|
Arsenic Acid
Arsenic acid or trihydrogen arsenate is the chemical compound with the formula . More descriptively written as , this colorless acid is the arsenic analogue of phosphoric acid. Arsenate and phosphate salts behave very similarly. Arsenic acid as such has not been isolated, but is only found in solution, where it is largely ionized. Its hemihydrate form () does form stable crystals. Crystalline samples dehydrate with condensation at 100 °C. Properties It is a tetrahedral species of idealized symmetry ''C''3v with As–O bond lengths ranging from 1.66 to 1.71 Å. Being a triprotic acid, its acidity is described by three equilibria: :, p''K''a1 = 2.19 :, p''K''a2 = 6.94 :, p''K''a3 = 11.5 These p''K''a values are close to those for phosphoric acid. The highly basic arsenate ion () is the product of the third ionization. Unlike phosphoric acid, arsenic acid is an oxidizer, as illustrated by its ability to convert iodide to iodine. Preparation Arsenic acid is pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hygroscopic
Hygroscopy is the phenomenon of attracting and holding water molecules via either absorption or adsorption from the surrounding environment, which is usually at normal or room temperature. If water molecules become suspended among the substance's molecules, adsorbing substances can become physically changed, e.g., changing in volume, boiling point, viscosity or some other physical characteristic or property of the substance. For example, a finely dispersed hygroscopic powder, such as a salt, may become clumpy over time due to collection of moisture from the surrounding environment. ''Deliquescent'' materials are sufficiently hygroscopic that they absorb so much water that they become liquid and form an aqueous solution. Etymology and pronunciation The word ''hygroscopy'' () uses combining forms of '' hygro-'' and '' -scopy''. Unlike any other ''-scopy'' word, it no longer refers to a viewing or imaging mode. It did begin that way, with the word ''hygroscope'' referring in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Triprotic
In computer science, ACID ( atomicity, consistency, isolation, durability) is a set of properties of database transactions intended to guarantee data validity despite errors, power failures, and other mishaps. In the context of databases, a sequence of database operations that satisfies the ACID properties (which can be perceived as a single logical operation on the data) is called a ''transaction''. For example, a transfer of funds from one bank account to another, even involving multiple changes such as debiting one account and crediting another, is a single transaction. In 1983, Andreas Reuter and Theo Härder coined the acronym ''ACID'', building on earlier work by Jim Gray who named atomicity, consistency, and durability, but not isolation, when characterizing the transaction concept. These four properties are the major guarantees of the transaction paradigm, which has influenced many aspects of development in database systems. According to Gray and Reuter, the IBM Inform ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dyestuff
A dye is a colored substance that chemically bonds to the substrate to which it is being applied. This distinguishes dyes from pigments which do not chemically bind to the material they color. Dye is generally applied in an aqueous solution and may require a mordant to improve the fastness of the dye on the fiber. There are two broad categories of dyes: natural and synthetic; Natural dyes are dyes extracted from plants, Insects, or minerals. The majority of natural dyes are vegetable dyes derived from plant sources such as roots, berries, bark, leaves, and wood, as well as other biological sources like fungi. Synthetic dyes are also referred to as "coal tar dyes" because they are derived from substances that, until recently, could only be extracted from coal tar. A synthetic dye consists of a chromophore and an auxochrome added to a benzene derivative. Both dyes and pigments are colored, because they absorb only some wavelengths of visible light. Dyes are usually soluble in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reagent
In chemistry, a reagent ( ) or analytical reagent is a substance or compound added to a system to cause a chemical reaction, or test if one occurs. The terms ''reactant'' and ''reagent'' are often used interchangeably, but reactant specifies a substance ''consumed'' in the course of a chemical reaction. ''Solvents'', though involved in the reaction mechanism, are usually not called reactants. Similarly, '' catalysts'' are not consumed by the reaction, so they are not reactants. In biochemistry, especially in connection with enzyme-catalyzed reactions, the reactants are commonly called substrates. Definitions Organic chemistry In organic chemistry, the term "reagent" denotes a chemical ingredient (a compound or mixture, typically of inorganic or small organic molecules) introduced to cause the desired transformation of an organic substance. Examples include the Collins reagent, Fenton's reagent, and Grignard reagents. Analytical chemistry In analytical chemistry, a reag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biocide
A biocide is defined in the European legislation as a chemical substance or microorganism intended to destroy, deter, render harmless, or exert a controlling effect on any harmful organism. The US Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) uses a slightly different definition for biocides as "a diverse group of poisonous substances including preservatives, insecticides, disinfectants, and pesticides used for the control of organisms that are harmful to human or animal health or that cause damage to natural or manufactured products". When compared, the two definitions roughly imply the same, although the US EPA definition includes plant protection products and some veterinary medicines. The terms "biocides" and " pesticides" are regularly interchanged, and often confused with "plant protection products". To clarify this, pesticides include both biocides and plant protection products, where the former refers to substances for non-food and feed purposes and the latter refers to substance ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wood Preservative
Wood easily degrades without sufficient preservation. Apart from structural wood preservation measures, there are a number of different chemical preservatives and processes (also known as "timber treatment", "lumber treatment" or "pressure treatment") that can extend the life of wood, timber, and their associated products, including engineered wood. These generally increase the durability and resistance from being destroyed by insects or fungi. History As proposed by Richardson, treatment of wood has been practiced for almost as long as the use of wood itself. There are records of wood preservation reaching back to ancient Greece during Alexander the Great's rule, where bridge wood was soaked in olive oil. The Romans protected their ship hulls by brushing the wood with tar. During the Industrial Revolution, wood preservation became a cornerstone of the wood processing industry. Inventors and scientists such as Bethell, Boucherie, Burnett and Kyan made historic developments in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ozone
Ozone (), or trioxygen, is an inorganic molecule with the chemical formula . It is a pale blue gas with a distinctively pungent smell. It is an allotrope of oxygen that is much less stable than the diatomic allotrope , breaking down in the lower atmosphere to (dioxygen). Ozone is formed from dioxygen by the action of ultraviolet (UV) light and electrical discharges within the Earth's atmosphere. It is present in very low concentrations throughout the latter, with its highest concentration high in the ozone layer of the stratosphere, which absorbs most of the Sun's ultraviolet (UV) radiation. Ozone's odour is reminiscent of chlorine, and detectable by many people at concentrations of as little as in air. Ozone's O3 structure was determined in 1865. The molecule was later proven to have a bent structure and to be weakly diamagnetic. In standard conditions, ozone is a pale blue gas that condenses at cryogenic temperatures to a dark blue liquid and finally a violet-black ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arsenic Pentoxide
Arsenic pentoxide is the inorganic compound with the formula As2O5. This glassy, white, deliquescent solid is relatively unstable, consistent with the rarity of the As(V) oxidation state. More common, and far more important commercially, is arsenic(III) oxide (As2O3). All inorganic arsenic compounds are highly toxic and thus find only limited commercial applications. Structure The structure consists of tetrahedral and octahedral centers linked by sharing corners. The structure differs from that of the corresponding phosphorus(V) oxide; as a result, although there is still a solid solution with that oxide, it only progresses to the equimolar point, at which point phosphorus has substituted for arsenic in all of its tetrahedral sites. Likewise, arsenic pentoxide can also dissolve up to an equimolar amount of antimony pentoxide, as antimony substitutes for arsenic only in its octahedral sites. Synthesis Historical Paracelsus Macquer found a crystallizable salt which he cal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
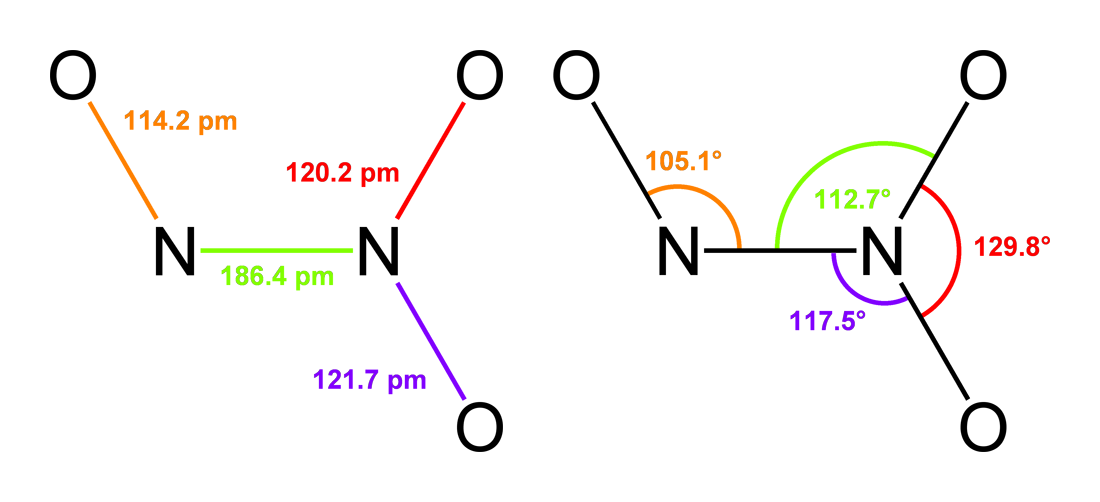
Dinitrogen Trioxide
Dinitrogen trioxide is the chemical compound with the formula N2O3. It is one of the simple nitrogen oxides. It forms upon mixing equal parts of nitric oxide and nitrogen dioxide and cooling the mixture below −21 °C (−6 °F): :NO + NO2 N2O3 Dinitrogen trioxide is only isolable at low temperatures, i.e. in the liquid and solid phases. In liquid and solid states, it has a deep blue color. At higher temperatures the equilibrium favors the constituent gases, with ''K''diss = 193 kPa (25 °C). This compound is sometimes called "nitrogen trioxide", but this name properly refers to another compound, the (uncharged) nitrate radical . Structure and bonding Typically, N–N bonds are similar in length to that in hydrazine (145 pm). Dinitrogen trioxide, however, has an unusually long N–N bond at 186 pm. Some other nitrogen oxides also possess long N–N bonds, including dinitrogen tetroxide (175 pm). The N2O3 molecule is planar and exhibits Cs symmetry. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nitric Acid
Nitric acid is the inorganic compound with the formula . It is a highly corrosive mineral acid. The compound is colorless, but older samples tend to be yellow cast due to decomposition into oxides of nitrogen. Most commercially available nitric acid has a concentration of 68% in water. When the solution contains more than 86% , it is referred to as ''fuming nitric acid''. Depending on the amount of nitrogen dioxide present, fuming nitric acid is further characterized as red fuming nitric acid at concentrations above 86%, or white fuming nitric acid at concentrations above 95%. Nitric acid is the primary reagent used for nitration – the addition of a nitro group, typically to an organic molecule. While some resulting nitro compounds are shock- and thermally-sensitive explosives, a few are stable enough to be used in munitions and demolition, while others are still more stable and used as pigments in inks and dyes. Nitric acid is also commonly used as a strong oxidizing age ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iodine
Iodine is a chemical element with the Symbol (chemistry), symbol I and atomic number 53. The heaviest of the stable halogens, it exists as a semi-lustrous, non-metallic solid at standard conditions that melts to form a deep violet liquid at , and boils to a violet gas at . The element was discovered by the French chemist Bernard Courtois in 1811 and was named two years later by Joseph Louis Gay-Lussac, after the Ancient Greek 'violet-coloured'. Iodine occurs in many oxidation states, including iodide (I−), iodate (), and the various periodate anions. It is the least abundant of the stable halogens, being the sixty-first most abundant element. As the heaviest essential mineral nutrient, iodine is required for the synthesis of thyroid hormones. Iodine deficiency affects about two billion people and is the leading preventable cause of intellectual disabilities. The dominant producers of iodine today are Chile and Japan. Due to its high atomic number and ease of attachment to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |