|
Barium Oxide
Barium oxide, also known as baria, is a white hygroscopic non-flammable chemical compound, compound with the formula BaO. It has a Cubic crystal system, cubic structure and is used in cathode-ray tubes, crown glass, and Catalysis, catalysts. It is harmful to human skin and if swallowed in large quantity causes irritation. Excessive quantities of barium oxide may lead to death. It is prepared by heating barium carbonate with coke (fuel), coke, carbon black or tar or by thermal decomposition of barium nitrate. Uses Barium oxide is used as a coating for hot cathodes, for example, those in cathode-ray tubes. It replaced lead(II) oxide in the production of certain kinds of glass such as optical crown glass (optics), crown glass. While lead oxide raised the refractive index, it also raised the optical dispersion, dispersive power, which barium oxide does not alter. Barium oxide also has use as an ethoxylation catalyst in the reaction of ethylene oxide and Alcohol (chemistry), alcohols ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barium Hydroxide
Barium hydroxide is a chemical compound with the chemical formula Ba(OH)2. The monohydrate (''x'' = 1), known as baryta or baryta-water, is one of the principal compounds of barium. This white granular monohydrate is the usual commercial form. Preparation and structure Barium hydroxide can be prepared by dissolving barium oxide (BaO) in water: :BaO + H2O → Ba(OH)2 It crystallises as the octahydrate, which converts to the monohydrate upon heating in air. At 100 °C in a vacuum, the monohydrate will yield BaO and water. The monohydrate adopts a layered structure (see picture above). The Ba2+ centers adopt a square antiprismatic geometry. Each Ba2+ center is bound by two water ligands and six hydroxide ligands, which are respectively doubly and triply bridging to neighboring Ba2+ centre sites. In the octahydrate, the individual Ba2+ centers are again eight coordinate but do not share ligands. Uses Industrially, barium hydroxide is used as the precursor to other bar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coke (fuel)
Coke is a grey, hard, and porous coal-based fuel with a high carbon content. It is made by heating coal or petroleum in the absence of air. Coke is an important industrial product, used mainly in iron ore smelting, but also as a fuel in stoves and forges. The unqualified term "coke" usually refers to the product derived from low-ash and low-sulphur bituminous coal by a process called coking. A similar product called petroleum coke, or pet coke, is obtained from crude petroleum in oil refinery, petroleum refineries. Coke may also be formed naturally by geology, geologic processes.B. Kwiecińska and H. I. Petersen (2004): "Graphite, semi-graphite, natural coke, and natural char classification — ICCP system". ''International Journal of Coal Geology'', volume 57, issue 2, pages 99-116. It is the residue of a destructive distillation process. Production Industrial coke furnaces The industrial production of coke from coal is called coking. The coal is baked in an airless k ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brin Process
Brin process is a now-obsolete industrial scale production process for oxygen. In this process barium oxide reacts at 500–600 °C with air to form barium peroxide which decomposes at above 800 °C by releasing oxygen. :2 BaO + O2 ⇌ 2 BaO2 The reaction was discovered by Joseph-Louis Gay-Lussac and Louis-Jacques Thenard in 1811 and Jean-Baptiste Boussingault tried to use this reaction to establish a process to produce oxygen in 1852. The process worked only for a few cycles and then became inefficient. Two students of Boussingault, Quentin and Arthur Leon Brin, discovered that traces of carbon dioxide formed barium carbonate. Removing the carbon dioxide with sodium hydroxide solved this problem. In 1884 they opened a factory producing oxygen by their improved process. In the commercial process, oxygen capture and release was controlled by pressure rather than temperature, with oxygen being captured at high pressure and released at low pressure. This allowed a faste ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alcohol (chemistry)
In chemistry, an alcohol (), is a type of organic compound that carries at least one hydroxyl () functional group bound to a Saturated and unsaturated compounds, saturated carbon atom. Alcohols range from the simple, like methanol and ethanol, to complex, like sugar alcohols and cholesterol. The presence of an OH group strongly modifies the properties of Hydrocarbon, hydrocarbons, conferring Hydrophile, hydrophilic (water-loving) properties. The OH group provides a site at which many reactions can occur. History The flammable nature of the exhalations of wine was already known to ancient natural philosophers such as Aristotle (384–322 BCE), Theophrastus (–287 BCE), and Pliny the Elder (23/24–79 CE). However, this did not immediately lead to the isolation of alcohol, even despite the development of more advanced distillation techniques in second- and third-century Roman Egypt. An important recognition, first found in one of the writings attributed to Jabir ibn Hayyan, J� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ethylene Oxide
Ethylene oxide is an organic compound with the chemical formula, formula . It is a cyclic ether and the simplest epoxide: a three-membered ring (chemistry), ring consisting of one oxygen atom and two carbon atoms. Ethylene oxide is a colorless and flammable gas with a faintly sweet odor. Because it is a strained ring, ethylene oxide easily participates in a number of addition reactions that result in ring-opening. Ethylene oxide is isomeric with acetaldehyde and with vinyl alcohol. Ethylene oxide is industrially produced by oxidation of ethylene in the presence of a silver catalyst. The reactivity that is responsible for many of ethylene oxide's hazards also makes it useful. Although too dangerous for direct household use and generally unfamiliar to consumers, ethylene oxide is used for making many consumer products as well as non-consumer chemicals and intermediates. These products include detergents, thickeners, solvents, plastics, and various organic chemicals such as ethylen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Catalyst
Catalysis () is the increase in rate of a chemical reaction due to an added substance known as a catalyst (). Catalysts are not consumed by the reaction and remain unchanged after it. If the reaction is rapid and the catalyst recycles quickly, very small amounts of catalyst often suffice; mixing, surface area, and temperature are important factors in reaction rate. Catalysts generally react with one or more reactants to form intermediates that subsequently give the final reaction product, in the process of regenerating the catalyst. The rate increase occurs because the catalyst allows the reaction to occur by an alternative mechanism which may be much faster than the noncatalyzed mechanism. However the noncatalyzed mechanism does remain possible, so that the total rate (catalyzed plus noncatalyzed) can only increase in the presence of the catalyst and never decrease. Catalysis may be classified as either homogeneous, whose components are dispersed in the same phase (usual ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ethoxylation
In organic chemistry, ethoxylation is a chemical reaction in which ethylene oxide () adds to a substrate. It is the most widely practiced alkoxylation, which involves the addition of epoxides to substrates. In the usual application, alcohols and phenols are converted into , where ''n'' ranges from 1 to 10. Such compounds are called alcohol ethoxylates. Alcohol ethoxylates are often converted to related species called ethoxysulfates. Alcohol ethoxylates and ethoxysulfates are surfactants, used widely in cosmetic and other commercial products. The process is of great industrial significance, with more than 2,000,000 metric tons of various ethoxylates produced worldwide in 1994. Production The process was developed at the Ludwigshafen laboratories of IG Farben by Conrad Schöller and during the 1930s. Alcohol ethoxylates Industrial ethoxylation is primarily performed upon alcohols. Lower alcohols react to give glycol ethers which are commonly used as solvents, while l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Optical Dispersion
Dispersion is the phenomenon in which the phase velocity of a wave depends on its frequency. Sometimes the term chromatic dispersion is used to refer to optics specifically, as opposed to wave propagation in general. A medium having this common property may be termed a dispersive medium. Although the term is used in the field of optics to describe light and other electromagnetic waves, dispersion in the same sense can apply to any sort of wave motion such as acoustic dispersion in the case of sound and seismic waves, and in gravity waves (ocean waves). Within optics, dispersion is a property of telecommunication signals along transmission lines (such as microwaves in coaxial cable) or the Pulse (signal processing), pulses of light in optical fiber. In optics, one important and familiar consequence of dispersion is the change in the angle of refraction of different colors of light, as seen in the spectrum produced by a dispersive Prism (optics), prism and in chromatic aberration ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Refractive Index
In optics, the refractive index (or refraction index) of an optical medium is the ratio of the apparent speed of light in the air or vacuum to the speed in the medium. The refractive index determines how much the path of light is bent, or refraction, refracted, when entering a material. This is described by Snell's law of refraction, , where and are the angle of incidence (optics), angle of incidence and angle of refraction, respectively, of a ray crossing the interface between two media with refractive indices and . The refractive indices also determine the amount of light that is reflectivity, reflected when reaching the interface, as well as the critical angle for total internal reflection, their intensity (Fresnel equations) and Brewster's angle. The refractive index, n, can be seen as the factor by which the speed and the wavelength of the radiation are reduced with respect to their vacuum values: the speed of light in a medium is , and similarly the wavelength in that me ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crown Glass (optics)
Crown glass is a type of optical glass used in lenses and other optical components. It has relatively low refractive index (≈1.52) and low dispersion (with Abbe numbers between 50 and 85). Crown glass is produced from alkali-lime silicates containing approximately 10% potassium oxide and is one of the earliest low dispersion glasses. History The term originated from crown-glass windows, a method of window production that began in France during the Middle Ages. A molten blob of glass was attached to a pole and spun rapidly, flattening it out into a large disk from which windows were cut. The center, called the "crown" or "bullseye", was too thick for windows, but was often used to make lenses or deck prisms.''A Dictionary of the English Language - Volume 1, Part 1'' by Samuel Johnson, Robert Gordon Latham, Henry John Todd -- longmans, Green & Co. 1866 Page 314 Types The borosilicate glass Schott BK7 ( glass code 517642) is an extremely common crown glass, used in precisi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lead(II) Oxide
Lead(II) oxide, also called lead monoxide, is the inorganic compound with the molecular formula Pb O. It occurs in two polymorphs: litharge having a tetragonal crystal structure, and massicot having an orthorhombic crystal structure. Modern applications for PbO are mostly in lead-based industrial glass and industrial ceramics, including computer components. Types Lead oxide exists in two polymorphs: * Red tetragonal (α-PbO), obtained at temperatures below * Yellow orthorhombic (β-PbO), obtained at temperatures above Synthesis PbO may be prepared by heating lead metal in air at approximately . At this temperature it is also the end product of decomposition of other oxides of lead in air: :PbO2->[] Pb12O19 ->[] Pb12O17 ->[] Pb3O4 ->[] PbO Thermal decomposition of lead(II) nitrate or lead carbonate, lead(II) carbonate also results in the formation of PbO: :2 → 2 PbO + 4 + : → PbO + PbO is produced on a large scale as an intermediate product in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
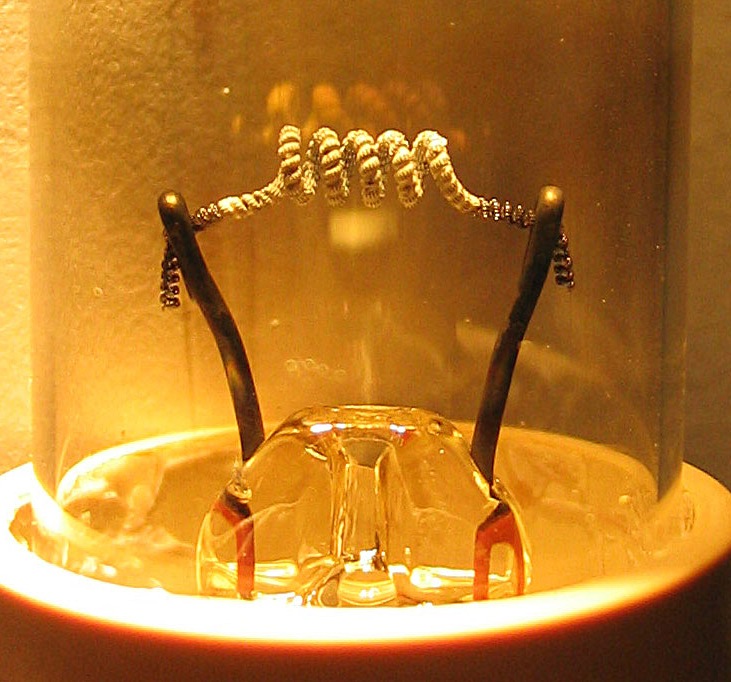
Hot Cathode
In vacuum tubes and gas-filled tubes, a hot cathode or thermionic cathode is a cathode electrode which is heated to make it emit electrons due to thermionic emission. This is in contrast to a cold cathode, which does not have a heating element. The heating element is usually an electrical filament heated by a separate electric current passing through it. Hot cathodes typically achieve much higher power density than cold cathodes, emitting significantly more electrons from the same surface area. Cold cathodes rely on field electron emission or secondary electron emission from positive ion bombardment, and do not require heating. There are two types of hot cathode. In a ''directly heated cathode'', the filament is the cathode and emits the electrons. In an ''indirectly heated cathode'', the filament or ''heater'' heats a separate metal cathode electrode which emits the electrons. From the 1920s to the 1960s, a wide variety of electronic devices used hot-cathode vacuum tubes. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |