|
Barycentric Coordinates (astronomy)
In astronomy, the barycenter (or barycentre; ) is the center of mass of two or more bodies that orbit one another and is the point about which the bodies orbit. A barycenter is a dynamical point, not a physical object. It is an important concept in fields such as astronomy and astrophysics. The distance from a body's center of mass to the barycenter can be calculated as a two-body problem. If one of the two orbiting bodies is much more massive than the other and the bodies are relatively close to one another, the barycenter will typically be located within the more massive object. In this case, rather than the two bodies appearing to orbit a point between them, the less massive body will appear to orbit about the more massive body, while the more massive body might be observed to wobble slightly. This is the case for the Earth–Moon system, whose barycenter is located on average from Earth's center, which is 74% of Earth's radius of . When the two bodies are of similar mas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
90 Antiope
90 Antiope is a double asteroid in the outer asteroid belt. It was discovered on 1 October 1866, by Karl Theodor Robert Luther, Robert Luther. In 2000, it was found to consist of two almost-equally-sized bodies orbiting each other. At average diameters of about 88 km and 84 km, both components are among the 500 largest asteroids. Antiope is a member of the Themis family of asteroids that share similar orbital elements. Naming The asteroid's proper name comes from Greek mythology, but it is disputed whether this is Antiope (Amazon), Antiope the Amazon or Antiope (mother of Amphion), Antiope the mother of Amphion and Zethus. Since the discovery of Antiope's binary nature, the name "Antiope" technically refers to the slightly larger of the two components, with the smaller component bearing the provisional designation S/2000 (90) 1. However, the name "Antiope" is also used to refer to the binary system as a whole. Properties The most remarkable feature of Antiope i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Celestial Reference System
The International Celestial Reference System (ICRS) is the current standard celestial reference system adopted by the International Astronomical Union (IAU). Its origin is at the barycenter of the Solar System, with axes that are intended to "show no global rotation with respect to a set of distant extragalactic objects". This fixed reference system differs from previous reference systems, which had been based on Catalogues of Fundamental Stars that had published the positions of stars based on direct "observations of heir equatorial coordinates, right ascension and declination" and had adopted as "privileged axes ... the mean equator and the dynamical equinox" at a particular date and time. The International Celestial Reference Frame (ICRF) is a realization of the International Celestial Reference System using reference celestial sources observed at radio wavelengths. In the context of the ICRS, a reference ''frame'' (RF) is the physical realization of a reference ''system,'' i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Binary System (astronomy)
A binary system is a system of two astronomical bodies of the same kind that are comparable in size. Definitions vary, but typically require the center of mass to be located outside of either object. (See animated examples.) The most common kinds of binary system are binary stars and binary asteroids, but brown dwarfs, planets, neutron stars, black holes and galaxies can also form binaries. A ''multiple system'' is similar but consists of three or more objects, for example triple stars and triple asteroids (a more common term than 'trinary'). Classification In a binary system, the brighter or more massive object is referred to as primary, and the other the secondary. Binary stars are also classified based on orbit. Wide binaries are objects with orbits that keep them apart from one another. They evolve separately and have very little effect on each other. Close binaries are close to each other and are able to transfer mass from one another. They can also be classifi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tide
Tides are the rise and fall of sea levels caused by the combined effects of the gravitational forces exerted by the Moon (and to a much lesser extent, the Sun) and are also caused by the Earth and Moon orbiting one another. Tide tables can be used for any given locale to find the predicted times and amplitude (or " tidal range"). The predictions are influenced by many factors including the alignment of the Sun and Moon, the phase and amplitude of the tide (pattern of tides in the deep ocean), the amphidromic systems of the oceans, and the shape of the coastline and near-shore bathymetry (see '' Timing''). They are however only predictions, the actual time and height of the tide is affected by wind and atmospheric pressure. Many shorelines experience semi-diurnal tides—two nearly equal high and low tides each day. Other locations have a diurnal tide—one high and low tide each day. A "mixed tide"—two uneven magnitude tides a day—is a third regular category. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kilometre
The kilometre (SI symbol: km; or ), spelt kilometer in American English, American and Philippine English, is a unit of length in the International System of Units (SI), equal to one thousand metres (kilo- being the SI prefix for ). It is the preferred measurement unit to express distances between geographical places on land in most of the world; notable exceptions are the United States and the United Kingdom where the statute mile is used. Pronunciation There are two common pronunciations for the word. # # The first pronunciation follows a pattern in English whereby SI units are pronounced with the stress on the first syllable (as in kilogram, kilojoule and kilohertz) and the pronunciation of the actual base unit does not change irrespective of the prefix (as in centimetre, millimetre, nanometre and so on). It is generally preferred by the British Broadcasting Corporation (BBC), the Canadian Broadcasting Corporation (CBC), and the Australian Broadcasting Corporation (ABC) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Primary And Secondary (relationship)
Primary or primaries may refer to: Arts, entertainment, and media Music Groups and labels * Primary (band), from Australia * Primary (musician), hip hop musician and record producer from South Korea * Primary Music, Israeli record label Works * ''Primary'' (album) by Rubicon (2002) * "Primary" (song) by The Cure * "Primary", song by Spoon from the album '' Telephono'' Other uses in arts, entertainment, and media * Primaries or primary beams, in E. E. Smith's science-fiction series '' Lensman'' * ''Primary'' (film), American political documentary (1960) Computing * PRIMARY, an X Window selection * Primary data storage, computer technology used to retain digital data * Primary server, main server on the server farm Education * Primary education, the first stage of compulsory education * Primary FRCA, academic examination for anaesthetists in the U.K. * Primary school, school providing primary education Mathematics * ''p''-group of prime power order * Primary deco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Significant Figures
Significant figures, also referred to as significant digits, are specific digits within a number that is written in positional notation that carry both reliability and necessity in conveying a particular quantity. When presenting the outcome of a measurement (such as length, pressure, volume, or mass), if the number of digits exceeds what the measurement instrument can resolve, only the digits that are determined by the resolution are dependable and therefore considered significant. For instance, if a length measurement yields 114.8 mm, using a ruler with the smallest interval between marks at 1 mm, the first three digits (1, 1, and 4, representing 114 mm) are certain and constitute significant figures. Further, digits that are uncertain yet meaningful are also included in the significant figures. In this example, the last digit (8, contributing 0.8 mm) is likewise considered significant despite its uncertainty. Therefore, this measurement contains ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Semi-major Axis
In geometry, the major axis of an ellipse is its longest diameter: a line segment that runs through the center and both foci, with ends at the two most widely separated points of the perimeter. The semi-major axis (major semiaxis) is the longest semidiameter or one half of the major axis, and thus runs from the centre, through a focus, and to the perimeter. The semi-minor axis (minor semiaxis) of an ellipse or hyperbola is a line segment that is at right angles with the semi-major axis and has one end at the center of the conic section. For the special case of a circle, the lengths of the semi-axes are both equal to the radius of the circle. The length of the semi-major axis of an ellipse is related to the semi-minor axis's length through the eccentricity and the semi-latus rectum \ell, as follows: The semi-major axis of a hyperbola is, depending on the convention, plus or minus one half of the distance between the two branches. Thus it is the distance from the ce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mass
Mass is an Intrinsic and extrinsic properties, intrinsic property of a physical body, body. It was traditionally believed to be related to the physical quantity, quantity of matter in a body, until the discovery of the atom and particle physics. It was found that different atoms and different elementary particle, elementary particles, theoretically with the same amount of matter, have nonetheless different masses. Mass in modern physics has multiple Mass in special relativity, definitions which are conceptually distinct, but physically equivalent. Mass can be experimentally defined as a measure (mathematics), measure of the body's inertia, meaning the resistance to acceleration (change of velocity) when a net force is applied. The object's mass also determines the Force, strength of its gravitational attraction to other bodies. The SI base unit of mass is the kilogram (kg). In physics, mass is Mass versus weight, not the same as weight, even though mass is often determined by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Distance
Distance is a numerical or occasionally qualitative measurement of how far apart objects, points, people, or ideas are. In physics or everyday usage, distance may refer to a physical length or an estimation based on other criteria (e.g. "two counties over"). The term is also frequently used metaphorically to mean a measurement of the amount of difference between two similar objects (such as statistical distance between probability distributions or edit distance between string (computer science), strings of text) or a degree of separation (as exemplified by distance (graph theory), distance between people in a social network). Most such notions of distance, both physical and metaphorical, are formalized in mathematics using the notion of a metric space. In the social sciences, distance can refer to a qualitative measurement of separation, such as social distance or psychological distance. Distances in physics and geometry The distance between physical locations can be defined ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
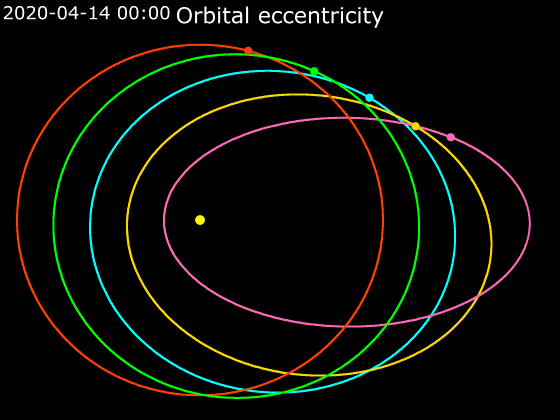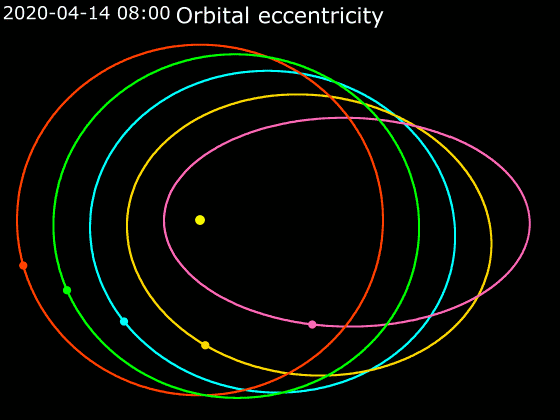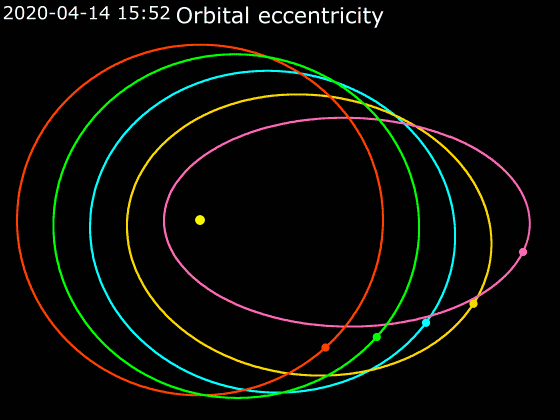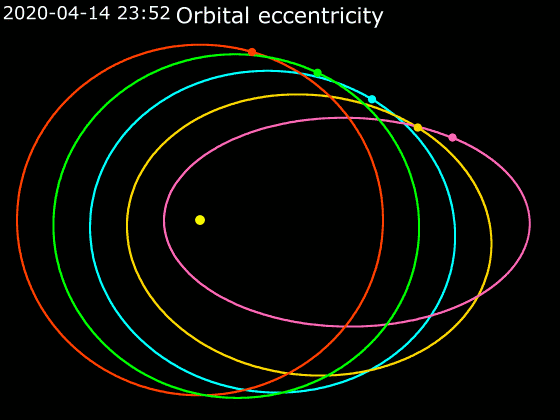
Elliptic Orbit
In astrodynamics or celestial mechanics, an elliptical orbit or eccentric orbit is an orbit with an eccentricity of less than 1; this includes the special case of a circular orbit, with eccentricity equal to 0. Some orbits have been referred to as "elongated orbits" if the eccentricity is "high" but that is not an explanatory term. For the simple two body problem, all orbits are ellipses. In a gravitational two-body problem, both bodies follow similar elliptical orbits with the same orbital period around their common barycenter. The relative position of one body with respect to the other also follows an elliptic orbit. Examples of elliptic orbits include Hohmann transfer orbits, Molniya orbits, and tundra orbits. Velocity Under standard assumptions, no other forces acting except two spherically symmetrical bodies (m_1) and (m_2), the orbital speed (v\,) of one body traveling along an elliptical orbit can be computed from the vis-viva equation as: :v = \sqrt where: * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Focus (geometry)
In geometry, focuses or foci (; : focus) are special points with reference to which any of a variety of curves is constructed. For example, one or two foci can be used in defining conic sections, the four types of which are the circle, ellipse, parabola, and hyperbola. In addition, two foci are used to define the Cassini oval and the Cartesian oval, and more than two foci are used in defining an n-ellipse, ''n''-ellipse. Conic sections Defining conics in terms of two foci An ellipse can be defined as the locus (mathematics), locus of points for which the sum of the distances to two given foci is constant. A circle is the special case of an ellipse in which the two foci coincide with each other. Thus, a circle can be more simply defined as the locus of points each of which is a fixed distance from a single given focus. A circle can also be defined as the Circles of Apollonius, circle of Apollonius, in terms of two different foci, as the locus of points having a fixed ratio of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |