|
Battle Of Cēsis (1919)
The Battle of Cēsis (; , Battle of Võnnu; , Battle of Wenden), fought near Cēsis (Wenden) in June 1919, was a decisive battle in the Estonian War of Independence and the Latvian War of Independence. After heavy fighting an Estonian force moving from the north, supplemented by Latvian units, repelled Baltic German attacks and went on full counter-attack. Background Latvia had declared independence in 1918, but was unable to stop the advance of the Red Army, resulting in the loss of Riga. The advance of the Red Latvian Riflemen was stopped by the German VI Reserve Corps. The Reserve Corps under general Rüdiger von der Goltz consisted of the '' Baltische Landeswehr'', the Freikorps Iron Division, and the Guard Reserve Division. The Latvian volunteers loyal to the Provisional Government were also placed under the command of the ''Baltische Landeswehr''. On 16 April 1919, the Latvian government of Kārlis Ulmanis was toppled by the Germans, who installed a puppet German P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Estonian War Of Independence
The Estonian War of Independence, also known as the War of Freedom in Estonia, was a defensive campaign of the Estonian Army and its allies, most notably the United Kingdom, against the Soviet Russian westward offensive of 1918–1919 and the 1919 aggression of the pro–German '' Baltische Landeswehr''. The campaign was the struggle of the newly established democratic state of Estonia for independence in the aftermath of World War I. It resulted in a victory for Estonia and was concluded in the 1920 Treaty of Tartu. Preface During the 1917 Russian Revolution, the newly elected provincial legislature ( State Diet or '' Maapäev'') of the Autonomous Governorate of Estonia proclaimed itself the highest sovereign authority in Estonia, instead of the new Bolshevik government of Russia. As a result, the local Bolsheviks soon dissolved the ''Maapäev'' and temporarily forced the democratically elected Estonian leadership underground in the capital Tallinn. A few months later, in F ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Estonian National Defence College
The Estonian Military Academy () is an institution of applied higher education for national defence in Tartu, Estonia. The institutions mission is to train and educate regular officers for the Estonian Defence Forces and Estonian Defence League, as well as for other military institutions. The academic program of EMA provides a balanced education in military and civilian subjects. The academic staff members of the EMA are supported by members of the academic community from universities throughout Estonia. History 1919-1940 The school was established on April 3, 1919, by the decree of the commander-in-chief of Estonian Defence Forces, General Major Johan Laidoner. During the Estonian War of Independence, preparation of non-commissioned officers was limited because men and resources were needed on the front line. However, after the war, there was a growing need for officers, who could train and teach soldiers. Thus a school for non-commissioned officers was formed. Cadets were t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
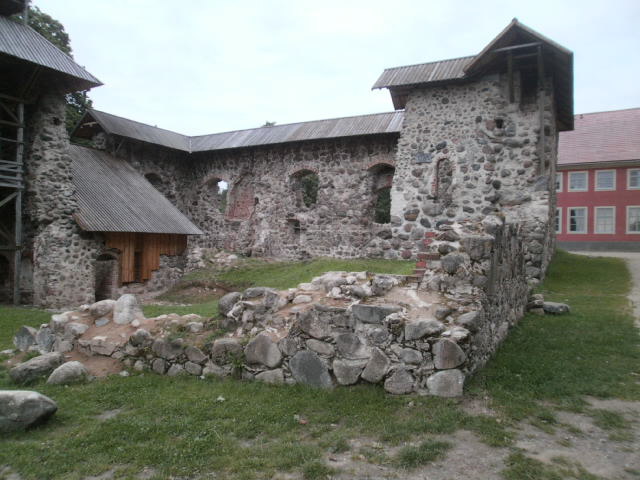
Limbaži
Limbaži (, , , ) is a town in the Vidzeme region of northern Latvia, with a population of 6,888. Limbaži is located 90 km northeast of the capital Riga. During the Middle Ages, as part of Livonia, Limbaži was a fortified town with stone walls, second in importance only to Riga. Etymology The name is believed to be a Latvianised version (hence the ''-aži'' ending) of the Livonian word ''Lembsel'' (''Lemesel'') meaning "wide isle in a forest swamp". The German ''Lemsahl'' (''Lemsal'') is derived from the Livonian name. According to folk etymology, the name ''Limbaži'' originated sometime in the 17th century. A recently arrived Swedish minister overheard the words "Limba" and "āži" (Latvian for ' male goats'). Mistakenly, he assumed this was the name of the place, and so the town was called "Limbaži". History In ancient times, Limbaži was a Livonian settlement known as ''Lemisele'', part of Metsepole. In the early 13th century, Bishop Albert and the Teutonic knigh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Latvian Independence War 1919
Latvian may refer to: *Something of, from, or related to Latvia **Latvians, a Baltic ethnic group, native to what is modern-day Latvia and the immediate geographical region **Latvian language, also referred to as Lettish **Latvian cuisine **Latvian culture **Latvian horse *Latvian Gambit, an opening in chess See also *Latvia (other) Latvia is a country in Europe. Latvia can also refer to: * Latvian Soviet Socialist Republic (1940–1990) * Latvia (European Parliament constituency) * 1284 Latvia - asteroid * Latvia Peak - mountain in Tajikistan Tajikistan, officially the ... * {{disambiguation Language and nationality disambiguation pages ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Allies Of World War I
The Allies or the Entente (, ) was an international military coalition of countries led by the French Republic, the United Kingdom, the Russian Empire, the United States, the Kingdom of Italy, and the Empire of Japan against the Central Powers of the German Empire, Austria-Hungary, the Ottoman Empire, and the Kingdom of Bulgaria in World War I (1914–1918). By the end of the first decade of the 20th century, the major European powers were divided between the Triple Entente and the Triple Alliance. The Triple Entente was made up of the United Kingdom, France, and Russia. The Triple Alliance was originally composed of Germany, Austria–Hungary, and Italy, but Italy remained neutral in 1914. As the war progressed, each coalition added new members. Japan joined the Entente in 1914 and, despite proclaiming its neutrality at the beginning of the war, Italy also joined the Entente in 1915. The term "Allies" became more widely used than "Entente", although the United Kingdom, Fran ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Estonia
Estonia, officially the Republic of Estonia, is a country in Northern Europe. It is bordered to the north by the Gulf of Finland across from Finland, to the west by the Baltic Sea across from Sweden, to the south by Latvia, and to the east by Russia. The territory of Estonia consists of the mainland, the larger islands of Saaremaa and Hiiumaa, and over 2,300 other islands and islets on the east coast of the Baltic Sea. Its capital Tallinn and Tartu are the two largest List of cities and towns in Estonia, urban areas. The Estonian language is the official language and the first language of the Estonians, majority of its population of nearly 1.4 million. Estonia is one of the least populous members of the European Union and NATO. Present-day Estonia has been inhabited since at least 9,000 BC. The Ancient Estonia#Early Middle Ages, medieval indigenous population of Estonia was one of the last pagan civilisations in Europe to adopt Christianity following the Northern Crusades in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jānis Balodis
Jānis Balodis (20 February 1881 – 8 August 1965) was an army general, Commander-in-Chief of the Armed Forces of Latvia (1919–1921), Minister of War (1931–1940), and a politician who was one of the principal figures during the Latvian War of Independence and the dictatorship of Kārlis Ulmanis, when he was officially the number two of the regime as the Minister of War, Deputy Prime Minister and Vice President. Early life and education Jānis Balodis father was historian and teacher Voldemārs Balodis. In 1898, he joined the Imperial Russian Army and served in Kaunas. From 1900 until 1902 he studied at the Vilnius War School. Military service Russo-Japanese War and World War I From November 1904 until July 1905, he participated in the Russo–Japanese War and was seriously wounded in the arm. From 1906 until 1914, Balodis served in Vilnius. At the beginning of World War I he was lightly wounded during the battles in East Prussia, for which he received a number of decorat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Andrievs Niedra
Andrievs Niedra ( old orthography: ''Andreews Needra''; 8 February 1871 – 25 September 1942) was a Latvian writer, Lutheran pastor and the Prime Minister of the German puppet government in Latvia between April and June 1919, during the Latvian War of Independence. Niedra's first collection of poems was published when he was only nineteen years old, and he was still in his teens when his stories based on history and folklore began to appear in the newspaper ''Baltijas Vēstnesis''. Between 1890 and 1899 he studied theology at the University of Dorpat (now Tartu). Aesthetically blending realistic fantasy with idealism, his stories, criticism and plays often treated the formation of the Latvian intelligentsia and the situation of the peasantry with regard to the dominant Baltic Germans. Believing that society can only develop through evolution rather than revolution, Niedra was a fierce opponent of socialism and came to be seen as a reactionary in an increasingly revolutionar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kārlis Ulmanis
Kārlis Augusts Vilhelms Ulmanis (; 4 September 1877 – 20 September 1942) was a Latvian politician and a dictator. He was one of the most prominent Latvian politicians of pre-World War II Latvia during the Interwar period of independence from November 1918 to June 1940 and served as the country's first Prime Minister of Latvia, prime minister. He served four times as prime minister, the last time as the head of an authoritarian regime, during which he subsequently also adopted the title of President of Latvia. The legacy of his dictatorship continues to divide public opinion in Latvia today. Early life Born in a prosperous farming family, Ulmanis studied agriculture at the ETH Zurich, Swiss Federal Institute of Technology Zurich and at Leipzig University. He then worked in Latvia as a writer, lecturer, and manager in agricultural positions. He was politically active during the 1905 Revolution, was briefly imprisoned in Pskov, and subsequently fled Latvia to avoid incarcera ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
California
California () is a U.S. state, state in the Western United States that lies on the West Coast of the United States, Pacific Coast. It borders Oregon to the north, Nevada and Arizona to the east, and shares Mexico–United States border, an international border with the Mexico, Mexican state of Baja California to the south. With almost 40million residents across an area of , it is the List of states and territories of the United States by population, largest state by population and List of U.S. states and territories by area, third-largest by area. Prior to European colonization of the Americas, European colonization, California was one of the most culturally and linguistically diverse areas in pre-Columbian North America. European exploration in the 16th and 17th centuries led to the colonization by the Spanish Empire. The area became a part of Mexico in 1821, following Mexican War of Independence, its successful war for independence, but Mexican Cession, was ceded to the U ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Santa Barbara, California
Santa Barbara (, meaning ) is a coastal city in Santa Barbara County, California, of which it is also the county seat. Situated on a south-facing section of coastline, the longest such section on the West Coast of the United States excepting Alaska, the city lies between the steeply rising Santa Ynez Mountains and the Pacific Ocean. Santa Barbara's climate is often described as Mediterranean climate, Mediterranean, and the city has been dubbed "The American Riviera". According to the 2020 United States census, 2020 U.S. census, the city's population was 88,665. In addition to being a popular tourist and resort destination, the city has a diverse economy that includes a large service sector, education, technology, health care, finance, agriculture, manufacturing, and local government. In 2004, the service sector accounted for 35% of local employment. Area institutions of higher learning include the University of California, Santa Barbara, Santa Barbara City College, Westmont Co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
German Army (German Empire)
The Imperial German Army (1871–1919), officially referred to as the German Army (), was the unified ground and air force of the German Empire. It was established in 1871 with the political unification of Germany under the leadership of Prussia, and was dissolved in 1919, after the defeat of the German Empire in World War I (1914–1918). In the Federal Republic of Germany, the term refers to the German Army, the land component of the . Formation and name The states that made up the German Empire contributed their armies; within the German Confederation, formed after the Napoleonic Wars, each state was responsible for maintaining certain units to be put at the disposal of the Confederation in case of conflict. When operating together, the units were known as the Federal Army (). The Federal Army system functioned during various conflicts of the 19th century, such as the First Schleswig War from 1848 to 1852. However, by the time of the Second Schleswig War of 1864, tensio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |