|
Battle Of Lwów (1939)
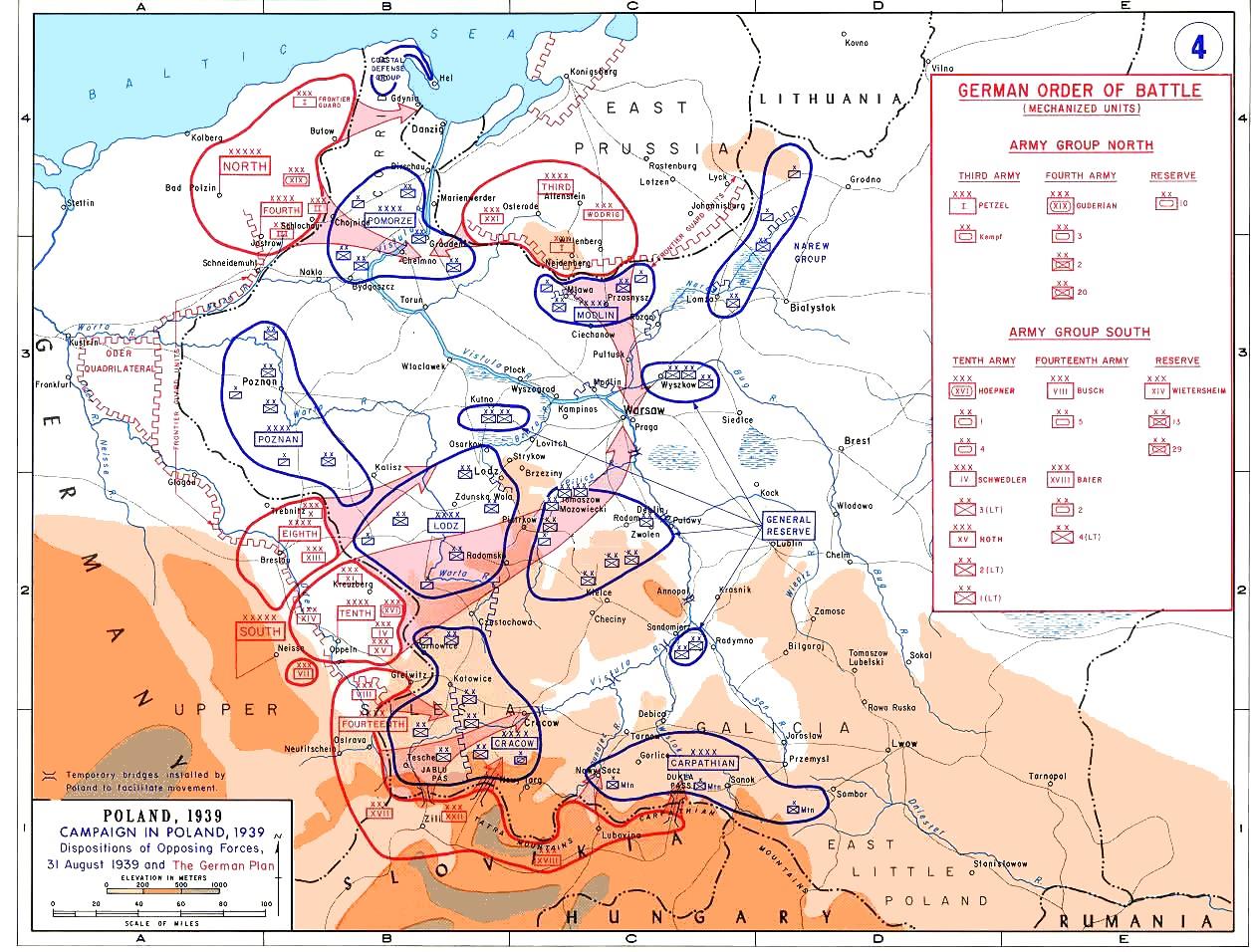
The Battle of Lwów (sometimes called the ''Siege of Lwów'') was a World War II battle for the control over the Poland, Polish city of Lviv, Lwów (now Lviv, Ukraine) between the Polish Army and the invading Wehrmacht and the Red Army. The city was seen as the key to the so-called Romanian Bridgehead and was defended at all costs. First clashes Initially, the city was not to be defended, as it was considered to be too deep behind the Polish lines and too important to Polish culture for warfare. However, the speed of the Nazi invasion and the almost-complete disintegration of the Polish reserve Prusy Army after the Battle of Łódź (1939), Battle of Łódź resulted in the city being in danger of a German assault. On September 7, 1939, General Władysław Langner started to organise the defence of the city., see also general reference No. 2 Initially, the Polish forces were to defend the Bełżec, Lublin Voivodeship, Bełżec – Rawa Ruska – Maheriv, Magierów line against th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lwów
Lviv ( or ; ; ; see #Names and symbols, below for other names) is the largest city in western Ukraine, as well as the List of cities in Ukraine, fifth-largest city in Ukraine, with a population of It serves as the administrative centre of Lviv Oblast and Lviv Raion, and is one of the main Ukrainian culture, cultural centres of Ukraine. Lviv also hosts the administration of Lviv urban hromada. It was named after Leo I of Galicia, the eldest son of Daniel of Galicia, Daniel, King of Ruthenia. Lviv (then Lwów) emerged as the centre of the historical regions of Red Ruthenia and Galicia (Eastern Europe), Galicia in the 14th century, superseding Halych, Chełm, Belz, and Przemyśl. It was the capital of the Kingdom of Galicia–Volhynia from 1272 to 1349, when it went to King Casimir III the Great of Kingdom of Poland, Poland in a Galicia–Volhynia Wars, war of succession. In 1356, Casimir the Great granted it town rights. From 1434, it was the regional capital of the Ruthenian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Poland
Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, is a country in Central Europe. It extends from the Baltic Sea in the north to the Sudetes and Carpathian Mountains in the south, bordered by Lithuania and Russia to the northeast, Belarus and Ukraine to the east, Slovakia and the Czech Republic to the south, and Germany to the west. The territory has a varied landscape, diverse ecosystems, and a temperate climate. Poland is composed of Voivodeships of Poland, sixteen voivodeships and is the fifth most populous member state of the European Union (EU), with over 38 million people, and the List of European countries by area, fifth largest EU country by area, covering . The capital and List of cities and towns in Poland, largest city is Warsaw; other major cities include Kraków, Wrocław, Łódź, Poznań, and Gdańsk. Prehistory and protohistory of Poland, Prehistoric human activity on Polish soil dates to the Lower Paleolithic, with continuous settlement since the end of the Last Gla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rudolf Prich
Rudolf Prich (6 August 1881 – 1940)Indeks Represjonowanych - Rudolf Prich (eng.) was a Polish military officer and a major general ( pol. '''') of the . He was among the Polish officers who were murdered by the |
Maheriv
Maheriv (; ) is a rural settlement in Lviv Raion, Lviv Oblast, western Ukraine. It is located approximately northeast of the city of Lviv. Maheriv hosts the administration of Dobrosyn-Maheriv settlement hromada, one of the hromadas of Ukraine. Population: History Until 18 July 2020, Maheriv belonged to Zhovkva Raion. The raion was abolished in July 2020 as part of the administrative reform of Ukraine, which reduced the number of raions of Lviv Oblast to seven. The area of Zhovkva Raion was merged into Lviv Raion. Until 26 January 2024, Maheriv was designated urban-type settlement. On this day, a new law entered into force which abolished this status, and Maheriv became a rural settlement. Economy Transportation Dobrosyn railway station is about east of the settlement. It is on the railway connecting Lviv via Zhovkva with Rava-Ruska. There is infrequent passenger traffic. The settlement has access to Highway M09 which connects Lviv with Rava-Ruska, crosses into Poland and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rawa Ruska
Rava-Ruska (, ; ; ) is a city in Lviv Raion, Lviv Oblast, western Ukraine. It is a border town between Ukraine and Poland. The border checkpoint is situated west of the city, along the international autoroute Warsaw–Lviv. Rava-Ruska hosts the administration of Rava-Ruska urban hromada, one of the hromadas of Ukraine. Its population is approximately History Rawa-Ruska was founded in 1455 by the Polish prince Władysław I of Płock, Duke of Bełz and Mazovia. He added the suffix "Ruska", meaning "Ruthenian" (during this time, the urban Ukrainian inhabitants were referred to as "Ruthenians"), to distinguish it from Rawa Mazowiecka located further west. Due to a convenient location along the merchant trail from Lublin to Lviv, the newly located town quickly developed. For centuries, Rawa was part of the Kingdom of Poland and the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth. It remained in private hands of several consecutive szlachta families, such as the Głogowski, Suchodolski, Rzecz ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Łódź (1939)
The Battle of Łódź was fought on September 6–8, 1939, between the armies of Poland and Nazi Germany in World War II during the Invasion of Poland. The Polish forces were led by General Juliusz Rómmel. Prelude The German aggression was anticipated by the Poles from the spring of 1939, when Poland refused to join the Axis against the Soviet Union (see Polish Soviet War of 1919-1920). Poland’s strategy during the forecasted war would be to withstand the initial German attack and trigger France and Great Britain to declare war on Germany, and, afterwards, to execute a fighting retreat to the Romanian Bridgehead. Polish General Juliusz Rómmel was given command of the Łódź Army and to buy time to finish the mobilization of his own army, he led three divisions in the direction of the border. He believed that only through mobility and continuous resistance ("fighting for every village"), the German advance could be slowed enough to finish mobilization of his own army. The h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prusy Army
The Prusy Army () was one of the Polish armies to fight during the Invasion of Poland in 1939. Created in the summer of 1939 as the main reserve of the Commander in Chief, it was commanded by Gen. Stefan Dąb-Biernacki. The word ''Prusy'' in the Polish language means Prussia, but this name only served as a codename and the region of operations of this army was far from East Prussia. This is in contrast to other Polish armies in 1939 which were named after the geographical regions where they formed. The Prusy Army, whose original name was Warszawa Army, was named so after a folwark in central Poland called Prusy, which served as the headquarters of General Dąb-Biernacki. Tasks According to the "Plan West" ('' Plan Zachód'', the code name for the Polish mobilization plan) it was to be composed of units mobilized as the second and third waves, and its main purpose was to cooperate with the nearby armies "Łódź" and "Kraków". It was being mobilized in two groups after the ou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Obrona Lwowa
Obrona is a village in the administrative district of Gmina Kleczew, within Konin County, Greater Poland Voivodeship, in west-central Poland. It lies approximately south-east of Kleczew, north of Konin, and east of the regional capital Poznań Poznań ( ) is a city on the Warta, River Warta in west Poland, within the Greater Poland region. The city is an important cultural and business center and one of Poland's most populous regions with many regional customs such as Saint John's .... References Villages in Konin County {{Konin-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Romanian Bridgehead
__NOTOC__ The Romanian Bridgehead (; ) was an area in southeastern Poland that is now located in Ukraine. During the invasion of Poland in 1939 at the start of the Second World War, the Polish commander-in-chief, Marshal of Poland Edward Rydz-Śmigły, ordered all Polish troops fighting east of the Vistula (approximately 20 divisions still retaining the ability to co-operate) to withdraw towards Lwów and then to the hills along the borders with Romania and the Soviet Union on 14 September. After the Soviets attacked on 17 September, Rydz-Śmigły ordered all units to withdraw to Romania and Hungary, but communications had become disrupted although smaller units crossed outside the major battles. The plan was a default plan in case it was impossible to defend the Polish borders, and it assumed that the Polish forces would be able to retreat to the area, organise a successful defence until the winter and hold out until the promised French offensive on the Western Front had s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Red Army
The Workers' and Peasants' Red Army, often shortened to the Red Army, was the army and air force of the Russian Soviet Republic and, from 1922, the Soviet Union. The army was established in January 1918 by a decree of the Council of People's Commissars to oppose the military forces of the new nation's adversaries during the Russian Civil War, especially the various groups collectively known as the White Army. In February 1946, the Red Army (which embodied the main component of the Soviet Armed Forces alongside the Soviet Navy) was renamed the "Soviet Army". Following the dissolution of the Soviet Union it was split between the post-Soviet states, with its bulk becoming the Russian Ground Forces, commonly considered to be the successor of the Soviet Army. The Red Army provided the largest land warfare, ground force in the Allies of World War II, Allied victory in the European theatre of World War II, and its Soviet invasion of Manchuria, invasion of Manchuria assisted the un ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wehrmacht
The ''Wehrmacht'' (, ) were the unified armed forces of Nazi Germany from 1935 to 1945. It consisted of the German Army (1935–1945), ''Heer'' (army), the ''Kriegsmarine'' (navy) and the ''Luftwaffe'' (air force). The designation "''Wehrmacht''" replaced the previously used term (''Reich Defence'') and was the manifestation of the Nazi regime's efforts to German rearmament, rearm Germany to a greater extent than the Treaty of Versailles permitted. After the Adolf Hitler's rise to power, Nazi rise to power in 1933, one of Adolf Hitler's most overt and bellicose moves was to establish the ''Wehrmacht'', a modern offensively-capable armed force, fulfilling the Nazi regime's long-term goals of regaining lost territory as well as gaining new territory and dominating its neighbours. This required the reinstatement of conscription and massive investment and Military budget, defence spending on the arms industry. The ''Wehrmacht'' formed the heart of Germany's politico-military po ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |