|
Battle Of Inkerman
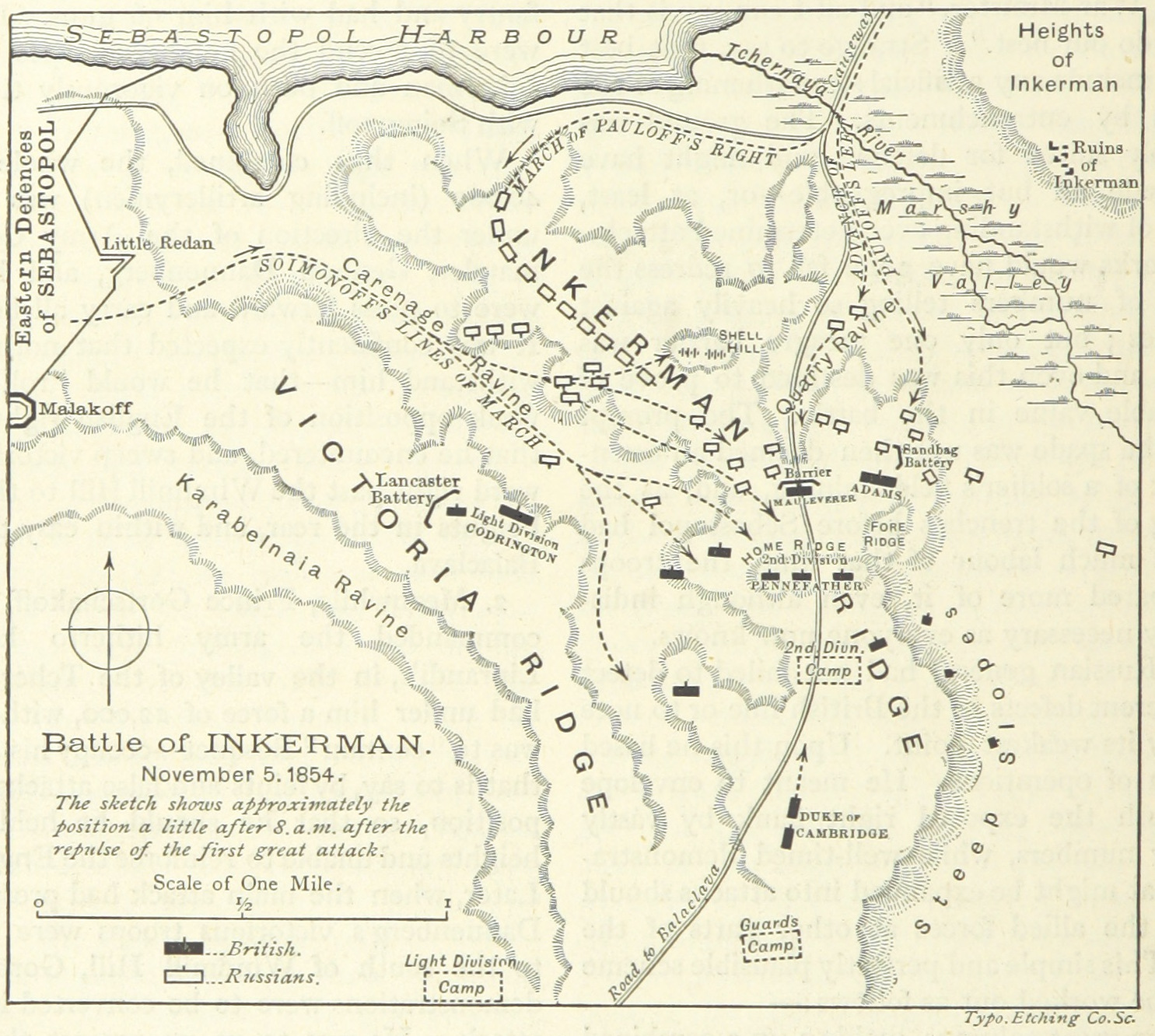
The Battle of Inkerman was fought during the Crimean War on 5 November 1854 between the allied armies of Britain and France against the Imperial Russian Army. The battle broke the will of the Russian Army to defeat the allies in the field, and was followed by the Siege of Sevastopol. The role of troops fighting mostly on their own initiative due to the foggy conditions during the battle has earned the engagement the name "The Soldier's Battle." Prelude to the battle The allied armies of Britain, France, Sardinia, and the Ottoman Empire had landed on the west coast of Crimea on 14 September 1854, intending to capture the Russian naval base at Sevastopol. The allied armies fought off and defeated the Russian Army at the Battle of Alma, forcing them to retreat in some confusion toward the River Kacha. While the allies could have taken this opportunity to attack Sevastopol before Sevastopol could be put into a proper state of defence, the allied commanders, British general FitzRoy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crimean War
The Crimean War was fought between the Russian Empire and an alliance of the Ottoman Empire, the Second French Empire, the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland, and the Kingdom of Sardinia (1720–1861), Kingdom of Sardinia-Piedmont from October 1853 to February 1856. Geopolitical causes of the war included the "Eastern question" (Decline and modernization of the Ottoman Empire, the decline of the Ottoman Empire, the "sick man of Europe"), expansion of Imperial Russia in the preceding Russo-Turkish wars, and the British and French preference to preserve the Ottoman Empire to maintain the European balance of power, balance of power in the Concert of Europe. The flashpoint was a dispute between France and Russia over the rights of Catholic Church, Catholic and Eastern Orthodox Church, Orthodox minorities in Palestine (region), Palestine. After the Sublime Porte refused Nicholas I of Russia, Tsar Nicholas I's demand that the Empire's Orthodox subjects were to be placed unde ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2nd Division (United Kingdom)
The 2nd Infantry Division was an infantry division of the British Army that was formed and disestablished numerous times between 1809 and 2012. It was raised by Lieutenant-General Arthur Wellesley for service in the Peninsular War (part of the Coalition Wars of the Napoleonic Wars) as the 2nd Division. It was disestablished in 1814, but re-formed the following year for service in the War of the Seventh Coalition. The formation fought at the Battle of Waterloo and played an important role in defeating the final French attack of the day. It then marched into France and became part of the Army of Occupation, and was the only British force allowed to march through Paris. In December 1818, the division was disbanded once again. During the mid- to late-19th century, several formations bearing the name 2nd Division were formed. Only two such were considered part of the division's lineage by Everard Wyrall, who compiled its First World War history. The first was created in 1854 t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peter Dannenberg (general)
Peter Andreyevich Dannenberg (; 9 June 1792 – 6 August 1872) was a Russian general, particularly notable for his command during the Crimean War. Life Born into a reformed church family on 19 June 1792 in Olonets Governorate, his early education was at the Sofia Institute of Forestry (1807–1810), from which he moved to the Imperial Forestry Institute in Saint Petersburg, from which he graduated in 1811, from the scientist and surveyor course, with the rank of 13th grade. On graduation he became a secretary-policeman but that same year decided to switch to military service and so enrolled in the Kolonnovozhatyh College. He successfully completed their science course and on 26 January 1812 was promoted to the rank of ensign in a quartermaster unit and a secondment to the 24th Infantry Division. In his twenties he fought the French invasion of Russia, seeing action at Smolensk on 12 June 1812, Borodino on 26 August, Tarutino on 6 October and Maloyaroslavets on 12 October. Fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zouave
The Zouaves () were a class of light infantry regiments of the French Army and other units modelled on it, which served between 1830 and 1962, and served in French North Africa. The zouaves were among the most decorated units of the French Army. It was initially intended that the zouaves would be a regiment of Berber volunteers from the Zwawa group of tribes in Algeria ("Zwawa" being the origin of the French term '' zouave'') who had gained a martial reputation fighting for local rulers under the Regency of Algiers. The regiment was to consist of 1,600 Zwawa Berbers, French non-commissioned officers and French officers. 500 Zwawa were recruited in August and September 1830. However, twelve years later, this idea was dropped. More zouave regiments were raised and the men recruited to serve in them were almost exclusively French or people of French descent born in French Algeria (''pieds-noirs''), a policy which continued until the final dissolution of these regiments after the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pierre Bosquet
Pierre François Joseph Bosquet (8 November 1810 – 5 February 1861) was a French Army general. He served during the French conquest of Algeria and in the Crimean War of 1853-1856; returning from Crimea he was made a Marshal of France and a Senator. Biography Bosquet was born in Mont-de-Marsan, Landes; he entered the artillery in 1833 and a year later went to Algeria. Here he soon made himself remarkable not only for technical skill but the moral qualities indispensable for high command. Becoming captain in 1839, he greatly distinguished himself at the actions of Sidi-Lakhdar and Oued-Melah. He was soon given the command of a battalion of native tirailleurs, and in 1843 was thanked in general orders for his brilliant work against the Flittahs. In 1845 he became lieutenant-colonel, and in 1847 colonel of a French line regiment. In the following year he was in charge of the Oran district, where his swift suppression of an insurrection won him further promotion to the grade ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prince George, Duke Of Cambridge
Prince George, Duke of Cambridge (George William Frederick Charles; 26 March 1819 – 17 March 1904) was a member of the British royal family, a grandson of King George III and cousin of Queen Victoria. The Duke was an army officer by profession and served as Commander-in-Chief of the Forces (military head of the British Army) from 1856 to 1895. He became Duke of Cambridge in 1850 and Field marshal (United Kingdom), field marshal in 1862. Deeply devoted to the old Army, he worked with Queen Victoria to defeat or minimise every reform proposal, such as setting up a Staff (military), general staff. His Army's weaknesses were dramatically revealed by the poor organisation at the start of the Second Boer War. Early life Prince George was born at Cambridge House, Hanover.Heathcote, p. 141 His father was Prince Adolphus, Duke of Cambridge, the seventh son of King George III and Charlotte of Mecklenburg-Strelitz, Queen Charlotte. His mother was the Duchess of Cambridge (née Princess ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crimean War 1854-56 Q71166
Crimea ( ) is a peninsula in Eastern Europe, on the northern coast of the Black Sea, almost entirely surrounded by the Black Sea and the smaller Sea of Azov. The Isthmus of Perekop connects the peninsula to Kherson Oblast in mainland Ukraine. To the east, the Crimean Bridge, constructed in 2018, spans the Strait of Kerch, linking the peninsula with Krasnodar Krai in Russia. The Arabat Spit, located to the northeast, is a narrow strip of land that separates the Syvash lagoons from the Sea of Azov. Across the Black Sea to the west lies Romania and to the south is Turkey. The population is 2.4 million, and the largest city is Sevastopol. The region, internationally recognized as part of Ukraine, has been under Russian occupation since 2014. Called the Tauric Peninsula until the early modern period, Crimea has historically been at the boundary between the classical world and the steppe. Greeks colonized its southern fringe and were absorbed by the Roman and Byzantine Empires ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chorna (river)
The Chorna, Chyornaya or Chorhun (, ''Chorna'', , ''Chyornaya'', ), which translates from the Ukrainian and Russian as "Black River", is a small river in southern Crimea. It is 34.5 km long. The Chorna River begins in the Baydar Valley northeast of the small town of Rodnikivs'ke (44° 28' N 33° 51' EG), just west of which it flows into a reservoir. From there it continues in a westerly direction to the town of Inkerman (Belokamensk) where it enters the Bay of Sevastopol, on the southwest coast of the Crimean peninsula. Inkerman was a key location during the Crimean War of 1853–1856 and the Chorna lends its name to the Battle of Chernaya (Chyornaya) River of 1855. Object 221 (Nora) Located at the coordinates +44° 31' 4.00", +33° 42' 5.00" near the Chorna River and Morozivka, which was previously known as Alsou or Alsu before 1948, in the Alsou tract about east of Balaklava Balaklava ( Ukrainian and , , ) is a settlement on the Crimean Peninsula and part of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Minié Ball
The Minié ball, or Minie ball, is a type of hollow-based bullet designed by Claude-Étienne Minié for muzzle-loaded, rifled muskets. Invented in 1846 shortly followed by the Minié rifle, the Minié ball came to prominence during the Crimean War and the American Civil War where it was found to inflict significantly more serious wounds than earlier round musket balls. Both the American Springfield Model 1861 and the British Pattern 1853 Enfield rifled muskets, the most common weapons found during the American Civil War, used the Minié ball. Rifling, the addition of spiral grooves inside a gun barrel, imparts a stabilizing spin to a projectile for better external ballistics, greatly increasing the effective range and accuracy of the gun. Before the introduction of the Minié ball, which themselves needed greasing, balls had to be rammed down the barrel, sometimes with a mallet, because gunpowder residue would foul a rifled bore after a relatively small number of shots, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Musket
A musket is a muzzle-loaded long gun that appeared as a smoothbore weapon in the early 16th century, at first as a heavier variant of the arquebus, capable of penetrating plate armour. By the mid-16th century, this type of musket gradually disappeared as the use of heavy armour declined, but ''musket'' continued as the generic term for smoothbore long guns until the mid-19th century. In turn, this style of musket was retired in the 19th century when rifled muskets (simply called rifles in modern terminology) using the Minié ball (invented by Claude-Étienne Minié in 1849) became common. The development of breech-loading firearms using self-contained Cartridge (firearms), cartridges, introduced by Casimir Lefaucheux in 1835, began to make muskets obsolete. The first reliable repeating rifles, the 1860 Henry rifle and its 1866 descendent the Winchester rifle, superseded muskets entirely. Repeating rifles quickly established themselves as the standard for rifle design, ending the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Smoothbore
A smoothbore weapon is one that has a barrel without rifling. Smoothbores range from handheld firearms to powerful tank guns and large artillery mortars. Some examples of smoothbore weapons are muskets, blunderbusses, and flintlock pistols. The opposite of smoothbore is rifling. History Early firearms had smoothly bored barrels that fired projectiles without significant spin. To minimize inaccuracy-inducing tumbling during flight, their projectiles required an aerodynamically uniform shape, such as a sphere. However, surface imperfections on the projectile and/or the barrel will cause even a sphere to rotate randomly during flight, and the Magnus effect will curve it off the intended trajectory when spinning on any axis not parallel to the direction of travel. Rifling the bore surface with spiral grooves or polygonal valleys imparts a stabilizing gyroscopic spin to a projectile that prevents tumbling in flight. Not only does this more than counter Magnus-induced drift, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Inkerman Map
A battle is an occurrence of combat in warfare between opposing military units of any number or size. A war usually consists of multiple battles. In general, a battle is a military engagement that is well defined in duration, area, and force commitment. An engagement with only limited commitment between the forces and without decisive results is sometimes called a skirmish. The word "battle" can also be used infrequently to refer to an entire operational campaign, although this usage greatly diverges from its conventional or customary meaning. Generally, the word "battle" is used for such campaigns if referring to a protracted combat encounter in which either one or both of the combatants had the same methods, resources, and strategic objectives throughout the encounter. Some prominent examples of this would be the Battle of the Atlantic, Battle of Britain, and the Battle of France, all in World War II. Wars and military campaigns are guided by military strategy, whereas batt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |