|
BMW 7 Series (G70)
G70 is the internal designation for the seventh generation of the BMW 7 Series, a range of luxury cars produced by the German luxury vehicle manufacturer BMW since July 2022. Introduced in April 2022, 7 Series and i7 are the respective designations for BMW's internal combustion and battery electric full-size luxury flagship models. BMW had unveiled the model on 20 April 2022 during the nameplate's 45th anniversary. Sold as a 2023 model, it is longer than its predecessor model. This model offers petrol and diesel models, come standard with a 48-volt mild hybrid powertrain; a plug-in hybrid system is available. The seventh-generation BMW 7 Series is often collectively referred to as the G70. The G70 commenced production on 1 July 2022, exactly seven years after the previous model. The i7 is the first 7 Series to offer a fully electric powertrain, which shares powertrains with the smaller G60 i5. Both 7 Series and i7 offer optional rear- or all-wheel drive drivetrains. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
BMW S68
The BMW S68 is a twin-turbocharged V8 engine produced by BMW. Its first use was in the 2022 revised BMW X7 as the M60i. A few weeks after its presentation, BMW showed a study of the BMW XM, XM with a more powerful version of the engine. In addition, the basic version is also used in BMW 7 Series (G70), BMW 760i, BMW X5 (G05), BMW X5 M60i, and BMW X6, BMW X6 M60i. Design The S68 has the same piston stroke of and displacement as its N63 predecessor, but the compression ratio of 10.5:1 corresponds to the higher compressed predecessor variants. It has one turbocharger per cylinder bank and both turbochargers are placed in the middle of the cylinder banks in a hot-vee design taken from the previous S63 variant; there is only one exhaust manifold. The S68 is the only current production V8 engine offered with a cross-pattern exhaust manifold for improved turbo charger pressure by combining exhaust pulses which comes at an expense of sound alternation, making the sound closer to a 180 de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dingolfing
Dingolfing () is a town in southern Bavaria, Germany. It is the seat of the Landkreis (district) Dingolfing-Landau. Dingolfing is home of a BMW assembly plant. History The area now called Dingolfing was first mentioned in ''Tinguluinga'' in the year 833. In the year 1251 the duke of Duchy of Bavaria, Bavaria, Otto II. awarded municipal rights to the town, which was the Upper City. The Lower City, around the church of St. John's, was an older settlement belonging to the Prince-Bishopric of Regensburg. By treaty of 1265 between Duke and Bishop, both cities were united. Dingolfing's large growth took place during the years of about 1315 to 1600. During this time the city prospered mostly through trade, fishing, leather craft and the production of wool cloths. The duke promoted these works, causing Dingolfing to prosper even more. The war of Austrian succession caused very heavy damage to the city and decimated the population by epidemics. The city became nothing more than debr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rear-motor, Rear-wheel-drive
In automotive design, an RR, or rear-engine, rear-wheel-drive layout places both the engine and drive wheels at the rear of the vehicle. In contrast to the RMR layout, the center of mass of the engine is between the rear axle and the rear bumper. Although very common in transit buses and coaches due to the elimination of the drive shaft with low-floor buses, this layout has become increasingly rare in passenger cars. Overview Most of the traits of the RR configuration are shared with the mid-engine rear-wheel-drive, or MR. Placing the engine near the driven rear wheels allows for a physically smaller, lighter, less complex, and more efficient drivetrain, since there is no need for a driveshaft, and the differential can be integrated with the transmission, commonly referred to as a transaxle. The front-engine front-wheel-drive layout also has this advantage. Since the engine is typically the heaviest component of the car, putting it near the rear axle usually results in mor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mild Hybrid
Mild hybrids (MHEV) (also known as smart hybrids, power-assist hybrids, battery-assisted hybrid vehicles or BAHVs) are generally cars with an internal combustion engine (ICE) equipped with a minimally extended battery and an auxiliary electric combined motor and generator in a parallel hybrid configuration that is only enough for an electric-only mode of propulsion at slow speed and allows the engine to be stopped whenever the car is coasting, braking, or stopped, and then restarted once power is required again. Mild hybrids may employ regenerative braking and some level of power assist to the internal combustion engine. Overview The mild hybrid's electric motor provides greater efficiency through the use of a single device that is essentially an integrated starter/alternator sometimes known as a generator-motor unit. A typical mild-hybrid setup uses a belt-powered generator-motor unit driven off the engine to supply power to a small battery. The generator is also powered throug ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
BMW B57
The BMW B57 is a turbo-diesel straight-six engine, produced by BMW since 2015. Design The B57 belongs to a family of modular engines, including the B37 and B47 diesel engines, and B38, B48, and B58 petrol engines. The engines utilise a common displacement of per cylinder. The B57 replaced the previous N57 diesel engine, and was first introduced in the G11 7 Series. The B57 is available in configurations of up to 4 turbochargers, that operate in a double-series layout. In addition to BMW's own brand vehicles, the BMW B57 is also used in a diesel variant of the Ineos Grenadier. Models B57D30O0 (Single turbo) * 2015–2022 G11 730d, 730Ld * 2017–2023 G30 530d * 2017–2023 G32 630d Gran Turismo * 2017–present G01 X3 xDrive30d * 2018–present G02 X4 xDrive30d * 2018–present G05 X5 xDrive30d * 2018–present G07 X7 xDrive30d * 2019–present G20 330d * 2019–present G06 X6 xDrive30d * 2022–present Ineos Grenadier The Ineos Grenadier is an off-ro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diesel Engine
The diesel engine, named after the German engineer Rudolf Diesel, is an internal combustion engine in which Combustion, ignition of diesel fuel is caused by the elevated temperature of the air in the cylinder due to Mechanics, mechanical Compression (physics), compression; thus, the diesel engine is called a compression-ignition engine (CI engine). This contrasts with engines using spark plug-ignition of the air-fuel mixture, such as a petrol engine (gasoline engine) or a gas engine (using a gaseous fuel like natural gas or liquefied petroleum gas). Introduction Diesel engines work by compressing only air, or air combined with residual combustion gases from the exhaust (known as exhaust gas recirculation, "EGR"). Air is inducted into the chamber during the intake stroke, and compressed during the compression stroke. This increases air temperature inside the Cylinder (engine), cylinder so that atomised diesel fuel injected into the combustion chamber ignites. The torque a dies ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plug-in Hybrid
A plug-in hybrid electric vehicle (PHEV) or simply plug-in hybrid is a type of hybrid electric vehicle equipped with a rechargeable battery pack that can be directly replenished via a charging cable plugged into an external electric power source, in addition to charging internally by its on-board internal combustion engine-powered generator. While PHEVs are predominantly passenger cars, there are also plug-in hybrid variants of sports cars, commercial vehicles, vans, utility trucks, buses, trains, motorcycles, mopeds, military vehicles and boats. Similar to battery electric vehicles (BEVs), plug-in hybrids can use centralized generators of renewable energy (e.g. solar, wind or hydroelectric) to be largely emission-free, or a fossil plant in which case they displace greenhouse gas emissions from the car tailpipe exhaust to the power station. As opposed to conventional hybrid electric vehicles (HEVs), PHEVs generally have a larger battery pack that can be recharged (the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
V8 Engine
A V8 engine is an eight- cylinder piston engine in which two banks of four cylinders share a common crankshaft and are arranged in a V configuration. Origins The first known V8 was the Antoinette, designed by Léon Levavasseur, and built in 1904 by the French Antoinette company for use in speedboat racing, cars, and later, airplanes. Also in 1904, V8 engines began small-scale production by Renault and Buchet for use in race cars. Design V-angle Most engines use a V-angle (the angle between the two banks of cylinders) of 90 degrees. This angle results in good engine balance, which results in low vibrations. However, the downside is the greater width of the engine compared to those that use a smaller V-angle. V8 engines with a 60-degree V-angle were used in the 1996–1999 Ford Taurus SHO, the 2005–2011 Volvo XC90, and the 2006–2009 Volvo S80. The Ford engine used a 60-degree V-angle because it was based on a V6 engine with a 60-degree V-angle. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
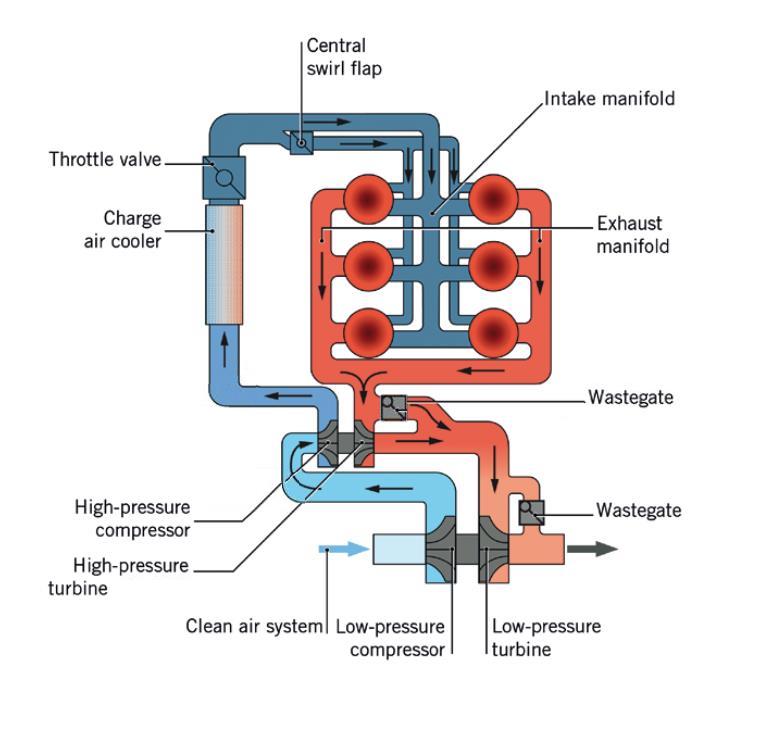
Twin-turbo
Twin-turbo is a type of turbo layout in which two turbochargers are used to compress the intake fuel/air mixture (or intake air, in the case of a direct-injection engine). The most common layout features two identical or mirrored turbochargers in parallel, each processing half of a V engine's produced exhaust through independent piping. The two turbochargers can either be matching or different sizes. The ga70 1ggte was the first inline 6 twin turbo in the world. Types and combinations There are three types of turbine setups used for twin-turbo setups: * Parallel * Sequential * Series These can be applied to any of the five types of compressor setups (which theoretically could have 15 different setups): * Compound Compressors * Staged Compound Compressors * Staged Sequential Compressors * Parallel Sequential Compressors * Parallel Compressors Parallel In a parallel configuration, two equally-sized turbochargers each receive half of the exhaust gases. Some designs combin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Straight-six Engine
A straight-six engine (also referred to as an inline-six engine; abbreviated I6 or L6) is a piston engine with six cylinders arranged in a straight line along the crankshaft. A straight-six engine has perfect primary and secondary engine balance, resulting in fewer vibrations than other designs of six or fewer cylinders. Until the mid-20th century, the straight-six layout was the most common design for engines with six cylinders. However, V6 engines gradually became more common in the 1970s and by the 2000s, V6 engines had replaced straight-six engines in most light automotive applications. Characteristics In terms of packaging, straight-six engines are almost always narrower than a V6 engine or V8 engine, but longer than straight-four engines, V6s, and most V8s. Compared to V-configuration engines with similar power and displacement, the straight configuration has fewer injectors, a single head, and a single exhaust manifold, all contributing to better reliability and perfor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Turbocharger
In an internal combustion engine, a turbocharger (also known as a turbo or a turbosupercharger) is a forced induction device that is powered by the flow of exhaust gases. It uses this energy to compress the intake air, forcing more air into the engine in order to produce more power for a given displacement. Turbochargers are distinguished from superchargers in that a turbocharger is powered by the kinetic energy of the exhaust gases, whereas a is mechanically powered (usually by a belt from the engine's crankshaft). However, up until the mid-20th century, a turbocharger was called a "turbosupercharger" and was considered a type of supercharger. History Prior to the inv ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
BMW B58
The BMW B58 is a Turbocharger, turbocharged straight-six engine, which began production in 2015. The B58 replaced the BMW N55, N55 and was launched in the BMW F30, F30 340i. The B58 is part of BMW's modular engine family, each engine using a displacement of per cylinder, following the BMW B38, B38 and BMW B48, B48 engine. The B58 engine was named to Ward's Ward's 10 Best Engines#Results, World's 10 Best Engines four times, in 2016 (installed in the BMW 3 Series (F30)#Petrol, 340i), 2017 (BMW 2 Series (F22)#Petrol engines, M240i), 2019 (BMW X5 (G05)#Petrol engines, X5) and 2020 (BMW 3 Series (G20)#Petrol engines, M340i). The S58 engine, which was released in early 2019, is the high-performance version of the B58. It was named to Ward's World's 10 Best Engines in 2023 (installed in the BMW M2#Second generation (G87; 2023–present), M2). Design Compared with its BMW N55 predecessor, the B58 features a 20% increase in boost pressure, a closed-deck engine block design, an increase ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |