment kn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Congress Of Vienna
The Congress of Vienna of 1814–1815 was a series of international diplomatic meetings to discuss and agree upon a possible new layout of the European political and constitutional order after the downfall of the French Emperor Napoleon, Napoleon Bonaparte. Participants were representatives of all European powers (other than the Ottoman Empire) and other stakeholders. The Congress was chaired by Austrian Empire, Austrian statesman Klemens von Metternich, and was held in Vienna from September 1814 to June 1815. The objective of the Congress was to provide a long-term peace plan for Europe by settling critical issues arising from the French Revolutionary Wars and the Napoleonic Wars through negotiation. The goal was not simply to restore old boundaries, but to resize the main powers so they could European balance of power, balance each other and remain at peace, being at the same time shepherds for the smaller powers. More generally, conservative leaders like Metternich also soug ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Senegal
Senegal, officially the Republic of Senegal, is the westernmost country in West Africa, situated on the Atlantic Ocean coastline. It borders Mauritania to Mauritania–Senegal border, the north, Mali to Mali–Senegal border, the east, Guinea to Guinea–Senegal border, the southeast and Guinea-Bissau to Guinea-Bissau–Senegal border, the southwest. Senegal nearly surrounds The Gambia, a country occupying a narrow sliver of land along the banks of the Gambia River, which separates Senegal's southern region of Casamance from the rest of the country. It also shares a maritime border with Cape Verde. Senegal's capital is Dakar. Senegal is the westernmost country in the mainland of the Old World, or Afro-Eurasia. It owes its name to the Senegal River, which borders it to the east and north. The climate is typically Sahelian, though there is a wet season, rainy season. Senegal covers a land area of almost and has a population of around 18 million. The state is a Presidential system ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gorée
(; "Gorée Island"; ) is one of the 19 (i.e. districts) of the city of Dakar, Senegal. It is an island located at sea from the main harbour of Dakar (), famous as a destination for people interested in the Atlantic slave trade. Its population as of the 2013 census was 1,680 inhabitants, giving a density of , which is only half the average density of the city of Dakar. Gorée is both the smallest and the least populated of the 19 of Dakar. Other important centres for the slave trade from Senegal were further north, at Saint-Louis, Senegal, or to the south in the Gambia, at the mouths of major rivers for trade.''Les Guides Bleus: Afrique de l'Ouest'' (1958 ed.), p. 123 It is a UNESCO World Heritage Site and was one of the first 12 locations in the world to be designated as such in 1978. The name is a corruption of its original Dutch language, Dutch name Goeree, named after the Dutch island of Goeree-Overflakkee, Goeree. The island was also known as Palma, or in Portuguese. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
West Indies
The West Indies is an island subregion of the Americas, surrounded by the Atlantic Ocean, North Atlantic Ocean and the Caribbean Sea, which comprises 13 independent island country, island countries and 19 dependent territory, dependencies in three archipelagos: the Greater Antilles, the Lesser Antilles, and the Lucayan Archipelago. The subregion includes all the islands in the Antilles, in addition to The Bahamas and the Turks and Caicos Islands, which are in the Atlantic Ocean, North Atlantic Ocean. The term is often interchangeable with "Caribbean", although the latter may also include coastal regions of Central America, Central and South American mainland nations, including Mexico, Belize, Honduras, Panama, Colombia, Venezuela, French Guiana, Guyana, and Suriname, as well as the Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic island nation of Bermuda, all of which are geographically distinct from the three main island groups, but culturally related. Terminology The English term ''Indie'' is deri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iroquois
The Iroquois ( ), also known as the Five Nations, and later as the Six Nations from 1722 onwards; alternatively referred to by the Endonym and exonym, endonym Haudenosaunee ( ; ) are an Iroquoian languages, Iroquoian-speaking Confederation#Indigenous confederations in North America, confederacy of Native Americans in the United States, Native Americans and First Nations in Canada, First Nations peoples in northeast North America. They were known by the French during the Colonial history of the United States, colonial years as the Iroquois League, and later as the Iroquois Confederacy, while the English simply called them the "Five Nations". Their country has been called wikt:Iroquoia, Iroquoia and Haudenosauneega in English, and '':fr:Iroquoisie, Iroquoisie'' in French. The peoples of the Iroquois included (from east to west) the Mohawk people, Mohawk, Oneida people, Oneida, Onondaga people, Onondaga, Cayuga people, Cayuga, and Seneca people, Seneca. After 1722, the Iroquoian-sp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
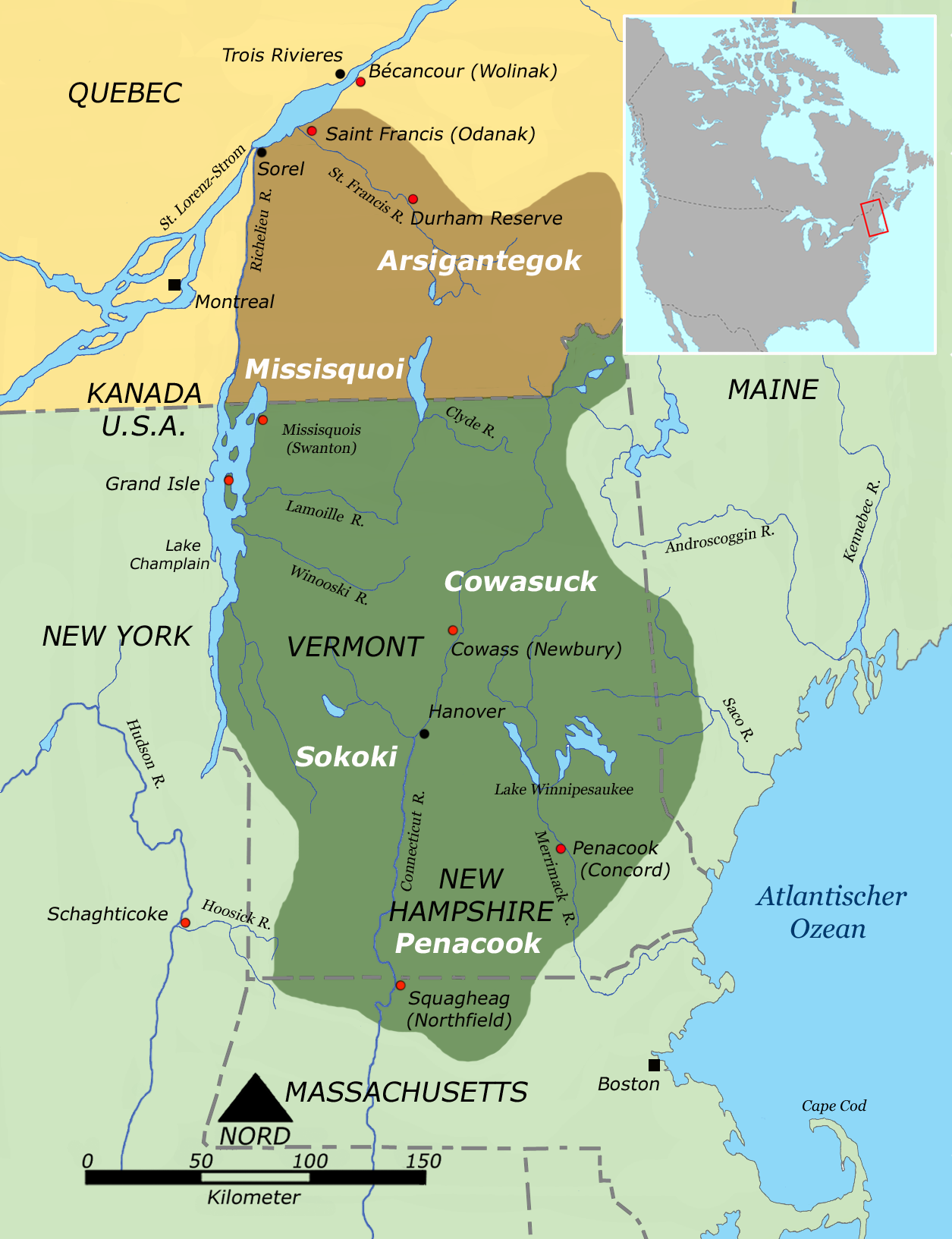
Abenaki
The Abenaki ( Abenaki: ''Wαpánahki'') are Indigenous people of the Northeastern Woodlands of Canada and the United States. They are an Algonquian-speaking people and part of the Wabanaki Confederacy. The Eastern Abenaki language was predominantly spoken in Maine, while the Western Abenaki language was spoken in Quebec, Vermont, and New Hampshire. While Abenaki peoples have shared cultural traits, they did not historically have a centralized government. They came together as a post-contact community after their original tribes were decimated by colonization, disease, and warfare. Names The word ''Abenaki'' and its syncope, ''Abnaki,'' are both derived from ''Wabanaki'', or ''Wôbanakiak,'' meaning "People of the Dawn Land" in the Abenaki language. While the two terms are often confused, the Abenaki are one of several tribes in the Wabanaki Confederacy. Alternate spellings include: ''Abnaki'', ''Abinaki'', ''Alnôbak'', ''Abanakee'', ''Abanaki'', ''Abanaqui'', ''Abana ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indigenous Peoples
There is no generally accepted definition of Indigenous peoples, although in the 21st century the focus has been on self-identification, cultural difference from other groups in a state, a special relationship with their traditional territory, and an experience of subjugation and discrimination under a dominant cultural model. Estimates of the population of Indigenous peoples range from 250 million to 600 million. There are some 5,000 distinct Indigenous peoples spread across every inhabited climate zone and inhabited continent of the world. Most Indigenous peoples are in a minority in the state or traditional territory they inhabit and have experienced domination by other groups, especially non-Indigenous peoples. Although many Indigenous peoples have experienced colonization by settlers from European nations, Indigenous identity is not determined by Western colonization. The rights of Indigenous peoples are outlined in national legislation, treaties and international law ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Landgraviate Of Hesse-Kassel
The Landgraviate of Hesse-Kassel (), spelled Hesse-Cassel during its entire existence, also known as the Hessian Palatinate (), was a state of the Holy Roman Empire. The state was created in 1567 when the Landgraviate of Hesse was divided upon the death of Philip I, Landgrave of Hesse. His eldest son William IV inherited the northern half of the Landgraviate and the capital of Kassel. The other sons received the Landgraviates of Hesse-Marburg, Hesse-Rheinfels and Hesse-Darmstadt. During the Napoleonic reorganisation of the Empire in 1803, the Landgrave of Hesse-Kassel was elevated to an Electorate and Landgrave William IX became an Imperial Elector. Many members of the House of Hesse-Kassel served in the Danish military, gaining high ranks and power in the realm because many Landgraves were married to Danish princesses. Members of the family who are known to have served Denmark-Norway include Prince Frederik of Hesse-Kassel, Prince Frederick of Hesse-Kassel, and Prince ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Personal Union
A personal union is a combination of two or more monarchical states that have the same monarch while their boundaries, laws, and interests remain distinct. A real union, by contrast, involves the constituent states being to some extent interlinked, such as by sharing some limited governmental institutions. Unlike a personal union, in a federation or a unitary state, a central (federal) government spanning all member states exists, with the degree of self-governance distinguishing the two. The ruler in a personal union does not need to be a hereditary monarch. The term was coined by German jurist Johann Stephan Pütter, introducing it into ''Elementa iuris publici germanici'' (Elements of German Public Law) of 1760. Personal unions can arise for several reasons, such as: * inheritance through a dynastic union, e.g. Louis X of France inherited France France, officially the French Republic, is a country located primarily in Western Europe. Overseas France, Its ov ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |