|
Bandicam
Bandicam (stylized as BANDICAM) is a closed-source screen capture and screen recording software originally developed by Bandisoft and later by Bandicam Company that can take screenshots or record screen changes. Bandicam consists of three main modes. One is the Screen Recording mode, which can be used for recording a certain area on the PC screen. The other is the Game Recording mode, which can record the target created in DirectX or OpenGL. And the last is the Device Recording mode which records Webcams and HDMI devices. Bandicam displays an FPS count in the corner of the screen while the DirectX/OpenGL window is in active mode. When the FPS count is shown in green, it means the program is ready to record, and when it starts recording, it changes the color of the FPS count to red. The FPS count is not displayed when the program is recording in the Screen Recording mode. This software has a maximum frame rate of 480 FPS. Bandicam is shareware, meaning that it can be tested f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Comparison Of Screencasting Software
This page provides a comparison of notable screencasting software, used to record activities on the computer screen. This software is commonly used for desktop recording, gameplay recording and video editing. Screencasting software is typically limited to streaming and recording desktop activity alone, in contrast with a software vision mixer, which has the capacity to mix and switch the output between various input streams. Comparison by specification Comparison by features The following table compares features of screencasting software. The table has seven fields, as follows: # Product name: Product's name; sometime includes edition if a certain edition is targeted # Audio: Specifies whether the product supports recording audio commentary on the video # Entire desktop: Specifies whether product supports recording the entire desktop # OpenGL: Specifies whether the product supports recording from video games and software that employ OpenGL to render digital image # Direct3D ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Screenshot Software
A screenshot (also known as screen capture or screen grab) is an analog or digital image that shows the contents of a computer display. A screenshot is created by a (film) camera shooting the screen or the operating system or software running on the device powering the display. Screenshot techniques Digital techniques The first screenshots were created with the first interactive computers around 1960. Through the 1980s, computer operating systems did not universally have built-in functionality for capturing screenshots. Sometimes text-only screens could be dumped to a text file, but the result would only capture the content of the screen, not the appearance, nor were graphics screens preservable this way. Some systems had a BSAVE (bitmap format), BSAVE command that could be used to capture the area of memory where screen data was stored, but this required access to a BASIC prompt. Systems with composite video output could be connected to a Videocassette recorder, VCR, and ent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nvidia NVENC
NVENC (short for Nvidia Encoder) is a feature in Nvidia graphics cards that performs video encoding, offloading this compute-intensive task from the CPU to a dedicated part of the GPU. It was introduced with the Kepler-based GeForce 600 series in March 2012 (GT 610, GT620 and GT630 is Fermi Architecture). The encoder is supported in many livestreaming and recording programs, such as vMix, Wirecast, Open Broadcaster Software (OBS) and Bandicam, as well as video editing apps, such as Adobe Premiere Pro or DaVinci Resolve. It also works with Share game capture, which is included in Nvidia's GeForce Experience software. Until March 2023 consumer-targeted GeForce graphics cards officially support no more than three simultaneously encoding video streams, regardless of the count of the cards installed, but this restriction can be circumvented on Linux and Windows systems by applying an unofficial patch to the drivers. Doing so also unlocks ''NVIDIA Frame Buffer Capture (NVFBC)'', ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microsoft Windows
Windows is a Product lining, product line of Proprietary software, proprietary graphical user interface, graphical operating systems developed and marketed by Microsoft. It is grouped into families and subfamilies that cater to particular sectors of the computing industry – Windows (unqualified) for a consumer or corporate workstation, Windows Server for a Server (computing), server and Windows IoT for an embedded system. Windows is sold as either a consumer retail product or licensed to Original equipment manufacturer, third-party hardware manufacturers who sell products Software bundles, bundled with Windows. The first version of Windows, Windows 1.0, was released on November 20, 1985, as a graphical operating system shell for MS-DOS in response to the growing interest in graphical user interfaces (GUIs). The name "Windows" is a reference to the windowing system in GUIs. The 1990 release of Windows 3.0 catapulted its market success and led to various other product families ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
BMP File Format
The BMP file format, or bitmap, is a raster graphics image file format used to store bitmap digital images, independently of the display device (such as a graphics adapter), especially on Microsoft Windows and OS/2 operating systems. The BMP file format is capable of storing two-dimensional digital images in various color depths, and optionally with data compression, alpha channels, and color profiles. The Windows Metafile (WMF) specification covers the BMP file format. Device-independent bitmaps and the BMP file format Microsoft has defined a particular representation of color bitmaps of different color depths, as an aid to exchanging bitmaps between devices and applications with a variety of internal representations. They called these device-independent bitmaps or DIBs, and the file format for them is called DIB file format or BMP image file format. According to Microsoft support: A device-independent bitmap (DIB) is a format used to define device-independent bitmaps ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2009 Software
9 (nine) is the natural number following and preceding . Evolution of the Hindu–Arabic digit Circa 300 BC, as part of the Brahmi numerals, various Indians wrote a digit 9 similar in shape to the modern closing question mark without the bottom dot. The Kshatrapa, Andhra and Gupta started curving the bottom vertical line coming up with a -look-alike. How the numbers got to their Gupta form is open to considerable debate. The Nagari continued the bottom stroke to make a circle and enclose the 3-look-alike, in much the same way that the sign @ encircles a lowercase ''a''. As time went on, the enclosing circle became bigger and its line continued beyond the circle downwards, as the 3-look-alike became smaller. Soon, all that was left of the 3-look-alike was a squiggle. The Arabs simply connected that squiggle to the downward stroke at the middle and subsequent European change was purely cosmetic. While the shape of the glyph for the digit 9 has an ascender in most modern typefa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crippleware
Crippleware is computer software or hardware that has been intentionally designed to have some of its features disabled or not working to its full capability until payment of some kind is rendered. In software, crippleware means that "vital features of the program such as printing or the ability to save files are disabled until the user purchases a registration key". While crippleware allows consumers to see the software before they buy, they are unable to test its complete functionality because of the disabled functions. Hardware crippleware is "a hardware device that has not been designed to its full capability". The functionality of the hardware device is limited to encourage consumers to pay for a more expensive upgraded version. Usually the hardware device considered to be crippleware can be upgraded to better or its full potential by way of a trivial change, such as removing a jumper wire. The manufacturer would most likely release the crippleware as a low-end or economy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intel Quick Sync Video
Intel Quick Sync Video is Intel's brand for its dedicated video encoding and decoding hardware core. Quick Sync was introduced with the Sandy Bridge CPU microarchitecture on 9 January 2011 and has been found on the die of Intel CPUs ever since. The name "Quick Sync" refers to the use case of quickly transcoding ("converting") a video from, for example, a DVD or Blu-ray Disc to a format appropriate to, for example, a smartphone, in situations where speed is more important than the best possible quality. Unlike video encoding on a CPU or a general-purpose GPU, Quick Sync is a dedicated hardware core on the processor die. This allows for much more power-efficient video processing. Availability Quick Sync Video is available on Core i3, Core i5, Core i7, and Core i9 and new Core Ultra processors starting with Sandy Bridge, and Celeron & Pentium processors starting with Haswell. Performance and quality Like most desktop hardware-accelerated encoders, Quick Sync has been praised for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Video Coding Engine
Video Code Engine (VCE, was earlier referred to as Video Coding Engine, Video Compression Engine or Video Codec Engine in official AMD documentation) is AMD's video encoding application-specific integrated circuit implementing the video codec H.264/MPEG-4 AVC. Since 2012 it was integrated into all of their GPUs and APUs except Oland. VCE was introduced with the Radeon HD 7000 series on 22 December 2011. VCE occupies a considerable amount of the die surface at the time of its introduction and is not to be confused with AMD's Unified Video Decoder (UVD). As of AMD Raven Ridge (released January 2018), UVD and VCE were succeeded by Video Core Next (VCN). Overview The handling of video data involves computation of data compression algorithms and possibly of video processing algorithms. As the template compression methods shows, lossy video compression algorithms involve the steps: motion estimation (ME), discrete cosine transform (DCT), and entropy encoding (EC). AMD V ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CUDA
In computing, CUDA (Compute Unified Device Architecture) is a proprietary parallel computing platform and application programming interface (API) that allows software to use certain types of graphics processing units (GPUs) for accelerated general-purpose processing, an approach called general-purpose computing on GPUs. CUDA was created by Nvidia in 2006. When it was first introduced, the name was an acronym for ''Compute Unified Device Architecture'', but Nvidia later dropped the common use of the acronym and now rarely expands it. CUDA is a software layer that gives direct access to the GPU's virtual instruction set and parallel computational elements for the execution of compute kernels. In addition to drivers and runtime kernels, the CUDA platform includes compilers, libraries and developer tools to help programmers accelerate their applications. CUDA is designed to work with programming languages such as C, C++, Fortran, Python and Julia. This accessibility makes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
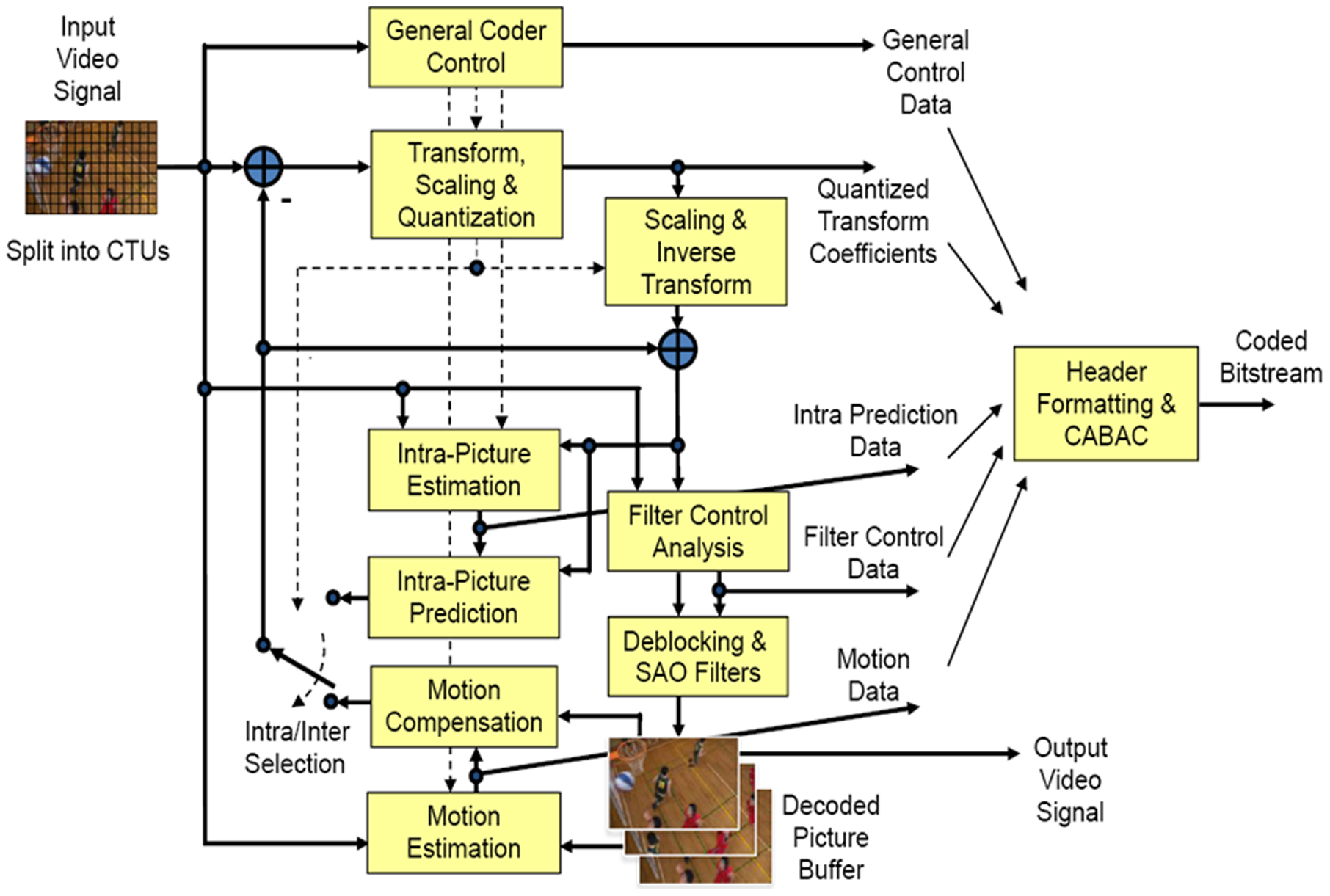
HEVC
High Efficiency Video Coding (HEVC), also known as H.265 and MPEG-H Part 2, is a video compression standard designed as part of the MPEG-H project as a successor to the widely used Advanced Video Coding (AVC, H.264, or MPEG-4 Part 10). In comparison to AVC, HEVC offers from 25% to 50% better data compression at the same level of video quality, or substantially improved video quality at the same bit rate. It supports resolutions up to 8192×4320, including 8K UHD, and unlike the primarily 8-bit AVC, HEVC's higher fidelity Main 10 profile has been incorporated into nearly all supporting hardware. While AVC uses the integer discrete cosine transform (DCT) with 4×4 and 8×8 block sizes, HEVC uses both integer DCT and discrete sine transform (DST) with varied block sizes between 4×4 and 32×32. The High Efficiency Image Format (HEIF) is based on HEVC. Concept In most ways, HEVC is an extension of the concepts in H.264/MPEG-4 AVC. Both work by comparing different parts of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |