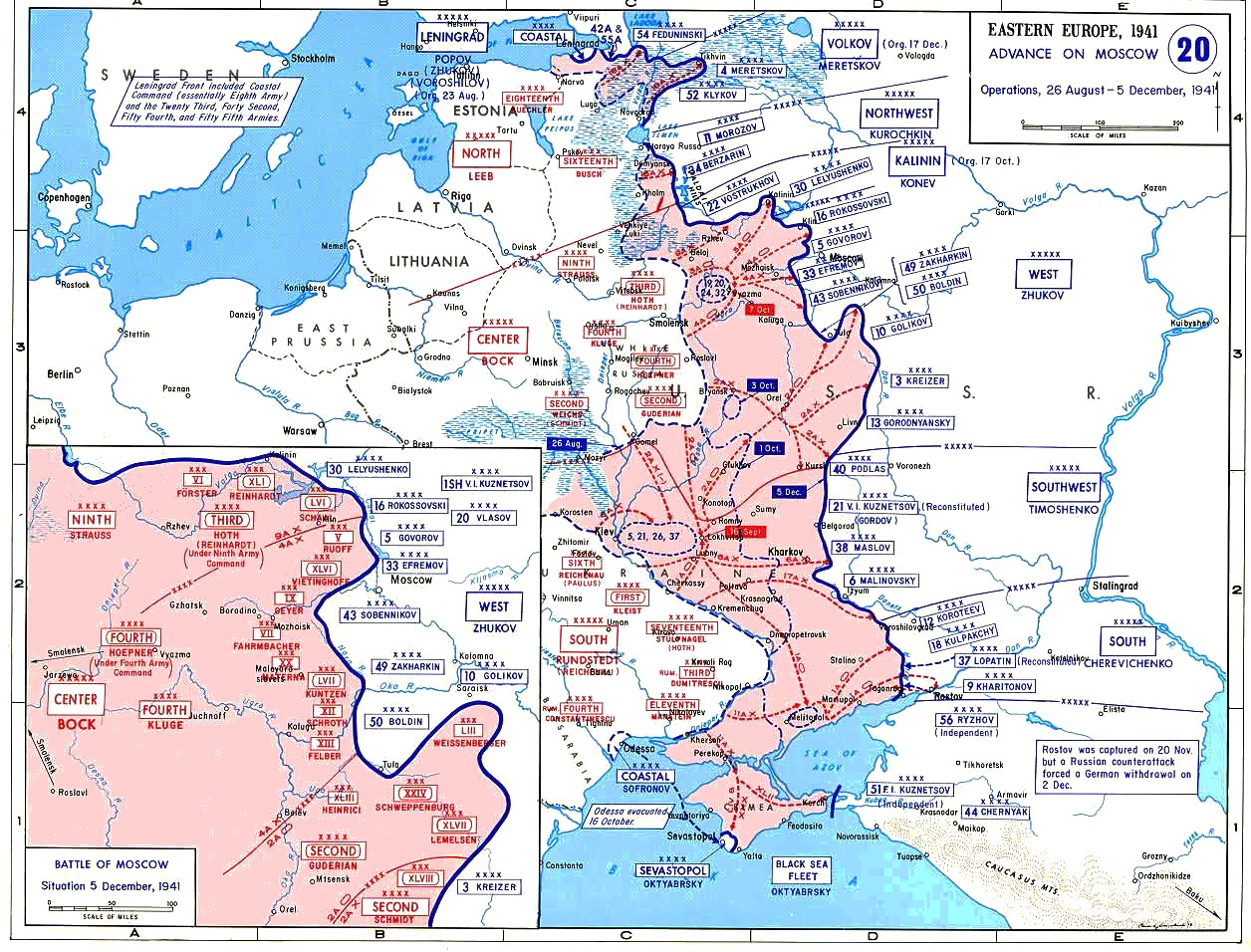
|
Battle Of Rostov (1941)
The Battle of Rostov (1941) took place on the Eastern Front of World War II around Rostov-on-Don and was fought between Army Group South of Nazi Germany and the Southern Front of the Soviet Union. The battle comprised three phases: the German Sea of Azov Offensive Operation by Army Group South (General Gerd von Rundstedt) (begun on 12 September 1941),p.87, Haupt, Army Group South the Soviet Rostov Defensive Operation (5 November 1941 – 16 November 1941) by the Southern Front (General Yakov Timofeyevich Cherevichenko), and the Rostov Offensive Operation (27 November 1941 – 2 December 1941) executed by the same Soviet Front. After forcing their way across the Mius River on 17 November, the German forces captured 10,000 Soviet troops and took Rostov on 21 November. Six days later the Southern Front, reinforced with the newly raised 37th Army, counterattacked from the north and threatened to surround the overstretched German III Motorized Army Corps. Rundstedt then order ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eastern Front (World War II)
The Eastern Front, also known as the Great Patriotic War (term), Great Patriotic War in the Soviet Union and its successor states, and the German–Soviet War in modern Germany and Ukraine, was a Theater (warfare), theatre of World War II fought between the European Axis powers and Allies of World War II, Allies, including the Soviet Union (USSR) and Polish Armed Forces in the East, Poland. It encompassed Central Europe, Eastern Europe, Northern Europe, Northeast Europe (Baltic states, Baltics), and Southeast Europe (Balkans), and lasted from 22 June 1941 to 9 May 1945. Of the estimated World War II casualties, 70–85 million deaths attributed to World War II, around 30 million occurred on the Eastern Front, including 9 million children. The Eastern Front was decisive in determining the outcome in the European theatre of World War II, European theatre of operations in World War II, eventually serving as the main reason for the defeat of Nazi Germany and the Axis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nazi Germany
Nazi Germany, officially known as the German Reich and later the Greater German Reich, was the German Reich, German state between 1933 and 1945, when Adolf Hitler and the Nazi Party controlled the country, transforming it into a Totalitarianism, totalitarian dictatorship. The Third Reich, meaning "Third Realm" or "Third Empire", referred to the Nazi claim that Nazi Germany was the successor to the earlier Holy Roman Empire (800–1806) and German Empire (1871–1918). The Third Reich, which the Nazis referred to as the Thousand-Year Reich, ended in May 1945, after 12 years, when the Allies of World War II, Allies defeated Germany and entered the capital, Berlin, End of World War II in Europe, ending World War II in Europe. After Hitler was appointed Chancellor of Germany in 1933, the Nazi Party began to eliminate political opposition and consolidate power. A 1934 German referendum confirmed Hitler as sole ''Führer'' (leader). Power was centralised in Hitler's person, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Voroshilovgrad
Luhansk (, ; , ), also known as Lugansk (, ; , ), is a city in the Donbas in eastern Ukraine. As of 2022, the population was estimated to be making Luhansk the Cities in Ukraine, 12th-largest city in Ukraine. Luhansk served as the administrative center of Luhansk Oblast, before pro-Russian separatists seized control of the city in 2014 and made it the capital of the self-proclaimed Luhansk People's Republic. The Ukrainian administration was located in Sievierodonetsk from 2014 to 2022 during the War in Donbas (2014–2022), war in Donbas, due to Ukraine not being in control of Luhansk. Sievierodonetsk was Battle of Sievierodonetsk (2022), captured by Russia in 2022 and Luhansk Oblast was later Russian annexation of Donetsk, Kherson, Luhansk and Zaporizhzhia oblasts, annexed by Russia in late 2022. Etimology The city was founded as a foundry in 1795-1796, following the decree of Empress Catherine II titled ''On the establishment of a foundry in the Donetsk uyezd by the Lugan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Poltava
Poltava (, ; , ) is a city located on the Vorskla, Vorskla River in Central Ukraine, Central Ukraine. It serves as the administrative center of Poltava Oblast as well as Poltava Raion within the oblast. It also hosts the administration of Poltava urban hromada, one of the hromadas of Ukraine. Poltava has a population of History It is still unknown when Poltava was founded, although the town was not attested before 1174. However, municipal authorities chose to celebrate the city's 1100th anniversary in 1999. The settlement is indeed an old one, as archeologists unearthed an ancient Paleolithic dwelling, as well as Scythian remains, within the city limits. Middle Ages The present name of the city is traditionally connected to the settlement Ltava, which is mentioned in the ''Hypatian Chronicle'' in 1174. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carl-Heinrich Von Stülpnagel
Carl-Heinrich Rudolf Wilhelm von Stülpnagel (2 January 1886 – 30 August 1944) was a German general in the Wehrmacht during World War II who was an army level commander. While serving as military commander of German-occupied France and as commander of the 17th Army in the Soviet Union during Operation Barbarossa, Stülpnagel participated in German war crimes, including authorising reprisal operations against civilian population and cooperating with the Einsatzgruppen in their mass murder of Jews. He was a member of the 20 July Plot to assassinate Adolf Hitler, being in charge of the conspirators' actions in France. After the failure of the plot, he was recalled to Berlin and attempted to commit suicide en route, but failed. Tried on 30 August 1944, he was convicted of treason and executed on the same day. Early life Born in Berlin into a noble family, Stülpnagel joined the Prussian Army straight from school in 1904, and served as a general staff officer in World War I. A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
First Battle Of Kharkov
The First Battle of Kharkov was a battle that took place from 20 to 24 October 1941 for control of the city of Kharkov, located in the Ukrainian SSR, during the final stage of Operation Barbarossa. The battle was fought between the German 6th Army (Wehrmacht), 6th Army, part of Army Group South, and the Soviet Southwestern Front (Soviet Union), Southwestern Front. The Soviet 38th Army (Soviet Union), 38th Army was tasked with defending the city while its factories were dismantled and moved to a more easterly location. The main objective for the German 6th Army was to capture Kharkov, which would help them close the growing gap between themselves and the German 17th Army (Wehrmacht), 17th Army. By 20 October, the Germans had advanced to the western edge of the city, and by 24 October, the 57th Infantry Division (Wehrmacht), 57th Infantry Division was able to take control of Kharkov. By this time, however, most of the city's industrial facilities had been evacuated or rendered ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
6th Army (Wehrmacht)
The 6th Army () was a field army of the German Army during World War II. It is widely known for its defeat by and subsequent surrender to the Red Army at the Battle of Stalingrad on 2 February 1943. It committed war crimes at Babi Yar while under the command of Field Marshal Walther von Reichenau during Operation Barbarossa. The 6th Army was reformed in March 1943, and participated in fighting in Ukraine and later Romania, before being almost completely destroyed in the Second Jassy-Kishinev Offensive in August 1944. Following this it would fight in Hungary, attempting to relieve Budapest, and subsequently retreating into Austria in the Spring of 1945. 6th Army surrendered to US Army forces on 9 May 1945. Western campaigns The 6th Army was formed on 10 October 1939 with General Walther von Reichenau in command through the redesignation of the 10th Army that had fought during the Invasion of Poland. During the invasion of the Low Countries the 6th Army saw active service ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sea Of Azov
The Sea of Azov is an inland Continental shelf#Shelf seas, shelf sea in Eastern Europe connected to the Black Sea by the narrow (about ) Strait of Kerch, and sometimes regarded as a northern extension of the Black Sea. The sea is bounded by Russia on the east, and by Ukraine on the northwest and southwest (the parts of Ukraine bordering the sea are currently Russian-occupied territories of Ukraine, under Russian occupation). It is an important access route for Central Asia, from the Caspian Sea via the Volga–Don Canal. The sea is largely affected by the inflow of the Don (river), Don, Kuban (river), Kuban, and other rivers, which bring sand, silt, and shells, which in turn form numerous bays, liman (landform), limans, and narrow spit (landform), spits. Because of these deposits, the sea bottom is relatively smooth and flat, with the depth gradually increasing toward the middle. Because of the river inflow, water in the sea has low salinity and a high amount of biomass (such a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dniepr River
The Dnieper or Dnepr ( ), also called Dnipro ( ), is one of the major transboundary rivers of Europe, rising in the Valdai Hills near Smolensk, Russia, before flowing through Belarus and Ukraine to the Black Sea. Approximately long, with a drainage basin of , it is the longest river of Ukraine and Belarus and the fourth- longest river in Europe, after the Volga, Danube, and Ural rivers. In antiquity, the river was part of the Amber Road trade routes. During the Ruin in the later 17th century, the area was contested between the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth and Russia, dividing what is now Ukraine into areas described by its right and left banks. During the Soviet period, the river became noted for its major hydroelectric dams and large reservoirs. The 1986 Chernobyl disaster occurred on the Pripyat River, a tributary of the Dnieper, just upstream from its confluence with the Dnieper. The Dnieper is an important navigable waterway for the economy of Ukraine and is c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Kiev (1941)
The First Battle of Kiev was the German name for the major battle that resulted in an encirclement of Red Army, Soviet troops in the vicinity of Kiev during World War II, the capital and most populous city of the Ukrainian Soviet Socialist Republic. This encirclement is the largest encirclement in the history of warfare by number of troops. The battle occurred from 7 July to 26 September 1941 as part of Operation Barbarossa, the Axis powers, Axis invasion of the Soviet Union. Despite being referred to as the "Battle of Kiev", the city of Kiev itself played a small and peripheral role in the overall battle. The battle took place over a large area in eastern Ukraine, with Kiev being the focal point of Soviet defenses and of the German encirclement. Much of the Southwestern Front (Soviet Union), Southwestern Front of the Red Army, commanded by Mikhail Kirponos, was encircled, but small groups of Red Army troops managed to escape the Pocket (military), pocket in the days after the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Franz Halder
Franz Halder (30 June 1884 – 2 April 1972) was a German general and the chief of staff of the Oberkommando des Heeres, Army High Command (OKH) in Nazi Germany from 1938 until September 1942. During World War II, he directed the planning and implementation of Operation Barbarossa, the 1941 invasion of the Soviet Union. Halder became instrumental in the radicalisation of warfare on the Eastern Front (World War II), Eastern Front. He had his staff draft both the Commissar Order (issued on 6 June 1941) and the Barbarossa Decree (signed on 13 May 1941) that allowed German soldiers to execute Soviet citizens for any reason without fear of later prosecution, leading to numerous war crimes and atrocities during the campaign. After the war, he had a decisive role in the development of the myth of the clean Wehrmacht, myth of the clean ''Wehrmacht''. Halder began his military service in 1914. In 1937 he met and became a supporter of Adolf Hitler. Halder participated in the strategic pla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oberkommando Des Heeres
The (; abbreviated OKH) was the high command of the Army of Nazi Germany. It was founded in 1935 as part of Adolf Hitler's rearmament of Germany. OKH was ''de facto'' the most important unit within the German war planning until the defeat at Moscow in December 1941. During World War II, OKH had the responsibility of strategic planning of Armies and Army Groups. The General Staff of the OKH managed operational matters. Each German Army also had an Army High Command ( or AOK). The Armed Forces High Command () then took over this function for theatres other than the Eastern front. The OKH commander held the title of Commander-in-chief of the Army (). After the Battle of Moscow, the OKH commander Field marshal Walther von Brauchitsch was removed from office, and Hitler appointed himself as Commander-in-Chief of the Army. From 1938, OKH was, together with () and () formally subordinated to the . OKH vs OKW OKH had been independent until February 1938, when Hitler creat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |