|
Battle Of Chester
The Battle of Chester (Old Welsh: ''Guaith Caer Legion''; Welsh: ''Brwydr Caer'') was a major victory for the Anglo-Saxons over the native Britons near the city of Chester, England in the early 7th century. Æthelfrith of Northumbria annihilated a combined force from the Welsh kingdoms of Powys and Rhôs (a cantref of the Kingdom of Gwynedd), and possibly from Mercia as well. It resulted in the deaths of Welsh leaders Selyf Sarffgadau of Powys, Cadwal Crysban of Rhôs, and numerous other high-ranking warriors such as Gwion ap Cyndrwyn of Pengwern. Circumstantial evidence suggests that King Iago of Gwynedd may have also been killed. Other sources state the battle may have been in 613 or even as early as 607 or 605 AD. According to Bede, a large number of monks from the monastery at Bangor on Dee who had come to witness the fight were killed on the orders of Æthelfrith before the battle. He told his warriors to massacre the clerics because although they bore no arms, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
England
England is a Countries of the United Kingdom, country that is part of the United Kingdom. It is located on the island of Great Britain, of which it covers about 62%, and List of islands of England, more than 100 smaller adjacent islands. It shares Anglo-Scottish border, a land border with Scotland to the north and England–Wales border, another land border with Wales to the west, and is otherwise surrounded by the North Sea to the east, the English Channel to the south, the Celtic Sea to the south-west, and the Irish Sea to the west. Continental Europe lies to the south-east, and Ireland to the west. At the 2021 United Kingdom census, 2021 census, the population was 56,490,048. London is both List of urban areas in the United Kingdom, the largest city and the Capital city, capital. The area now called England was first inhabited by modern humans during the Upper Paleolithic. It takes its name from the Angles (tribe), Angles, a Germanic peoples, Germanic tribe who settled du ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Brut Y Brenhinedd
''Brut y Brenhinedd'' ("Chronicle of the Kings") is a collection of variant Middle Welsh versions of Geoffrey of Monmouth's Latin ''Historia Regum Britanniae''. About 60 versions survive, with the earliest dating to the mid-13th century. Adaptations of Geoffrey's ''Historia'' were extremely popular throughout Western Europe during the Middle Ages, but the ''Brut'' proved especially influential in medieval Wales, where it was largely regarded as an accurate account of the early history of the Celtic Britons. Geoffrey's ''Historia'' and the ''Brut y Brenhinedd'' Geoffrey's ''Historia Regum Britanniae'' (completed by ) purports to narrate the history of the Kings of Britain from its eponymous founder Brutus of Troy to Cadwaladr, the last in the line. Geoffrey professed to have based his history on "a certain very ancient book" written in ''britannicus sermo'' (the "British tongue", i.e. Common Brittonic, Welsh, Cornish or Breton) which he had received from Walter of Oxford. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Anglo-Saxon Chronicle
The ''Anglo-Saxon Chronicle'' is a collection of annals in Old English, chronicling the history of the Anglo-Saxons. The original manuscript of the ''Chronicle'' was created late in the ninth century, probably in Wessex, during the reign of King Alfred the Great (r. 871–899). Its content, which incorporated sources now otherwise lost dating from as early as the seventh century, is known as the "Common Stock" of the ''Chronicle''.Hunter Blair, ''Roman Britain'', p. 11. Multiple copies were made of that one original and then distributed to monasteries across England, where they were updated, partly independently. These manuscripts collectively are known as the ''Anglo-Saxon Chronicle''. Almost all of the material in the ''Chronicle'' is in the form of annals, by year; the earliest is dated at 60 BC (the annals' date for Julius Caesar's invasions of Britain). In one case, the ''Chronicle'' was still being actively updated in 1154. Nine manuscripts of the ''Chronicle'', none of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Charles Plummer (historian)
Charles Plummer, FBA (1851–1927) was an English historian and cleric, best known as the editor of Sir John Fortescue's ''The Governance of England'', and for coining the term "bastard feudalism". He was the fifth son of Matthew Plummer of St Leonards-on-Sea, Sussex. He matriculated at Corpus Christi College, Oxford in 1869, graduating B.A. and S.C.L. in 1873 and becoming a Fellow. Works Plummer was an editor of Bede, and also edited numerous Irish and Hiberno-Latin texts, including the two volume ''Vitae Sanctorum Hiberniae'' (1910), a modern companion volume to which is Richard Sharpe's ''Medieval Irish saints' lives: an introduction to Vitae Sanctorum Hiberniae''. Plummer edited John Earle's ''Two of the Saxon Chronicles Parallel'' (1865), producing a ''Revised Text'' with notes, appendices, and glossary in 1892. This work presented the A and E texts of the ''Anglo-Saxon Chronicle''. Plummer delivered the Ford Lectures at Oxford University The University of Oxf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Penda Of Mercia
Penda (died 15 November 655)Manuscript A of the ''Anglo-Saxon Chronicle'' gives the year as 655. Bede also gives the year as 655 and specifies a date, 15 November. R. L. Poole (''Studies in Chronology and History'', 1934) put forward the theory that Bede began his year in September, and consequently November 655 would actually fall in 654; Frank Stenton also dated events accordingly in his ''Anglo-Saxon England'' (1943). 1 Others have accepted Bede's given dates as meaning what they appear to mean, considering Bede's year to have begun on 25 December or 1 January (see S. Wood, 1983: "Bede's Northumbrian dates again"). The historian D. P. Kirby suggested the year 656 as a possibility, alongside 655, in case the dates given by Bede are off by one year (see Kirby's "Bede and Northumbrian Chronology", 1963). The '' Annales Cambriae'' gives the year as 657Annales Cambriae at Fordham University/ref> was a 7th-century king of Mercia, the Anglo-Saxon kingdom in what is today the Midla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Battle Of The River Idle
The Battle of the River Idle was a major victory for Rædwald of East Anglia over Æthelfrith of Northumbria in 616 in what is now Nottinghamshire. Background Æthelfrith was King of Bernicia from c. 593. Around 604 under unknown circumstances, he gained control of neighbouring Deira, and forced into exile two notable members of the Deiran royal family, Edwin, son of the former king Ælla, and Hereric, Edwin's nephew. Hereric was poisoned while at the court of Ceretic, king of Elmet. It was probably Æthelfrith who is to blame for this killing. The second exile, Edwin, ended up eventually under the protection of Rædwald in East Anglia. Æthelfrith sent messengers to Rædwald asking him to kill Edwin. Rædwald did not comply, and instead, he raised an army to confront Æthelfrith. Battle Rædwald assembled an army and marched north, accompanied by his son Rægenhere, to confront Æthelfrith. They met on the western boundary of the kingdom of Lindsey, on the east bank o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Rædwald Of East Anglia
Rædwald (, ; 'power in counsel'), also written as Raedwald or Redwald (), (died c. AD 624) was a List of monarchs of East Anglia, king of East Anglia, an Anglo-Saxons, Anglo-Saxon kingdom which included the present-day English counties of Norfolk and Suffolk. He was the son of Tytila of East Anglia and a member of the Wuffingas dynasty (named after his grandfather, Wuffa of East Anglia, Wuffa), who were the first kings of the Kingdom of East Anglia, East Angles. Details about Rædwald's reign are scarce, primarily because the Vikings in East Anglia, Viking invasions of the 9th century destroyed the Monastery, monasteries in East Anglia where many documents would have been kept. Rædwald reigned from about 599 until his death around 624, initially under the overlordship of Æthelberht of Kent. In 616, as a result of fighting the Battle of the River Idle and defeating Æthelfrith of Northumbria, he was able to install Edwin of Northumbria, Edwin, who was acquiescent to his authority ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Bangor On Dee
Bangor-on-Dee ( or standardised ) is a village and community in Wrexham County Borough, Wales, on the banks of the River Dee. Until 1974 it was in the exclave of Flintshire known as the Maelor Saesneg, and from 1974 to 1996 in the county of Clwyd. The community had a population of 1,110 at the 2011 Census. Etymology The anglicised name refers to the village's proximity to the River Dee. However, the older Welsh name, ''Bangor-is-y-Coed'' (or ''Bangor Is-Coed'') literally means "Bangor" (a settlement with a wattle enclosure) "below the wood/trees". This form was first recorded in 1699, while an alternative name of the parish, "Bangor Monachorum" ("Bangor of the monks"), was first recorded in 1677.Bangor, St Dunawd ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Bede
Bede (; ; 672/326 May 735), also known as Saint Bede, Bede of Jarrow, the Venerable Bede, and Bede the Venerable (), was an English monk, author and scholar. He was one of the most known writers during the Early Middle Ages, and his most famous work, '' Ecclesiastical History of the English People'', gained him the title "The Father of English History". He served at the monastery of St Peter and its companion monastery of St Paul in the Kingdom of Northumbria of the Angles. Born on lands belonging to the twin monastery of Monkwearmouth–Jarrow in present-day Tyne and Wear, England, Bede was sent to Monkwearmouth at the age of seven and later joined Abbot Ceolfrith at Jarrow. Both of them survived a plague that struck in 686 and killed the majority of the population there. While Bede spent most of his life in the monastery, he travelled to several abbeys and monasteries across the British Isles, even visiting the archbishop of York and King Ceolwulf of Northumbria. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Cardiff
Cardiff (; ) is the capital city, capital and List of urban areas in the United Kingdom, largest city of Wales. Cardiff had a population of in and forms a Principal areas of Wales, principal area officially known as the City and County of Cardiff (). The city is the List of cities in the United Kingdom, eleventh largest in the United Kingdom. Located in the South East Wales, southeast of Wales and in the Cardiff Capital Region, Cardiff is the county town of the Historic counties of Wales, historic county of Glamorgan and in 1974–1996 of South Glamorgan. It belongs to the Eurocities network of the largest European cities. A small town until the early 19th century, its prominence as a port for coal when mining began in the region helped its expansion. In 1905, it was ranked as a city and in 1955 proclaimed capital of Wales. The Cardiff urban area covers a larger area outside the county boundary, including the towns of Dinas Powys and Penarth. Cardiff is the main commercial ce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
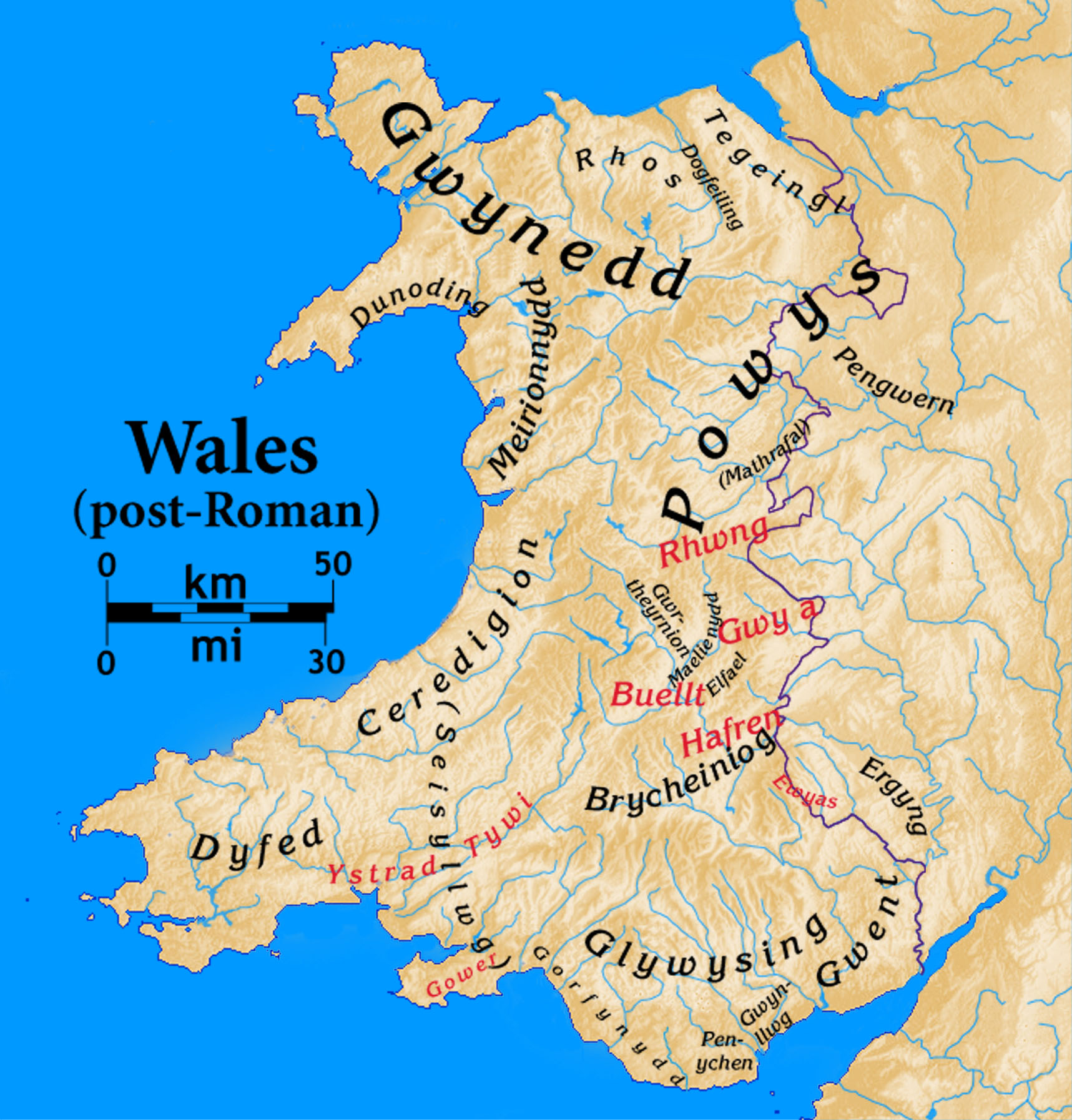
Pengwern
Pengwern was a Brythonic settlement of sub-Roman Britain situated in what is now the English county of Shropshire, adjoining the modern Welsh border. It is regarded as possibly being the early seat of the kings of Powys before its establishment at Mathrafal, further west, but the theory that it was an early kingdom (or a sub-kingdom of Powys itself) has also been postulated. Its precise location is uncertain. History and legend Nothing is known about the foundation of Pengwern, although according to Welsh tradition it was part of the Welsh kingdom of Powys in the early Middle Ages. Early Powys, much larger in extent than the later medieval kingdom, seems to have roughly coincided with the territory of the Celtic Cornovii tribe, whose ''civitas'' under Roman rule (capital or administrative centre) was '' Viroconium Cornoviorum'' (now Wroxeter), replacing a fort located on the Wrekin, which was abandoned. Once the Roman legions left the area, Viroconium Cornoviorum had ta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |