|
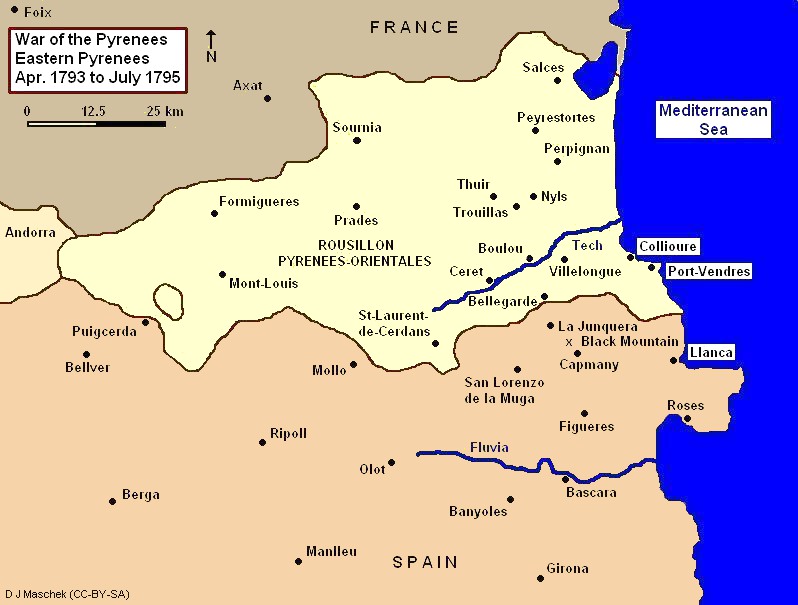
Battle Of Sant Llorenç De La Muga
The Battle of Sant Llorenç de la Muga (in Catalan, in ) was fought on 13 August 1794 between an attacking Spanish–Portuguese army led by the Conde de la Unión and a French army commanded by Jacques François Dugommier. The local French defenders headed by Pierre Augereau and Dominique Pérignon repulsed the allies. The Spanish garrison of Fort de Bellegarde surrendered a month later. Background In 1793 the Spanish army defeated the ill-trained French armies where the Franco-Spanish border touches the Mediterranean Sea. The Siege of Bellegarde resulted in the surrender of the fort to the Spanish army on 24 June. The Spanish army won the Battle of Truillas and several other actions, and seized the port of Collioure in December. In January 1794, the Army of the Eastern Pyrenees received a new commander in General of Division Jacques François Dugommier. Fresh from his triumph at the Siege of Toulon, the new leader reorganized the army. Dugommier set up supply depots, est ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
War Of The Pyrenees
The War of the Pyrenees, also known as War of Roussillon or War of the Convention, was the Pyrenees, Pyrenean front of the First Coalition's war against the First French Republic. It pitted Revolutionary France against the kingdoms of History of Spain (1700–1810), Spain and Kingdom of Portugal, Portugal from March 1793 to July 1795 during the French Revolutionary Wars. The war was fought in the eastern and western Pyrenees, at the French port of Toulon, and at sea. In 1793, a Spanish army invaded Roussillon in the eastern Pyrenees and maintained itself on French soil through April 1794. The French Revolutionary Army drove the Spanish Army back into Catalonia and inflicted a serious defeat in November 1794. After February 1795, the war in the eastern Pyrenees became a stalemate. In the western Pyrenees, the French began to win in 1794. By 1795, the French army controlled a portion of northeast Spain. The war was brutal in at least two ways. The Committee of Public Safety dec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siege Of Bellegarde (1793)
The siege of Bellegarde commenced on 23 May 1793 and ended on 24 June 1793 when Colonel Boisbrulé's French garrison surrendered the Fort de Bellegarde to a Spanish army under the command of Antonio Ricardos. The capture of the fort gave Spain control of an important road through the Pyrenees. The siege took place during the War of the Pyrenees, part of the French Revolutionary Wars. Fort de Bellegarde is on a height overlooking the border town of Le Perthus, which lies on the modern A9 autoroute and Autovía A-7. Background King Louis XIV of France built Fort de Bellegarde after 1678 according to a plan drawn up by Sébastien de Vauban. This strong masonry fortress defended the Col du Perthus which crosses the Pyrenees at an altitude of . The pass is the most important route from Spain into France in the eastern Pyrenees. As Vauban noted, "Nothing overlooks this place", and the fortress is situated on the highest ground in the area. When Spain went to war with revolu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Militia
A militia ( ) is a military or paramilitary force that comprises civilian members, as opposed to a professional standing army of regular, full-time military personnel. Militias may be raised in times of need to support regular troops or serve as a pool of available manpower for regular forces to draw from. When acting independently, militias are generally unable to hold ground against regular forces. Militias commonly support regular troops by skirmishing, holding fortifications, or conducting irregular warfare, instead of undertaking offensive campaigns by themselves. However, militias may also engage in defense activities to protect a community, its territory, property, and laws. For example, naval militias may comprise fishermen and other civilians which are organized and sanctioned by a state to enforce its maritime boundaries. Beginning in the late 20th century, some militias (in particular officially recognized and sanctioned militias of a government) act as profe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eastern Theater Pyrenees War 1793 To 1795
Eastern or Easterns may refer to: Transportation Airlines *China Eastern Airlines, a current Chinese airline based in Shanghai * Eastern Air, former name of Zambia Skyways *Eastern Air Lines, a defunct American airline that operated from 1926 to 1991 * Eastern Air Lines (2015), an American airline that began operations in 2015 *Eastern Airlines, LLC, previously Dynamic International Airways, a U.S. airline founded in 2010 *Eastern Airways, an English/British regional airline *Eastern Provincial Airways, a defunct Canadian airline that operated from 1949 to 1986 Roads *Eastern Avenue (other), various roads *Eastern Parkway (other), various parkways * Eastern Freeway, Melbourne, Australia *Eastern Freeway Mumbai, Mumbai, India Other *Eastern Railway (other), various railroads *, a cargo liner in service 1946-65 Education *Eastern University (other) *Eastern College (other) Sports * Easterns (cricket team), South African c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
La Junquera
La Jonquera (; ) is a municipality in the ''comarca'' of l'Alt Empordà, in Catalonia, Spain. It is situated next to the border with Northern Catalonia, nowadays France, opposite the municipality of Le Perthus. History The area has always been an important passage through the Pyrenees. The contemporary AP-7 highway extends not far from the ancient Roman road, the Via Augusta. Nearby there is an altar erected by Pompey on the Coll de Panissars. The name comes precisely from the Roman mansion of Iuncaria, which is not located under the current population but several kilometers away, in Figueras.6 La Junquera was the scene of a conflict involving retreating French crusaders in 1285 that ended in their defeat. From the 13th century until the end of the manorial regime, in the mid-19th century, it was the possession of the Rocabertí family. The Treaty of the Pyrenees (1659) placed the new border between the Spanish and French monarchies in the Albera mountain range, a fact that mar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Boulou
The Second Battle of Boulou (29 April to 1 May 1794) took place during the War of the Pyrenees, part of the French Revolutionary Wars. This battle saw the French Army of the Eastern Pyrenees led by General of Division (GD) Jacques François Dugommier attack the joint Spanish-Portuguese Army of Catalonia under Lieutenant General (LG) Luis Fermín de Carvajal, Conde de la Unión. Dugommier's decisive victory resulted in the French regaining nearly all the land they lost to the Kingdom of Spain in 1793. The town of Le Boulou is on the Tech River south of the department capital at Perpignan and north of the France–Spain border. The spring of 1794 found the Spanish army holding a slice of French territory south of the Tech River and north of the Pyrenees. The Spanish right wing on the Mediterranean coast was separated from the center and left wing by a mountainous gap. First, Dugommier mounted a successful feint with his right wing that drew Spanish troops away from the c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
André De La Barre
André de La Barre (; 30 November 1749 – 7 June 1794) was born in New France and joined France's colonial forces at a very young age. In 1764, he trained as an artillerist, but transferred to a cavalry unit as a volunteer three years later. In 1772 he officially joined the French Royal Army as a sous lieutenant of dragoons. In 1779, he was wounded at Savannah in the American Revolutionary War. By 1788, he was a staff officer with the rank of major. The start of the War of the First Coalition allowed officers chances for rapid advancement. Named a general of brigade in August 1793, La Barre fought at Toulon that year. Going to the Army of the Eastern Pyrenees, he distinguished himself at Boulou in May 1794. He was killed leading his cavalrymen in action at La Junquera on 7 June 1794. Early career André de La Barre was born on 30 November 1749 in "''le fort de Missouri (Etats-Unis)''" in New France.The statement, "The fort of Missouri", is vague as to the actual location. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pierre François Sauret
Pierre François Sauret de la Borie (23 March 1742, Gannat, Allier – 24 June 1818) led a combat division under the command of Napoleon Bonaparte during the Castiglione Campaign in 1796. He enlisted in the French army as a private in 1756. During the Seven Years' War he fought at Hastenbeck and Rossbach. He became a first lieutenant in 1789 and a lieutenant colonel in 1792. Assigned to the Army of the Eastern Pyrenees, served with distinction during the War of the Pyrenees against Spain. He was promoted to general officer in 1793 and became one of three infantry division commanders in the field army. He led his division at Palau, Boulou, Collioure, Black Mountain, Roses, and Bascara. He transferred to the Army of Italy in 1795. Bonaparte called him a very good soldier, but unlucky. He retired from active military service in order to enter politics. Early career Born in Gannat on 23 March 1742, Sauret joined the French royal army in 1756 as an enlisted man in the Guyenne Re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Catherine-Dominique De Pérignon
Catherine-Dominique de Pérignon, 1st Marquis de Pérignon (, 31 May 1754 in Grenade – 25 December 1818) was a French general during the French Revolutionary Wars, and was appointed Marshal of the Empire in 1804 by Napoleon Bonaparte. Early life Pérignon was born to a family of the lesser nobility in Grenade-sur-Garonne, Languedoc. After a ''roturier'' appointment in the grenadier corps of the Aquitaine Regiment, he retired to his estate. Pérignon welcomed the French Revolution, and gained a seat in the Legislative Assembly (1791), where he sat on the Right, but soon resigned and made his military career during the French Revolutionary Wars. Revolutionary Wars From 1793 to 1795, Pérignon held commands in the Army of the Eastern Pyrenees, defeating the Spanish troops at the battle of Escola with "a sombre kind of energy". He succeeded Jacques François Dugommier as army commander after that general's death at the Battle of the Black Mountain. He successfully conclu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siege Of Toulon (1793)
The siege of Toulon (29 August – 19 December 1793) was a military engagement that took place during the Federalist revolts and the War of the First Coalition, part of the French Revolutionary Wars. It was undertaken by forces of the French Republic against Royalist rebels supported by Anglo-Spanish forces in the southern French city of Toulon. It was during this siege that young Napoleon Bonaparte first won fame and promotion when his plan, involving the capture of fortifications above the harbour, was credited with forcing the city to capitulate and the Anglo-Spanish fleet to withdraw. The siege marked the first involvement of the British Royal Navy with the French Revolution. Background After the arrest of the Girondist deputies on the 2 June 1793, there followed a series of insurrections within the French cities of Lyon, Avignon, Nîmes, and Marseille known as Federalist revolts. In Toulon, the federalists evicted the local chapter of the Jacobin Club, but were soon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
General Of Division
Divisional general is a general officer rank who commands an army division. The rank originates from the French Revolutionary System, and is used by a number of countries. The rank is above a brigade general, and normally below an army corps general. The rank is mostly used in countries where it is used as a modern alternative to a previous older rank of major-general or lieutenant-general. Specific countries Brazil The Brazilian rank ''general-de-divisão'' translates literally as "general of division", and is used by the army. This rank is equivalent to lieutenant-general. The air force equivalent is ''major-brigadeiro''(literally "major-brigadier"). The navy equivalent is ''vice-almirante'' (literally, vice-admiral) Chile The Chilean rank ''general de división'' translates literally as "general of division", and is used by the army. This rank is equivalent to lieutenant-general. The air force equivalent is ''general de aviación'' (literally "aviation general"). These ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |