|
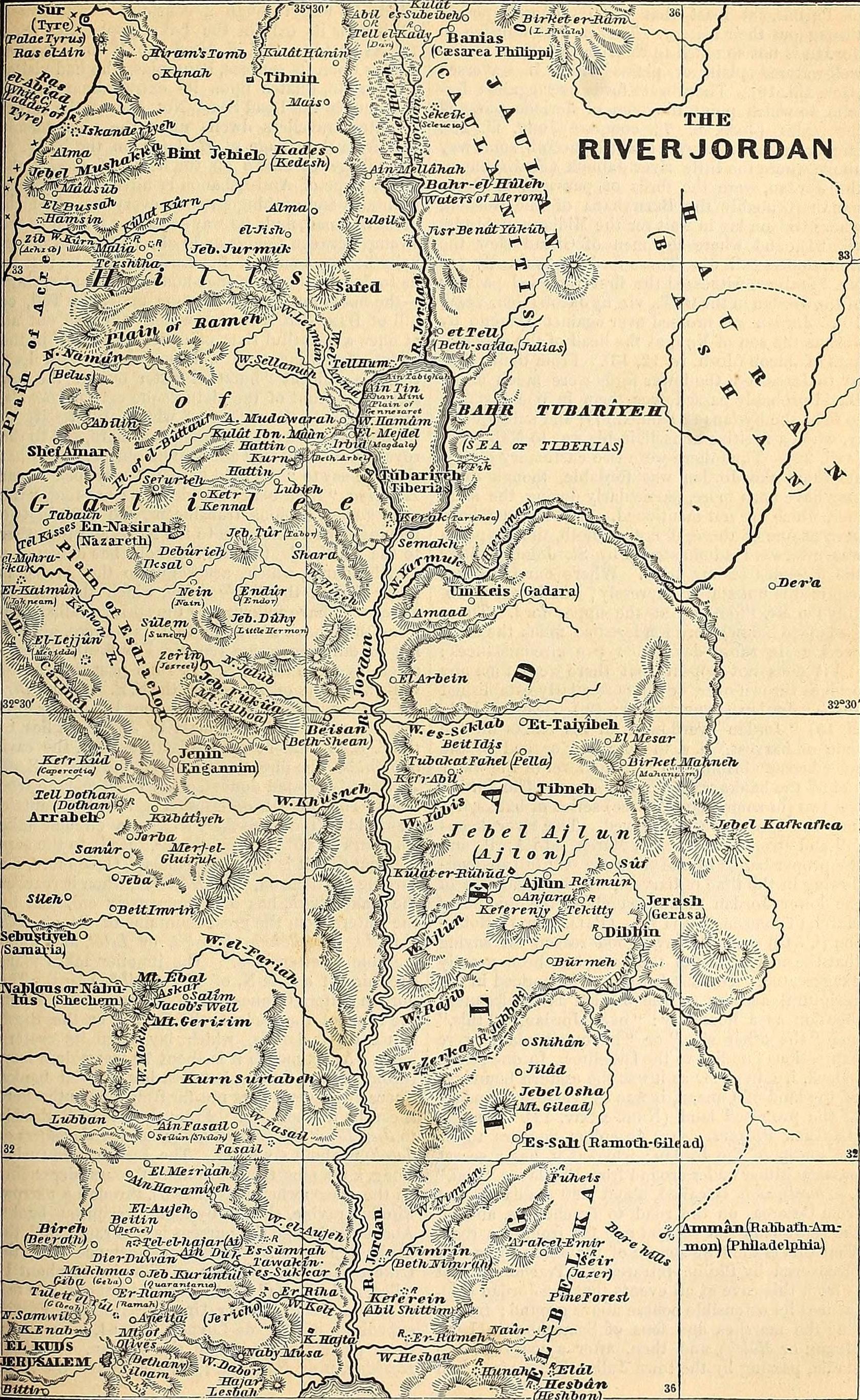
Battle Of Uqḥuwāna
The Battle of al-Uqhuwana () was fought at a place east of Lake Tiberias in May 1029 between the Fatimid Caliphate under general Anushtakin al-Dizbari and a coalition of Syrian Bedouin tribes. The latter was represented by the Tayy tribe of Palestine led by the Jarrahid emir Hassan ibn al-Mufarrij and the Kilab tribe of Aleppo under the Mirdasid emir Salih ibn Mirdas. The Fatimids were backed by one of the Bedouin coalition's former constituent tribes, the Kalb under the emir Rafi ibn Abi'l-Layl. The battle ended in the Fatimids' most decisive victory over the Bedouin tribes of Syria. Salih was slain and the Mirdasids' quickly lost several strategic towns, while Hassan and the Tayy long retreated from their traditional stomping grounds. Fatimid rule was consequently reasserted over Palestine and southern Syria, including Damascus, after years of Bedouin domination since 1024. Location Al-Uqhuwana was located off the eastern shore of Lake Tiberias. It was close to where the Riv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sea Of Galilee
The Sea of Galilee (, Judeo-Aramaic languages, Judeo-Aramaic: יַמּא דטבריא, גִּנֵּיסַר, ), also called Lake Tiberias, Genezareth Lake or Kinneret, is a freshwater lake in Israel. It is the lowest freshwater lake on Earth and the second-lowest lake in the world (after the Dead Sea, a salt lake), with its elevation fluctuating between below sea level (depending on rainfall). It is approximately in circumference, about long, and wide. Its area is at its fullest, and its maximum depth is approximately .Data Summary: Lake Kinneret (Sea of Galilee) The lake is fed partly by underground springs, but its main source is the Jordan River, which flows through it from north to south with the outflow controlled by the Degania Dam. |
Hassan Ibn Al-Mufarrij
Hassan, Hasan, Hassane, Haasana, Hassaan, Asan, Hassun, Hasun, Hassen, Hasson or Hasani may refer to: People *Hassan (given name), Arabic given name and a list of people with that given name *Hassan (surname), Arabic, Jewish, Irish, and Scottish surname and a list of people with that surname Places *Hassan (crater), an impact crater on Enceladus, a moon of Saturn Africa * Abou El Hassan District, Algeria *Hassan Tower, the minaret of an incomplete mosque in Rabat, Morocco *Hassan I Dam, on the Lakhdar River in Morocco *Hassan I Airport, serving El Aaiún, Western Sahara Americas *Chanhassen, Minnesota, a city in Minnesota, United States *Hassan Township, Minnesota, a city in Minnesota, United States Asia *Hassan, Karnataka, a city and district headquarters in Karnataka, India **Hassan District, a district headquartered in Karnataka, India **Hassan (Lok Sabha constituency) **Hassan Airport, Karnataka *Hasan, Ilam, a village in Ilam Province, Iran *Hasan, North Khorasan, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jund Dimashq
''Jund Dimashq'' () was the largest of the sub-provinces (''ajnad'', sing. '' jund''), into which Syria was divided under the Umayyad and Abbasid dynasties. It was named after its capital and largest city, Damascus ("Dimashq"), which in the Umayyad period was also the capital of the Caliphate. Geography and administrative division Unlike any other province of the Caliphate, Syria was divided by the early Umayyads into several (originally four, later five) sub-provinces or ''ajnad'' (singular '' jund'', "army division"), which in their original inception were the areas from which a particular army division drew its pay, provisions and recruits. The province of Damascus, ''jund Dimashq'', was the largest of the ''ajnad'', comprising most of central Syria. Its borders encompassed roughly the former Byzantine provinces of Phoenice Prima, Phoenice Libanensis, and Arabia. Later Arab geographers divide the ''jund'' of Damascus into the following districts: the Ghuta plain around Da ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cairo
Cairo ( ; , ) is the Capital city, capital and largest city of Egypt and the Cairo Governorate, being home to more than 10 million people. It is also part of the List of urban agglomerations in Africa, largest urban agglomeration in Africa, List of largest cities in the Arab world, the Arab world, and List of largest metropolitan areas of the Middle East, the Middle East. The Greater Cairo metropolitan area is List of largest cities, one of the largest in the world by population with over 22.1 million people. The area that would become Cairo was part of ancient Egypt, as the Giza pyramid complex and the ancient cities of Memphis, Egypt, Memphis and Heliopolis (ancient Egypt), Heliopolis are near-by. Located near the Nile Delta, the predecessor settlement was Fustat following the Muslim conquest of Egypt in 641 next to an existing ancient Roman empire, Roman fortress, Babylon Fortress, Babylon. Subsequently, Cairo was founded by the Fatimid Caliphate, Fatimid dynasty in 969. It ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Al-Hakim Bi-Amr Allah
Abu Ali al-Mansur (; 13 August 985 – 13 February 1021), better known by his regnal name al-Hakim bi-Amr Allah (), was the sixth Fatimid caliph and 16th Ismaili imam (996–1021). Al-Hakim is an important figure in a number of Shia Ismaili sects, such as the world's 15 million Nizaris and 1–2 million Musta'lis, in addition to 2 million Druze. (''Which page?'') Histories of al-Hakim can prove controversial, as diverse views of his life and legacy exist. Historian Paul Walker writes "Ultimately, both views of him, the mad and despotic tyrant (like Germanic and Roman despots) irrationally given to killing those around him on a whim, and the ideal supreme ruler, divinely ordained and chosen, whose every action was just and righteous, were to persist, the one among his enemies and those who rebelled against him, and the other in the hearts of true believers, who, while perhaps perplexed by events, nonetheless remained avidly loyal to him to the end." Appraisals of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fatimid
The Fatimid Caliphate (; ), also known as the Fatimid Empire, was a caliphate extant from the tenth to the twelfth centuries CE under the rule of the Fatimid dynasty, Fatimids, an Isma'ili Shi'a dynasty. Spanning a large area of North Africa and West Asia, it ranged from the western Mediterranean Sea, Mediterranean in the west to the Red Sea in the east. The Fatimids traced their ancestry to the Islamic prophet Muhammad's daughter Fatima and her husband Ali, the first Shia, Shi'a imam. The Fatimids were acknowledged as the rightful imams by different Isma'ili communities as well as by denominations in many other Muslim lands and adjacent regions. Originating during the Abbasid Caliphate, the Fatimids initially conquered Ifriqiya (roughly present-day Tunisia and north-eastern Algeria). They extended their rule across the Mediterranean coast and ultimately made Egypt the center of the caliphate. At its height, the caliphate included—in addition to Egypt—varying areas of the M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Karaite Judaism
Karaite Judaism or Karaism is a Rabbinic Judaism, non-Rabbinical Jewish religious movements, Jewish sect characterized by the recognition of the written Tanakh alone as its supreme religious text, authority in ''halakha'' (religious law) and theology. Karaites believe that all of the Mitzvah, divine commandments which were handed down to Moses by God were recorded in the written Torah without any additional Oral Torah, Oral Law or explanation. Unlike mainstream Rabbinic Judaism, which regards the Oral Torah, codified in the Talmud and subsequent works, as authoritative interpretations of the Torah, Karaite Jews do not treat the written collections of the oral tradition in the Midrash or the Talmud as binding. Karaite interpretation of the Torah strives to adhere to the plain or most obvious meaning (''peshat'') of the text; this is not necessarily the literal meaning of the text—instead, it is the meaning of the text that would have been naturally understood by the ancient He ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moshe Gil
Moshe Gil (; February 8, 1921 – January 23, 2014) was an Israeli historian. Academic career Moshe Gil specialized in the historical interaction between Islam and the Jews, including the history of Palestine under Islamic rule, the institution of the Exilarchate, and Jewish merchants such as the Radhanites. Gil was professor emeritus of the Chaim Rosenberg School of Jewish Studies at Tel Aviv University and held the Joseph and Ceil Mazer Chair in the History of the Jews in Muslim Lands. Awards In 1998, Gil was awarded the Israel Prize, for Land of Israel studies, primarily for his work analyzing some 846 document fragments from the Cairo Genizah and for his work in documenting the role of Jewish merchants in the development of medieval society. Published works *(1997) "The Babylonian Encounter and the Exilarchic House in the Light of Cairo Geniza Documents and Parallel Arab Sources." (Conference Paper in ''Proceedings: Judaeo-Arabic studies proceedings of the Founding Confer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beisan
Beit She'an ( '), also known as Beisan ( '), or Beth-shean, is a town in the Northern District of Israel. The town lies at the Beit She'an Valley about 120 m (394 feet) below sea level. Beit She'an is believed to be one of the oldest cities in the region. It has played an important role in history due to its geographical location at the junction of the Jordan River Valley and the Jezreel Valley. Beth She'an's ancient tell contains remains beginning in the Chalcolithic period. When Canaan came under Imperial Egyptian rule in the Late Bronze Age, Beth She'an served as a major Egyptian administrative center. The city came under Israelite rule in the monarchic period. It probably fell under Philistine control during the time of Saul, when, according to the Bible, his body was displayed there along with his sons. During the Hellenistic period, the settlement was known as Scythopolis (Ancient Greek: ''Σκυθόπολις''). After the region came under Roman rule, Scythopoli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fiq, Syria
Fiq () was a Syrian town in the Golan Heights that administratively belonged to Quneitra Governorate. It sat at an altitude of and had a population of 2,800 in 1967. It was the administrative center of the Fiq District, the southern district of the Golan. Fiq was evacuated during and after the Six-Day War in June 1967. The Israeli settlement of Kibbutz Afik was built close by. History Fiq was an ancient town covering about 100 dunams on a tell (archaeological mound). The surveys and limited excavations undertaken at the site have produced a small number of sherds from the Middle Bronze Age II, Hellenistic, and Middle Roman periods, whereas most of the finds were dated to the Byzantine, Umayyad, Abbasid and Mamluk periods. Late antiquity Fiq was identified by the 4th-century writer Eusebius with biblical Aphek. During late antiquity, Fiq had a mixed population of Christians, Jews and pagans. Many inscriptions in Latin and Greek have been found at the site. One of these i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
River Jordan
The Jordan River or River Jordan (, ''Nahr al-ʾUrdunn''; , ''Nəhar hayYardēn''), also known as ''Nahr Al-Sharieat'' (), is a endorheic basin, endorheic river in the Levant that flows roughly north to south through the Sea of Galilee and drains to the Dead Sea. The river passes by or through Jordan, Syria, Israel, and the Palestinian territories. Jordan and the Israeli occupied territories, Israeli-occupied Golan Heights border the river to the east, while Israel and the Israeli-occupied West Bank lie to its west. Both Jordan and the West Bank derive their names in relation to the river. The river holds major significance in Judaism and Christianity. According to the Bible, the Israelites crossed it into the Promised Land and Jesus, Jesus of Nazareth Baptism of Jesus, was baptized by John the Baptist in it. Etymology Several hypotheses for the origin of most of the river's names in modern languages (e.g., Jordan, Yarden, Urdunn), one is that it comes from Semitic 'Yard, on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Damascus
Damascus ( , ; ) is the capital and List of largest cities in the Levant region by population, largest city of Syria. It is the oldest capital in the world and, according to some, the fourth Holiest sites in Islam, holiest city in Islam. Known colloquially in Syria as () and dubbed, poetically, the "City of Jasmine" ( ), Damascus is a major cultural center of the Levant and the Arab world. Situated in southwestern Syria, Damascus is the center of a large metropolitan area. Nestled among the eastern foothills of the Anti-Lebanon mountain range inland from the eastern shore of the Mediterranean on a plateau above sea level, Damascus experiences an arid climate because of the rain shadow effect. The Barada, Barada River flows through Damascus. Damascus is one of the List of oldest continuously inhabited cities, oldest continuously inhabited cities in the world. First settled in the 3rd millennium BC, it was chosen as the capital of the Umayyad Caliphate from 661 to 750. Afte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |